
Points A and B are situated perpendicular to the axis of a $2\;cm$ long bar magnet at large distances X and 3X from its centre on opposite sides. The ratio of the magnetic fields at A and B will be approximately equal to
\[\begin{align}
& A.1:9 \\
& B.2:9 \\
& C.27:1 \\
& D.9:1 \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Biot-Savart law gives the magnetic field produced due to a current carrying conductor. To find the intensity of the magnetic field at the centre of the current carrying rod of length $l$, which is carrying a current $I$, we can use this law.
Formula Used: $dB= \dfrac{\mu_{0}}{4\pi}\times \dfrac{I dl Sin\theta}{r^{2}}$
Complete step-by-step solution
Biot-Savart law states that the magnetic field $B$ produced at any point near a current-carrying conductor is proportional to the material of the medium $\mu_{0}$, the current $I$ flowing in the conductor, the small length of the wire $d\;l$ involved, and inversely proportional to distance $r$ between the point and the conductor.
Mathematically, $dB \propto \mu_{0}$, $dB\propto I$, $dB \propto dl$ and $dB \propto \dfrac{1}{r^{2}}$
Then, $dB= \dfrac{\mu_{0}}{4\pi}\times \dfrac{I dl Sin\theta}{r^{2}}$, where $\theta$ is the angle between $d\;l$ and $r$.
The Biot-Savart law is given on the basis of magnetostatics and it gives the relationship between the current and the magnetic field for any shape of conductor. It is derived from the ampere's circuital law.
Here, given that A and B are at distances X and 3X from its center on opposite sides.
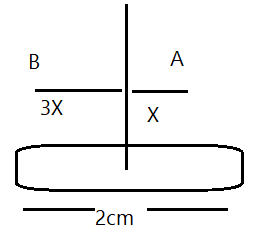
From $dB \propto \dfrac{1}{r^{2}}$, but since the points A and B lie on the axial line of the given rod, we get, $dB\propto\dfrac{1}{r^{3}}$, then on substitution we get,
$\dfrac{B_{A}}{B_{B}}=\dfrac{(3X)^{3}}{X^{3}}$
$\implies \dfrac{B_{A}}{B_{B}}=\dfrac{27}{1}$
$\therefore C.27:1$ is the required correct answer.
Note: From the formula, it is clear that the magnetic field produced depends on the nature of the conductor and the amount of current flowing in the circuit. Note that, we are taking the cross product of the current and the small length, which is why we have a $\theta$ in the equation. Also, note that the length of the rod is not taken into account for calculation.
Formula Used: $dB= \dfrac{\mu_{0}}{4\pi}\times \dfrac{I dl Sin\theta}{r^{2}}$
Complete step-by-step solution
Biot-Savart law states that the magnetic field $B$ produced at any point near a current-carrying conductor is proportional to the material of the medium $\mu_{0}$, the current $I$ flowing in the conductor, the small length of the wire $d\;l$ involved, and inversely proportional to distance $r$ between the point and the conductor.
Mathematically, $dB \propto \mu_{0}$, $dB\propto I$, $dB \propto dl$ and $dB \propto \dfrac{1}{r^{2}}$
Then, $dB= \dfrac{\mu_{0}}{4\pi}\times \dfrac{I dl Sin\theta}{r^{2}}$, where $\theta$ is the angle between $d\;l$ and $r$.
The Biot-Savart law is given on the basis of magnetostatics and it gives the relationship between the current and the magnetic field for any shape of conductor. It is derived from the ampere's circuital law.
Here, given that A and B are at distances X and 3X from its center on opposite sides.

From $dB \propto \dfrac{1}{r^{2}}$, but since the points A and B lie on the axial line of the given rod, we get, $dB\propto\dfrac{1}{r^{3}}$, then on substitution we get,
$\dfrac{B_{A}}{B_{B}}=\dfrac{(3X)^{3}}{X^{3}}$
$\implies \dfrac{B_{A}}{B_{B}}=\dfrac{27}{1}$
$\therefore C.27:1$ is the required correct answer.
Note: From the formula, it is clear that the magnetic field produced depends on the nature of the conductor and the amount of current flowing in the circuit. Note that, we are taking the cross product of the current and the small length, which is why we have a $\theta$ in the equation. Also, note that the length of the rod is not taken into account for calculation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




