
What is the product formed when acetyl chloride reacts with aniline in the presence of pyridine?
(A) Acetanilide
(B) Acetic anhydride
(C) Benzoylacetate
(D) Benzanilide
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: Reaction of acetyl chloride with aniline in presence of pyridine is Nucleophiles substitution of aromatic amines with acid. It forms N-substituted amides. In nucleophilic substitution nucleophile is substituted by other nucleophile
Step by step answer: Aniline is Aromatic amines in which amino group is attached to the benzene ring.
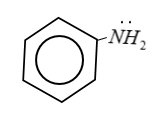
In the reaction of acetyl chloride $C{H_3}COCl$ with aniline, H-atom of $ - N{H_2}$ group is replaced by acetyl group $[C{H_3}C{O^ - }]$ therefore this is a type of nucleophilic substitution.
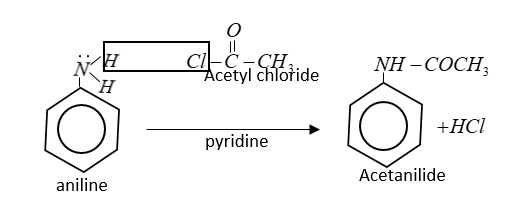
In this reaction $HCl$is lost which reacts with pyridine to form hydrochloride salt of pyridine.
This reaction is also known as Schotten Baumann reaction.
Role pyridine in reaction: Pyridine is a nucleophile for carbonyl groups. It is used as a catalyst in acylation reactions.
N-atoms in pyridine are nucleophilic because the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen cannot be delocalized around the ring.
Mechanism:
(i) Mechanism includes regular attack of nucleophile of an amine on a carbonyl.
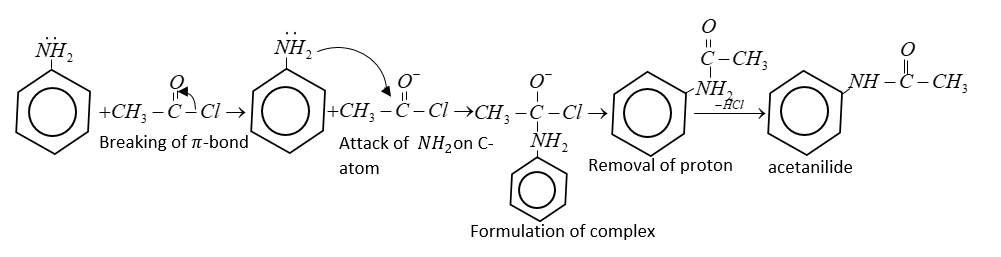
In the final step proton is accepted from $ - N{H_2}$ and from acetanilide.
Therefore, from the above explanation the correct option is (A) Acetanilide.
Note: N-acetylation of aniline with acetyl chloride leads to production of one equivalent acid $(HCl),$ which is formed from salt with unreacted pyridine.
If we add an equivalent base to neutralize $HCl,$ catalytic amount of pyridine yields more in a shorter period.
Step by step answer: Aniline is Aromatic amines in which amino group is attached to the benzene ring.

In the reaction of acetyl chloride $C{H_3}COCl$ with aniline, H-atom of $ - N{H_2}$ group is replaced by acetyl group $[C{H_3}C{O^ - }]$ therefore this is a type of nucleophilic substitution.

In this reaction $HCl$is lost which reacts with pyridine to form hydrochloride salt of pyridine.
This reaction is also known as Schotten Baumann reaction.
Role pyridine in reaction: Pyridine is a nucleophile for carbonyl groups. It is used as a catalyst in acylation reactions.
N-atoms in pyridine are nucleophilic because the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen cannot be delocalized around the ring.
Mechanism:
(i) Mechanism includes regular attack of nucleophile of an amine on a carbonyl.

In the final step proton is accepted from $ - N{H_2}$ and from acetanilide.
Therefore, from the above explanation the correct option is (A) Acetanilide.
Note: N-acetylation of aniline with acetyl chloride leads to production of one equivalent acid $(HCl),$ which is formed from salt with unreacted pyridine.
If we add an equivalent base to neutralize $HCl,$ catalytic amount of pyridine yields more in a shorter period.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




