
Population growth curve in most animals, except humans is:
A. S-shaped
B. J-shaped
C. J-shaped with tail
D. S-shaped with tail
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: Human is also an animal but it is different from other animals in many ways and here population growth curve is being discussed which is similar initially for all the animals but it changes midpoint for human beings.
Complete answer:
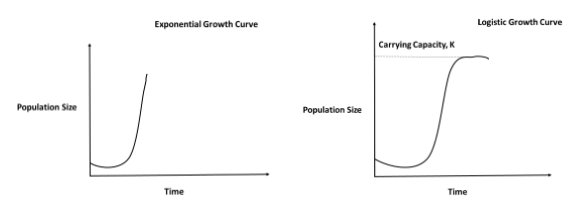
To keep a track on the rise and fall in the population of different living organisms found on our planet, population growth curves were being developed. This is an ecological tool. Growth of an organism depends on different factors like: availability of food, predation, disease and competition of different other resources. These curves are graphs plotted for population size against time and are divided into S- shaped and J-shaped.
- The J shaped growth curves are also known as exponential growth curves. This type of growth curve shows that the organisms grow very rapidly when the resources on which they are dependent are abundant but the growth slows down as the resources start to get exhausted and are less in number.
-The S shaped growth curve is also known as logistic growth curves. This type of growth curve is also known as extended exponential curve and is possible only hypothetically when the resources are unlimited which does not happen in reality. There is always competition for the resources and the fittest organism survives. Every habitat has its own carrying capacity which is the maximum resources present in a habitat for the consumption by the organisms present in that particular habitat. Beyond that carrying capacity no organism survives or the population growth saturates as shown in the graph. The dotted line is of carrying capacity.
- The S shaped growth phase is observed in many microorganisms like Yeast and many animas. The J shaped growth curve is observed in human beings.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Additional information:
-Logistic growth curve explains the real world population dynamics where the resources are limited.
-Carrying capacity of a habitat keeps on changing from season to season as it can be different in summers and totally different in winters or monsoon.
-Natural disasters also affect the carrying capacity.
Note: No population ever exists in isolation is always in competition with other species that are present in its habitat and this type of competition is known as interspecific competition.
Complete answer:
To keep a track on the rise and fall in the population of different living organisms found on our planet, population growth curves were being developed. This is an ecological tool. Growth of an organism depends on different factors like: availability of food, predation, disease and competition of different other resources. These curves are graphs plotted for population size against time and are divided into S- shaped and J-shaped.
- The J shaped growth curves are also known as exponential growth curves. This type of growth curve shows that the organisms grow very rapidly when the resources on which they are dependent are abundant but the growth slows down as the resources start to get exhausted and are less in number.
-The S shaped growth curve is also known as logistic growth curves. This type of growth curve is also known as extended exponential curve and is possible only hypothetically when the resources are unlimited which does not happen in reality. There is always competition for the resources and the fittest organism survives. Every habitat has its own carrying capacity which is the maximum resources present in a habitat for the consumption by the organisms present in that particular habitat. Beyond that carrying capacity no organism survives or the population growth saturates as shown in the graph. The dotted line is of carrying capacity.
- The S shaped growth phase is observed in many microorganisms like Yeast and many animas. The J shaped growth curve is observed in human beings.

Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Additional information:
-Logistic growth curve explains the real world population dynamics where the resources are limited.
-Carrying capacity of a habitat keeps on changing from season to season as it can be different in summers and totally different in winters or monsoon.
-Natural disasters also affect the carrying capacity.
Note: No population ever exists in isolation is always in competition with other species that are present in its habitat and this type of competition is known as interspecific competition.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




