
How to prepare 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol?
Answer
535.2k+ views
Hint: Aromatic compounds (benzene) can have carbon chain added through Friedal-crafts reactions. Organolithium reagents help in nucleophilic addition reactions. Sodium borohydrides are used as reducing agents for carbonyl compounds.
Complete answer:
We have been given to write about the preparation method of 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol. As the name suggests, this compound contains a benzene ring with a 4-carbon chain on the first carbon of benzene. This 4-carbon chain has a methyl group on carbon-3 and a hydroxyl group on carbon-2, which makes it a secondary alcohol.
The preparation of 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol involves friedel-craft acylation of benzene employing a catalyst used to synthesis organic compounds called oxalyl chloride\[(COC{{l}_{2}})\] that helps its formation into a carbon chain on position-1. Then the carbonyl adjacent from the benzene on this carbon chain is reduced, while the other carbonyl is unaffected. Then an organolithium reagent $({{C}_{3}}{{H}_{8}}Li)$ is used to carry a nucleophilic addition that removes the chloride group. The last step involves the use of a reducing agent, sodium borohydride $(NaB{{H}_{4}})$ and water that converts the carbonyl into secondary alcohol. Water helps in the addition of the hydrogen to the oxygen anion. The reaction is as follows:
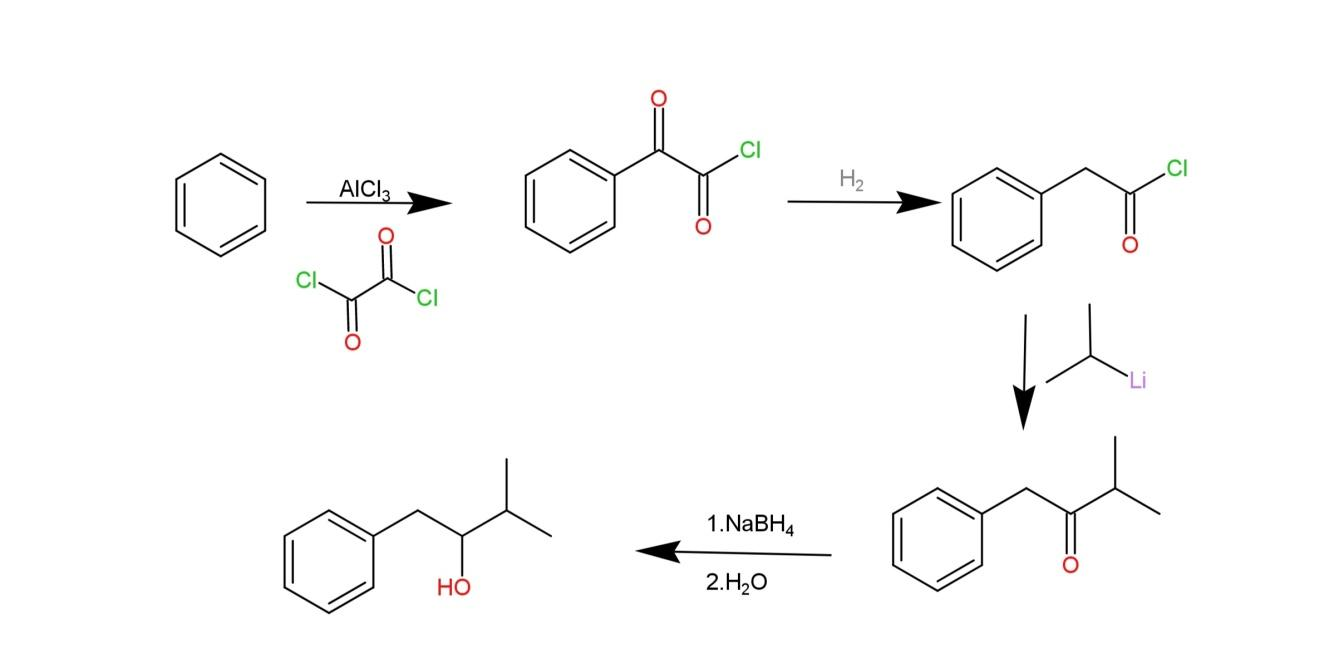
Hence, through the above reaction we can prepare 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol.
Note:
Friedel-crafts acylation is used in this reaction because; we have to obtain a secondary alcohol, which can be formed from the acyl group. While, friedel-crafts alkylation will be involved if we have to add up only a carbon chain to the benzene ring.
Complete answer:
We have been given to write about the preparation method of 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol. As the name suggests, this compound contains a benzene ring with a 4-carbon chain on the first carbon of benzene. This 4-carbon chain has a methyl group on carbon-3 and a hydroxyl group on carbon-2, which makes it a secondary alcohol.
The preparation of 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol involves friedel-craft acylation of benzene employing a catalyst used to synthesis organic compounds called oxalyl chloride\[(COC{{l}_{2}})\] that helps its formation into a carbon chain on position-1. Then the carbonyl adjacent from the benzene on this carbon chain is reduced, while the other carbonyl is unaffected. Then an organolithium reagent $({{C}_{3}}{{H}_{8}}Li)$ is used to carry a nucleophilic addition that removes the chloride group. The last step involves the use of a reducing agent, sodium borohydride $(NaB{{H}_{4}})$ and water that converts the carbonyl into secondary alcohol. Water helps in the addition of the hydrogen to the oxygen anion. The reaction is as follows:

Hence, through the above reaction we can prepare 1-phenyl-3-methyl-2-butanol.
Note:
Friedel-crafts acylation is used in this reaction because; we have to obtain a secondary alcohol, which can be formed from the acyl group. While, friedel-crafts alkylation will be involved if we have to add up only a carbon chain to the benzene ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




