
What is Polaroid? Write any two uses of it. How will you identify the polarized light, the partially polarized light and unpolarized light?
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: Light is an electromagnetic wave produced by vibrating electric charges. Depending on the vibration of the emitting particle, the wave also vibrates at different planes. Light is a transverse wave, and it can have this property in any direction.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Polaroid is a filter which can filter the light so that it has only one plane of vibration instead of having multiple planes. We can explain the working principle of a polaroid using the following diagram.
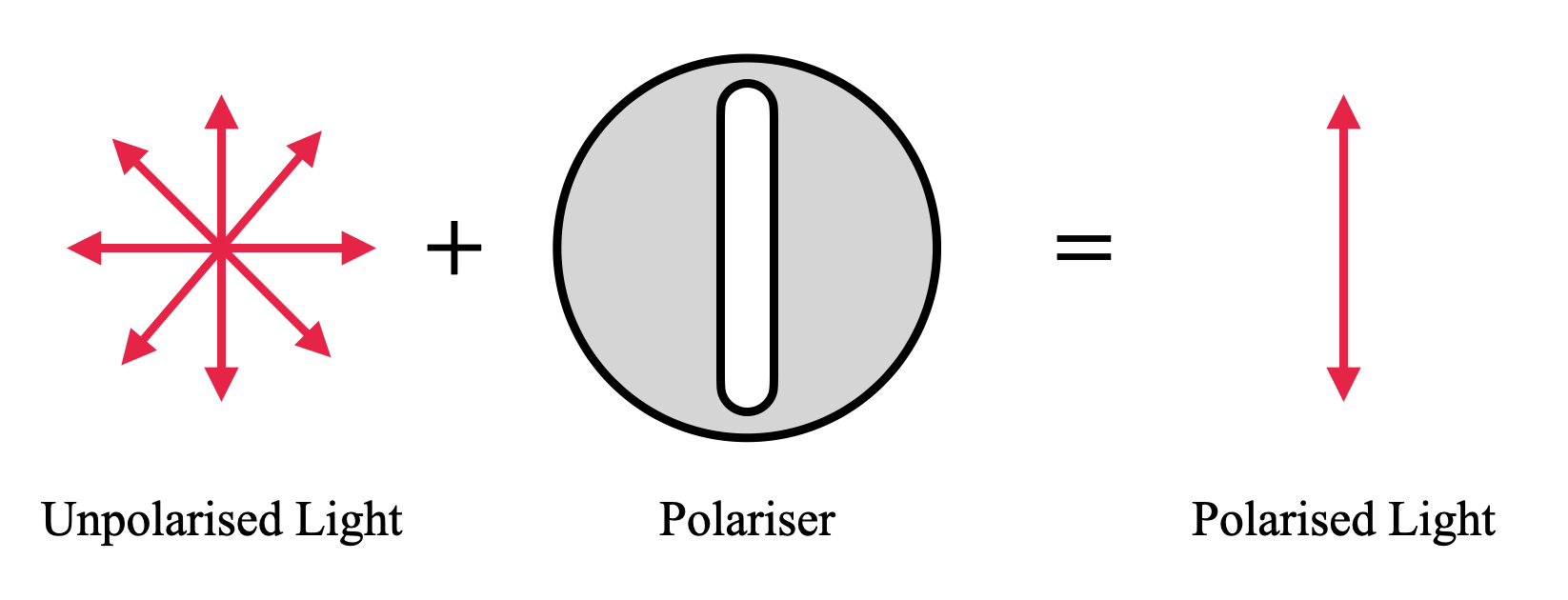
Polaroid filter or Polariser is an instrument which is used to restrict the poles of vibration except the required one. In the above diagram, the unpolarised light is passed through a polariser which allows only one plane of vibration.
Two of the primary uses of polaroid are -
(i) Polaroid filters can be used in spectacles to reduce glare.
(ii) In chemistry, polaroid is used to determine the chirality of molecules.
The polarized light can be of three kinds -
(a) Unpolarized light
(b) Semi Polarized light
(c) Polarized light.
In Unpolarized light, light waves can have planes of vibration. Semi polarized light can have two perpendicular planes of vibration. A fully polarized light can have only one plane of vibration.
There is an easy way to differentiate between these three types of light waves -
Pass a light beam through a polaroid which allows only one mode of vibration. Now, rotate the polaroid and observe the light that is coming out of the polaroid.
(i) If the light intensity is maximum only once after one complete rotation, it is a polarized light.
(ii) If the intensity is maximum twice, then the light is semi polarized.
(iii) If the intensity is the same throughout the rotation, the light is unpolarized.
Note:
Polarizer is primarily constructed using minerals, in which the crystal orientation only allows a specific plane of vibration to pass through. The general rule is that the electromagnetic vibrations that are in a direction parallel to the alignment of the molecule are absorbed.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Polaroid is a filter which can filter the light so that it has only one plane of vibration instead of having multiple planes. We can explain the working principle of a polaroid using the following diagram.

Polaroid filter or Polariser is an instrument which is used to restrict the poles of vibration except the required one. In the above diagram, the unpolarised light is passed through a polariser which allows only one plane of vibration.
Two of the primary uses of polaroid are -
(i) Polaroid filters can be used in spectacles to reduce glare.
(ii) In chemistry, polaroid is used to determine the chirality of molecules.
The polarized light can be of three kinds -
(a) Unpolarized light
(b) Semi Polarized light
(c) Polarized light.
In Unpolarized light, light waves can have planes of vibration. Semi polarized light can have two perpendicular planes of vibration. A fully polarized light can have only one plane of vibration.
There is an easy way to differentiate between these three types of light waves -
Pass a light beam through a polaroid which allows only one mode of vibration. Now, rotate the polaroid and observe the light that is coming out of the polaroid.
(i) If the light intensity is maximum only once after one complete rotation, it is a polarized light.
(ii) If the intensity is maximum twice, then the light is semi polarized.
(iii) If the intensity is the same throughout the rotation, the light is unpolarized.
Note:
Polarizer is primarily constructed using minerals, in which the crystal orientation only allows a specific plane of vibration to pass through. The general rule is that the electromagnetic vibrations that are in a direction parallel to the alignment of the molecule are absorbed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




