
Polygonum type of embryo sac, at maturity, has
(a) 4 nuclei
(b) 14 nuclei
(c) 8 nuclei
(d) 18 nuclei
Answer
536.1k+ views
Hint: The monosporic, or Polygonum-type embryo sac includes meiosis of the diploid megaspore mother cell in the nucellus which in turn produces four haploid megaspores. Three of which degenerate that leaves only one functional megaspore, which undergoes several events to form the characteristic embryo sac of angiosperms with a specific number of nuclei.
Complete answer:
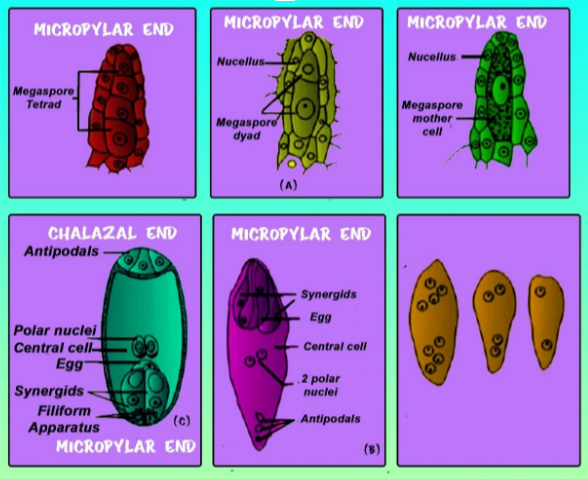
-The female gametophyte, is additionally referred to as megagametophyte or embryo sac, which is developed within the carpel and contains one or several ovules.
-In each ovule meiosis of the megaspore mother cell results in four haploid cells called megaspores. As the monosporic pattern continues, three of these megaspores degenerate while the closest cell to the chalazal region remains viable and develops into a single functional megaspore.
-This megaspore develops and undergoes two times mitosis without cytokinesis, which leads to a four-nucleate coenocyte with two nuclei present at each pole. During the third mitosis, phragmoplasts ( phragmoplast is a plant cell-specific structure that forms during late cytokinesis) and cell plates form between sister and non-sister nuclei, the female gametophyte cells quickly become surrounded by cell walls entirely.
-The polar nuclei migrate toward the middle of the developing female gametophyte and they fuse. These events result in a structure that consists of three antipodal cells, one central cell, two synergid cells, and one egg cell. Therefore the embryo sac becomes a 7 celled and 8 nucleate structure.
Additional information:
Embryo sacs are divided into three types:
Monosporic type: Also referred to as Polygonum-type embryo sac.
Bisporic type: In this type of embryo sac, meiosis produces two megaspores which contain two haploid nuclei. After this, the second meiotic division starts due to the absence of cytokinesis and cell plate formation. The megaspore then degenerates that leaves behind a single functional megaspore with two haploid nuclei.
Tetrasporic type: The cell plates fail to form after both meiotic divisions, resulting in a single four-nucleate in the tetrasporic embryo sac.
So, the correct answer is '8 nuclei'.
Note:
The nuclei present in both bisporic and tetrasporic embryo sacs are not genetically the same as they are in monosporic embryo sacs, because they develop from two or four different meiotic divisions.
Complete answer:
-The female gametophyte, is additionally referred to as megagametophyte or embryo sac, which is developed within the carpel and contains one or several ovules.
-In each ovule meiosis of the megaspore mother cell results in four haploid cells called megaspores. As the monosporic pattern continues, three of these megaspores degenerate while the closest cell to the chalazal region remains viable and develops into a single functional megaspore.
-This megaspore develops and undergoes two times mitosis without cytokinesis, which leads to a four-nucleate coenocyte with two nuclei present at each pole. During the third mitosis, phragmoplasts ( phragmoplast is a plant cell-specific structure that forms during late cytokinesis) and cell plates form between sister and non-sister nuclei, the female gametophyte cells quickly become surrounded by cell walls entirely.
-The polar nuclei migrate toward the middle of the developing female gametophyte and they fuse. These events result in a structure that consists of three antipodal cells, one central cell, two synergid cells, and one egg cell. Therefore the embryo sac becomes a 7 celled and 8 nucleate structure.
Additional information:
Embryo sacs are divided into three types:
Monosporic type: Also referred to as Polygonum-type embryo sac.
Bisporic type: In this type of embryo sac, meiosis produces two megaspores which contain two haploid nuclei. After this, the second meiotic division starts due to the absence of cytokinesis and cell plate formation. The megaspore then degenerates that leaves behind a single functional megaspore with two haploid nuclei.
Tetrasporic type: The cell plates fail to form after both meiotic divisions, resulting in a single four-nucleate in the tetrasporic embryo sac.
So, the correct answer is '8 nuclei'.
Note:
The nuclei present in both bisporic and tetrasporic embryo sacs are not genetically the same as they are in monosporic embryo sacs, because they develop from two or four different meiotic divisions.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




