
How many plants are dihybrid in ${F_2}$ generation of dihybrid cross?
a. One
b. Two
c. Four
d. Sixteen
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: Mendel conducted his experiments using several true-breeding lines of Pisum sativum where a true breeding line is that having undergone continuous self-pollination, shows the stable trait inheritance and expression for several generations.
Complete answer:
Mendel selected a total of 14 true-breeding pea plant varieties, such as the height of the stem whether tall or dwarf as pairs which were similar except for one character with contrasting traits. It means, Mendel selected 7 characters that are seed shape, seed colour, pod colour in pea plant for carrying out hybridization experiments and to study inheritance. He crossed pea plants that differed in two characters and called this a dihybrid cross. A cross was made that is they are allowed for pollination between a pure round yellow-seeded pea plant (RRYY) with wrinkled green-seeded pea plant (rryy).
Yellow colour is dominant that it can be shown with or without green seeds over green and round seed shape over wrinkled seed shape.
Such phenotypic ratio \[\left( {9:3:3:1} \right)\] in ${F_2}$, generation was observed for several pairs of traits that Mendel studied. Mendel found that plants of the ${F_1}$, have all yellow and round seeds because yellow and round traits are respectively dominant and can be shown with each other or independently over green and wrinkled traits.
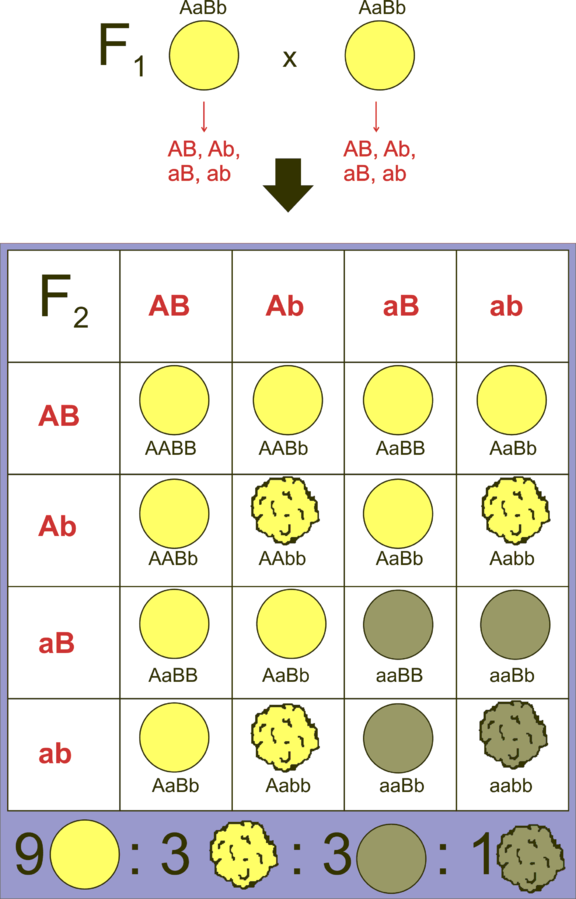
So the ratio of the dihybrid cross was found to be \[\left( {9:3:3:1} \right)\] and dihybrid plants are $4$.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Based upon the results obtained in dihybrid crosses, Mendel proposed a second set of generalisations that we call Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment. This law states that "when two pairs of traits say for instance seeds shape and pod colour are combined in a hybrid, the separation of 1 pair of traits is independent of the one pair of traits".
Complete answer:
Mendel selected a total of 14 true-breeding pea plant varieties, such as the height of the stem whether tall or dwarf as pairs which were similar except for one character with contrasting traits. It means, Mendel selected 7 characters that are seed shape, seed colour, pod colour in pea plant for carrying out hybridization experiments and to study inheritance. He crossed pea plants that differed in two characters and called this a dihybrid cross. A cross was made that is they are allowed for pollination between a pure round yellow-seeded pea plant (RRYY) with wrinkled green-seeded pea plant (rryy).
Yellow colour is dominant that it can be shown with or without green seeds over green and round seed shape over wrinkled seed shape.
Such phenotypic ratio \[\left( {9:3:3:1} \right)\] in ${F_2}$, generation was observed for several pairs of traits that Mendel studied. Mendel found that plants of the ${F_1}$, have all yellow and round seeds because yellow and round traits are respectively dominant and can be shown with each other or independently over green and wrinkled traits.

So the ratio of the dihybrid cross was found to be \[\left( {9:3:3:1} \right)\] and dihybrid plants are $4$.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Based upon the results obtained in dihybrid crosses, Mendel proposed a second set of generalisations that we call Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment. This law states that "when two pairs of traits say for instance seeds shape and pod colour are combined in a hybrid, the separation of 1 pair of traits is independent of the one pair of traits".
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




