
How do primary , secondary and tertiary amines react with nitrous acid ?
-Elucidate the structure of glucose .
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint:
a)Primary , secondary and tertiary amines react differently with nitrous acid , that is we get different products .
b)Glucose is a monosaccharide which contains six carbon atoms and has the formula ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$ .
Complete step by step answer:
(a) Nitrous acid is a weak and unstable acid .The reaction of nitrous acid with amines is used to distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
When nitrous acid reacts with primary amines, a colourless and odourless gas is evolved along with nitrogen .
$C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2} + HN{O_2} \to C{H_2}C{H_2}OH + {N_2} + {H_2}O$
Sometimes along with propan-1-ol, propan-2-ol, 1 chloropropane and propene are also obtained.
When nitrous acid reacts with secondary amines no gas is produced and we only get a carcinogenic compound, that is, nitrosamine.
${(C{H_3}C{H_2})_2}NH + HN{O_2} \to {(C{H_3}C{H_2})_2}N - N = O + {H_2}O$
When nitrous acid reacts with tertiary amines we get a colourless solution, that is, an ion is formed by reaction with the acid which is soluble in water .
${(C{H_3}C{H_2})_3}N + HN{O_2} \to [{(C{H_3}C{H_2})_3}N{H^ + }]N{O_2}^ - $
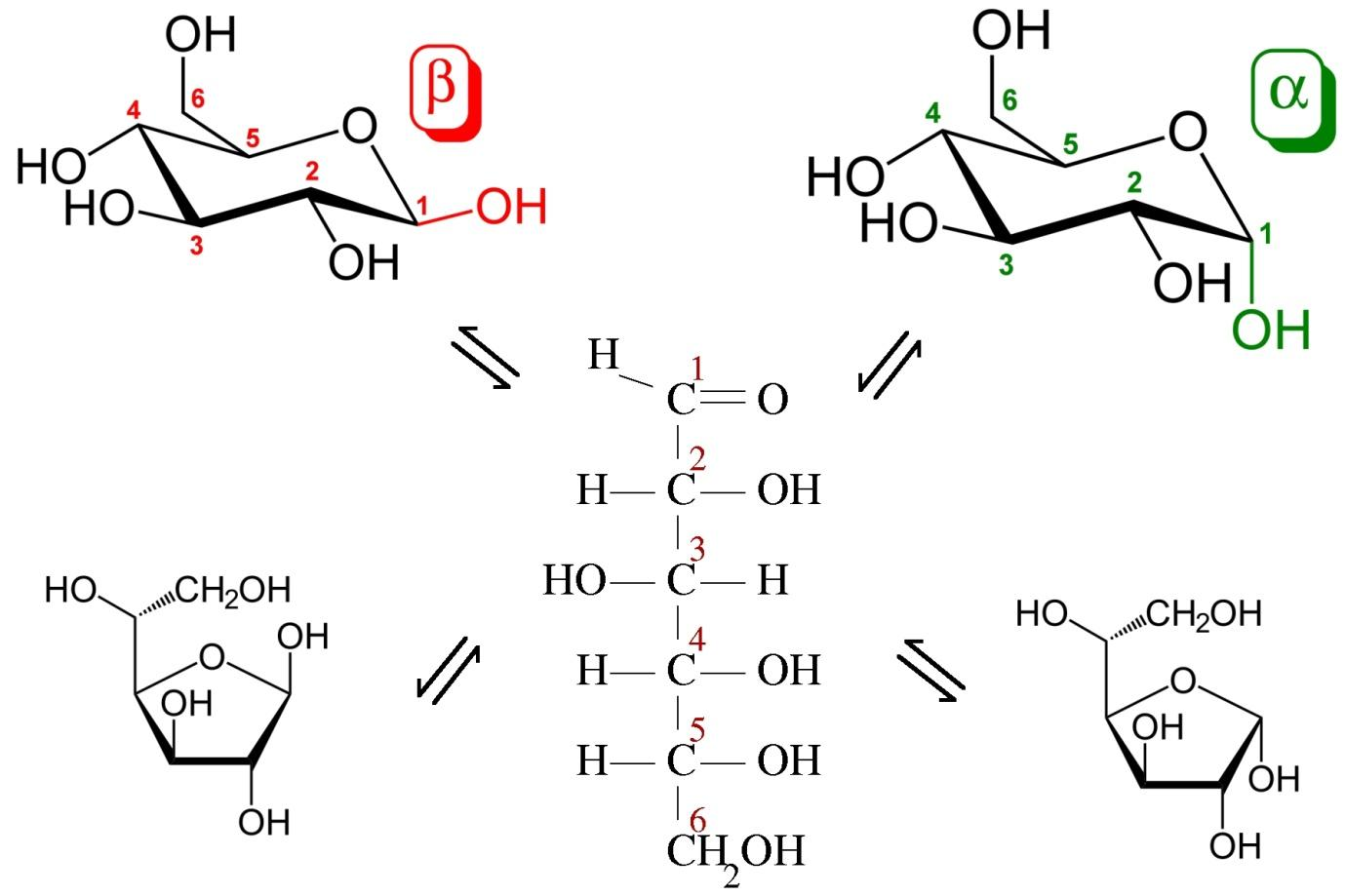
(b) Structure of glucose.
Glucose is an aldohexose which means it contains an aldehyde group with a chain of six carbon atoms in a straight chain . It contains five hydroxyl groups and one aldehyde group .
One of the hydroxyl groups is primary and the other four are secondary .
Formula of glucose is ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$
There are different structures of glucose, that is, open chain structure or the Fischer structure, cyclic structure and ring structure or the pyranose structure.
The structures of glucose are as follows :
Note:(a) Nitrous acid reacts with aliphatic amines to distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary amines. It is a bronsted acid and is prepared immediately before use as it is unstable. With this ,all amines undergo reversible salt formation.
(b) The structure of glucose can be confirmed by many tests like reacting it with $HI$ which gives n-hexane indicating that it has six atoms in a straight chain . When it is treated with $HCN$, glucose-cyanohydrin is formed indicating the presence of a carbonyl group.
a)Primary , secondary and tertiary amines react differently with nitrous acid , that is we get different products .
b)Glucose is a monosaccharide which contains six carbon atoms and has the formula ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$ .
Complete step by step answer:
(a) Nitrous acid is a weak and unstable acid .The reaction of nitrous acid with amines is used to distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
When nitrous acid reacts with primary amines, a colourless and odourless gas is evolved along with nitrogen .
$C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2} + HN{O_2} \to C{H_2}C{H_2}OH + {N_2} + {H_2}O$
Sometimes along with propan-1-ol, propan-2-ol, 1 chloropropane and propene are also obtained.
When nitrous acid reacts with secondary amines no gas is produced and we only get a carcinogenic compound, that is, nitrosamine.
${(C{H_3}C{H_2})_2}NH + HN{O_2} \to {(C{H_3}C{H_2})_2}N - N = O + {H_2}O$
When nitrous acid reacts with tertiary amines we get a colourless solution, that is, an ion is formed by reaction with the acid which is soluble in water .
${(C{H_3}C{H_2})_3}N + HN{O_2} \to [{(C{H_3}C{H_2})_3}N{H^ + }]N{O_2}^ - $
(b) Structure of glucose.
Glucose is an aldohexose which means it contains an aldehyde group with a chain of six carbon atoms in a straight chain . It contains five hydroxyl groups and one aldehyde group .
One of the hydroxyl groups is primary and the other four are secondary .
Formula of glucose is ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$
There are different structures of glucose, that is, open chain structure or the Fischer structure, cyclic structure and ring structure or the pyranose structure.
The structures of glucose are as follows :

Note:(a) Nitrous acid reacts with aliphatic amines to distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary amines. It is a bronsted acid and is prepared immediately before use as it is unstable. With this ,all amines undergo reversible salt formation.
(b) The structure of glucose can be confirmed by many tests like reacting it with $HI$ which gives n-hexane indicating that it has six atoms in a straight chain . When it is treated with $HCN$, glucose-cyanohydrin is formed indicating the presence of a carbonyl group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




