
Position of octahedral voids in fcc structure is/are:
a) Edge centres of unit cell
b) Body centres of unit cell
c) Corners of unit cell
d) Face-centres of unit cell
Answer
526.1k+ views
Hint: When the atoms or ions are closely packed in a structure, they leave behind some gaps in between the constituent particles which are called voids. These closed packed structures can be One dimensional(1D), Two dimensional(2D) and Three dimensional (3D).
Complete step by step solution:
Firstly, let’s know how an octahedral void is formed.
Suppose there is a two-dimensional hexagonal close packed layer called ‘A’ and we place a similar layer above it in such a manner that the spheres of the second layer are placed in the depressions of the first layer.
We now know that the two layers are aligned differently so let's call the second layer ‘B’.
We can see that the spheres of the layer B covers the Depressions of the layer A But not all the Depressions. The depressions which are covered by layer B are called tetrahedral voids.
Now the triangular voids of layer A which were not covered by the spheres of layer B are covered by another tetrahedral void of layer B. But these voids do not overlap each other, one of them has the apex of the triangle pointing upwards and the other pointing downwards.
Such voids are surrounded by 6 spheres and are called octahedral voids.
Let's see how an octahedral void is located in fcc structure.
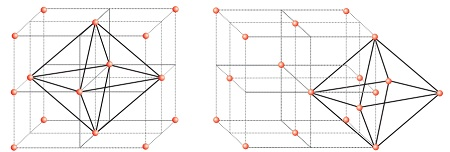
Let us consider a unit cell of fcc lattice, in this structure the body center of the lattice is not occupied but it is surrounded by the six face centres. When each of the six face centres is connected or joined by the other four adjacent face centres it forms an octahedron. This unit cell has one octahedral void at the body center.
Other than the body center there is one of the octahedral voids at the center of each of the 12 edges Which is surrounded by 6 atoms, four belonging to the same unit cell and two belonging to two other adjacent unit cells.
Now you can see that each edge of the cube is shared between 4 adjacent unit cells, and the octahedral void is located on it. So, only 1/4th of each void belongs to a particular unit cell.
From the above statements we can conclude that the position of the octahedral voids is:
Body centres of unit cells as shown in fig (a).
Edge centres of unit cells as shown in fig (b).
Note: Number of octahedral voids present in a lattice is equal to the number of closed packed particles and the tetrahedral voids are double the number of the octahedral voids.
For example, the number of octahedral voids for fcc lattice is 4 and the tetrahedral voids are 8.
Complete step by step solution:
Firstly, let’s know how an octahedral void is formed.
Suppose there is a two-dimensional hexagonal close packed layer called ‘A’ and we place a similar layer above it in such a manner that the spheres of the second layer are placed in the depressions of the first layer.
We now know that the two layers are aligned differently so let's call the second layer ‘B’.
We can see that the spheres of the layer B covers the Depressions of the layer A But not all the Depressions. The depressions which are covered by layer B are called tetrahedral voids.
Now the triangular voids of layer A which were not covered by the spheres of layer B are covered by another tetrahedral void of layer B. But these voids do not overlap each other, one of them has the apex of the triangle pointing upwards and the other pointing downwards.
Such voids are surrounded by 6 spheres and are called octahedral voids.
Let's see how an octahedral void is located in fcc structure.
Let us consider a unit cell of fcc lattice, in this structure the body center of the lattice is not occupied but it is surrounded by the six face centres. When each of the six face centres is connected or joined by the other four adjacent face centres it forms an octahedron. This unit cell has one octahedral void at the body center.
Other than the body center there is one of the octahedral voids at the center of each of the 12 edges Which is surrounded by 6 atoms, four belonging to the same unit cell and two belonging to two other adjacent unit cells.
Now you can see that each edge of the cube is shared between 4 adjacent unit cells, and the octahedral void is located on it. So, only 1/4th of each void belongs to a particular unit cell.
From the above statements we can conclude that the position of the octahedral voids is:
Body centres of unit cells as shown in fig (a).
Edge centres of unit cells as shown in fig (b).

Note: Number of octahedral voids present in a lattice is equal to the number of closed packed particles and the tetrahedral voids are double the number of the octahedral voids.
For example, the number of octahedral voids for fcc lattice is 4 and the tetrahedral voids are 8.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




