
How will you prepare \[2 - methy - propan - 2 - ol\] from methyl magnesium bromide?
Answer
507k+ views
Hint: The synthesis of an organic product can be done only by keeping its structure in mind. The IUPAC name of the desired product \[2 - methy - propan - 2 - ol\] suggests that it is a tertiary alcohol, therefore think of different methods of preparing tertiary alcohols.
Complete answer:
The organic compound \[2 - methy - propan - 2 - ol\] contains a branched carbon chain of four carbon atoms with branching present at the second position and a hydroxyl functional group attached at the same position. This is the formula of a tertiary alcohol.
The reagent given to us is methyl magnesium bromide which is known as the Grignard’s reagent. This is a special organometallic compound containing magnesium metal bonded to a halogen (bromine in this case) and an alkyl group (methyl in this case). Due to the electronegativity differences, the molecule is polarized and the carbon atom of the alkyl group gets a partial negative charge and the magnesium metal gets a partial positive charge.
The negatively polarized alkyl group becomes a good nucleophile that is capable of reacting with highly electrophilic functional group like the carbonyl compounds. Hence, a reaction between an aldehyde or ketone with a Grignard reagent can be used to synthesize corresponding alcohols with the same number of carbon atoms as the parent carbonyl compound.
The carbonyl compound is selected on the basis of the type of alcohol desired. Since our desired product is \[2 - methy - propan - 2 - ol\] which is a tertiary alcohol, a ketone containing three carbon atoms would be a perfect choice. The methyl group from methyl magnesium bromide will provide the fourth carbon atom. A symmetrical ketone that fits this criteria is acetone or \[propan - 2 - one\].
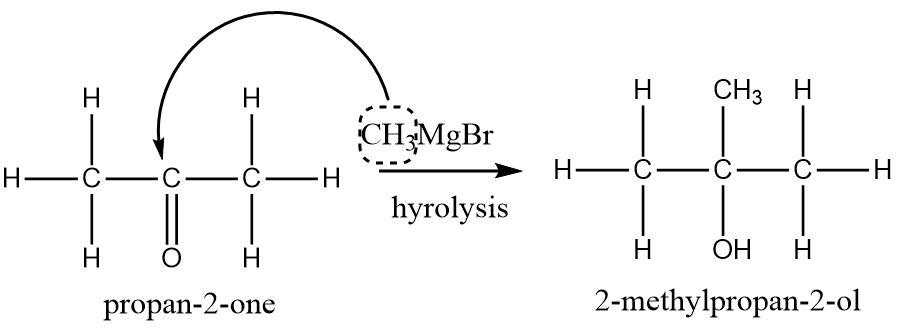
Hence, \[2 - methy - propan - 2 - ol\] can be produced by a reaction between \[propan - 2 - one\] and methyl magnesium bromide (Grignard’s reagent).
Note:
The methyl magnesium bromide must be used along with dry ether in the reaction. The Grignard’s reagent is a very reactive organometallic compound that can react with even traces of water to produce an alkane corresponding to the alkyl present in the reagent.
Complete answer:
The organic compound \[2 - methy - propan - 2 - ol\] contains a branched carbon chain of four carbon atoms with branching present at the second position and a hydroxyl functional group attached at the same position. This is the formula of a tertiary alcohol.
The reagent given to us is methyl magnesium bromide which is known as the Grignard’s reagent. This is a special organometallic compound containing magnesium metal bonded to a halogen (bromine in this case) and an alkyl group (methyl in this case). Due to the electronegativity differences, the molecule is polarized and the carbon atom of the alkyl group gets a partial negative charge and the magnesium metal gets a partial positive charge.
The negatively polarized alkyl group becomes a good nucleophile that is capable of reacting with highly electrophilic functional group like the carbonyl compounds. Hence, a reaction between an aldehyde or ketone with a Grignard reagent can be used to synthesize corresponding alcohols with the same number of carbon atoms as the parent carbonyl compound.
The carbonyl compound is selected on the basis of the type of alcohol desired. Since our desired product is \[2 - methy - propan - 2 - ol\] which is a tertiary alcohol, a ketone containing three carbon atoms would be a perfect choice. The methyl group from methyl magnesium bromide will provide the fourth carbon atom. A symmetrical ketone that fits this criteria is acetone or \[propan - 2 - one\].

Hence, \[2 - methy - propan - 2 - ol\] can be produced by a reaction between \[propan - 2 - one\] and methyl magnesium bromide (Grignard’s reagent).
Note:
The methyl magnesium bromide must be used along with dry ether in the reaction. The Grignard’s reagent is a very reactive organometallic compound that can react with even traces of water to produce an alkane corresponding to the alkyl present in the reagent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




