
Please show the mechanism of Oxymercuration – demercuration? Give an example to make it understand.
Answer
555.3k+ views
Hint:In Oxymercuration – demercuration reaction alkene is converted to alcohol. In this reaction the reagent used is mercury (II) acetate in tetrahydrofuran which is used as the solvent. During the reaction, reduction is also taking place with the help of reducing agents.
Complete step by step answer:The oxymercuration-demercuration reaction is a type of addition reaction which is used to convert the alkene into alcohol. In this reaction, the alkene first reacts with mercury (II) acetate $(Hg{(OAc)_2})$ in aqueous solution of THF, which is followed by the reduction reaction done by sodium borohydride ($NaB{H_4}$)
The example of oxymercuration-demercuration reaction is shown below.
Propene is converted to isopropanol.
The reaction is shown below.
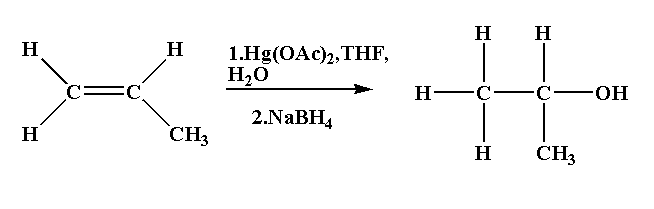
In this reaction propene is reacted with mercury(II) acetate in presence of tetrahydrofuran followed by reduction using sodium borohydride to form isopropanol.
The mechanism of this reaction follows Markonikov’s rule of regioselectivity where the hydroxyl group is joined to the most substituted carbon atom and the hydrogen atom is joined to the least substituted carbon atom.
The mechanism of the reaction is shown below.
Step 1: In this step, the nucleophile C=C bond will attack the electrophile Hg and as a result acetate ion leaves as the leaving group and forms cyclic mercurinium ion.
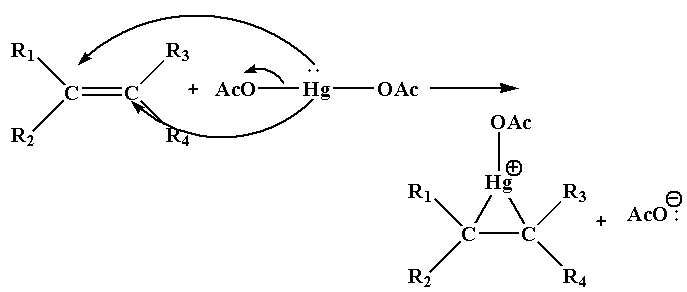
Step 2: In this step the nucleophile attacks one of the carbon joined to Hg which results in the cleavage of C-Hg bond.
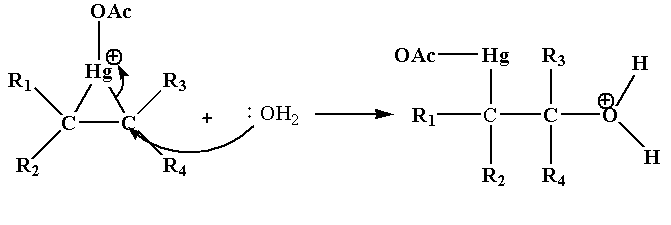
Step 3: In this step deprotonation of oxonium ion takes place in the presence of base acetate ion which gives alcohol.
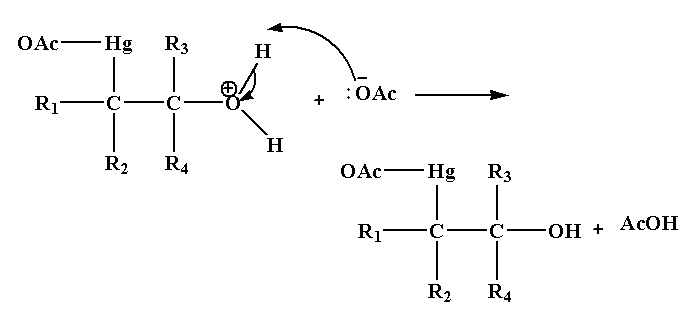
Step 4: In the last step, addition of sodium borohydride replaces the acetyl mercury by a hydrogen atom forming a new C-H bond results in the formation of alcohol.
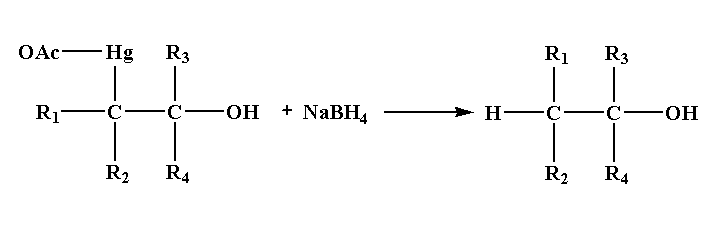
Note:
The Oxymercuration-demercuration reaction is not a stereoselective reaction, as the intermediate form is not a carbocation. The intermediate form in this reaction is a mercurinium ion.
Complete step by step answer:The oxymercuration-demercuration reaction is a type of addition reaction which is used to convert the alkene into alcohol. In this reaction, the alkene first reacts with mercury (II) acetate $(Hg{(OAc)_2})$ in aqueous solution of THF, which is followed by the reduction reaction done by sodium borohydride ($NaB{H_4}$)
The example of oxymercuration-demercuration reaction is shown below.
Propene is converted to isopropanol.
The reaction is shown below.

In this reaction propene is reacted with mercury(II) acetate in presence of tetrahydrofuran followed by reduction using sodium borohydride to form isopropanol.
The mechanism of this reaction follows Markonikov’s rule of regioselectivity where the hydroxyl group is joined to the most substituted carbon atom and the hydrogen atom is joined to the least substituted carbon atom.
The mechanism of the reaction is shown below.
Step 1: In this step, the nucleophile C=C bond will attack the electrophile Hg and as a result acetate ion leaves as the leaving group and forms cyclic mercurinium ion.

Step 2: In this step the nucleophile attacks one of the carbon joined to Hg which results in the cleavage of C-Hg bond.

Step 3: In this step deprotonation of oxonium ion takes place in the presence of base acetate ion which gives alcohol.

Step 4: In the last step, addition of sodium borohydride replaces the acetyl mercury by a hydrogen atom forming a new C-H bond results in the formation of alcohol.
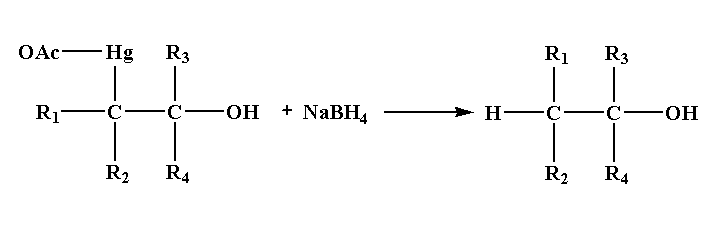
Note:
The Oxymercuration-demercuration reaction is not a stereoselective reaction, as the intermediate form is not a carbocation. The intermediate form in this reaction is a mercurinium ion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




