
Plot a graph showing the variation of acceleration due to gravity with the distance from the centre of the earth.
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint:We have to take distance from earth on the x-axis as it is an independent value, and acceleration due to gravity on y-axis as it is dependent on the distance from the centre of the earth for this graph.
Complete step by step solution:
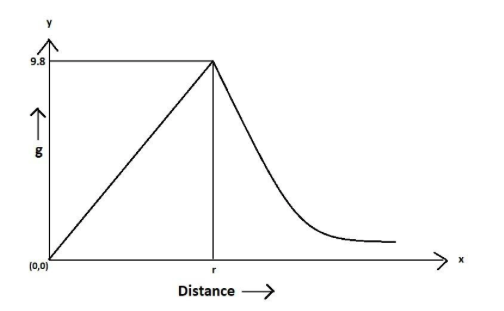
We need to plot this graph between two quantities – distance and acceleration due to gravity, called $g$. Since acceleration due to gravity is a dependent function, being dependent on distance from the centre of the earth, it will be plotted over the y-axis and distance, being an independent quantity, will be plotted over the x-axis.
We need to take the centre of the earth as a reference for measuring distance, as given in the question. This means that the centre of the earth will be taken as an initial distance. In other words, at the centre of the earth, distance will be equal to zero. Also, we know that at the centre of the earth acceleration due to gravity is zero. Therefore, we get the coordinates $\left( {0,0} \right)$ to satisfy the graph, indicating that at the centre of the earth acceleration due to gravity will be zero.
Now, we know that the value of acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth, i.e. at a distance equal to the radius of the earth, is equal to $9.8\,m{s^{ - 2}}$ and also that the value of the acceleration due to gravity is highest at a distance equal to the radius of the earth. Hence, if we take the radius of the earth to be $r$, we get the point $(r,9.8)$ for our graph.
Now, it has been proven that the acceleration due to gravity increases uniformly till a distance equal to the radius of the earth, where it becomes highest, and then decreases exponentially. Hence, from the origin to the point $(r,9.8)$ graph will be a straight line and after the point $(r,9.8)$ the graph will decrease exponentially, tending to zero as distance tends to infinity.
Therefore, the graph will be as below:
Note:It has been scientifically proven that acceleration due to gravity increases uniformly till a distance equal to the radius of the earth, where it becomes highest, and then decreases exponentially. The acceleration due to gravity never becomes zero. No matter how far we go from earth, there will always be some of it acting on us except for when we reach the centre of earth, where it becomes zero.
Complete step by step solution:
We need to plot this graph between two quantities – distance and acceleration due to gravity, called $g$. Since acceleration due to gravity is a dependent function, being dependent on distance from the centre of the earth, it will be plotted over the y-axis and distance, being an independent quantity, will be plotted over the x-axis.
We need to take the centre of the earth as a reference for measuring distance, as given in the question. This means that the centre of the earth will be taken as an initial distance. In other words, at the centre of the earth, distance will be equal to zero. Also, we know that at the centre of the earth acceleration due to gravity is zero. Therefore, we get the coordinates $\left( {0,0} \right)$ to satisfy the graph, indicating that at the centre of the earth acceleration due to gravity will be zero.
Now, we know that the value of acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth, i.e. at a distance equal to the radius of the earth, is equal to $9.8\,m{s^{ - 2}}$ and also that the value of the acceleration due to gravity is highest at a distance equal to the radius of the earth. Hence, if we take the radius of the earth to be $r$, we get the point $(r,9.8)$ for our graph.
Now, it has been proven that the acceleration due to gravity increases uniformly till a distance equal to the radius of the earth, where it becomes highest, and then decreases exponentially. Hence, from the origin to the point $(r,9.8)$ graph will be a straight line and after the point $(r,9.8)$ the graph will decrease exponentially, tending to zero as distance tends to infinity.
Therefore, the graph will be as below:

Note:It has been scientifically proven that acceleration due to gravity increases uniformly till a distance equal to the radius of the earth, where it becomes highest, and then decreases exponentially. The acceleration due to gravity never becomes zero. No matter how far we go from earth, there will always be some of it acting on us except for when we reach the centre of earth, where it becomes zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




