
Products obtained when cold $HI$ reacts with isopropyl methyl ether at $273K$ are:
(A) Isopropyl iodine and methyl alcohol
(B) Isopropyl alcohol and methyl iodine
(C) Isopropyl iodine and water
(D) Methyl iodine and water
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: $HI$ reacts with isopropyl methyl ether by undergoing substitution reaction. Substitution reaction is a reaction in which one functional group of the compound gets substituted with another group. Substitution reaction is of two types i.e. nucleophilic substitution reaction and electrophilic substitution reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
When isopropyl methyl ether reacts with cold $HI$ , it undergoes $S{N_2}$ reaction. In $S{N_2}$ reaction, the elimination of the leaving group and attack of the nucleophile occurs simultaneously.
In the reaction, isopropyl methyl ether (mixed ether) or reacting with cold $HI$ yields methyl iodine (lower alkyl halide) and isopropyl alcohol (higher alcohol), as show in the reaction below:
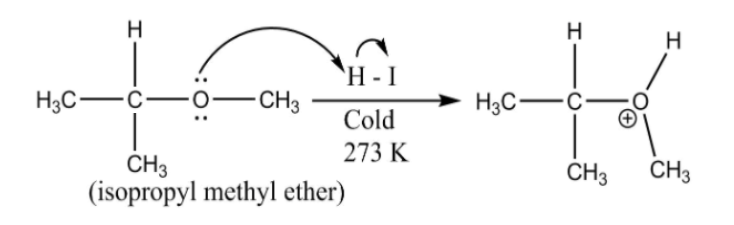
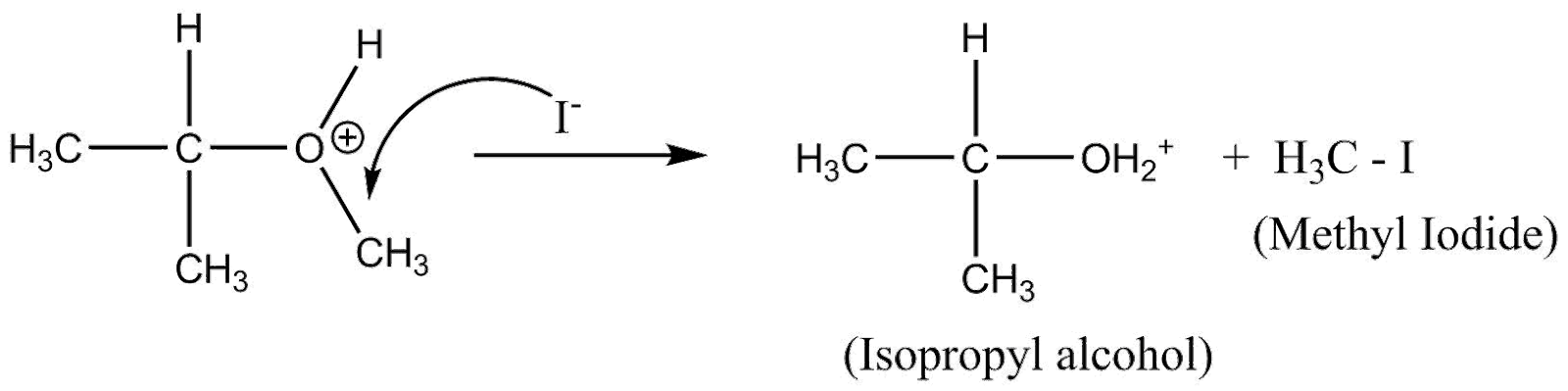
The ${(C{H_3})_2} - CH - O - $ is formed and $H$ from $H - I$ attaches to it. Whereas, the $I$ from $H - I$ attaches to $ - C{H_3}$ (leaving group)
Additional Information:
When isopropyl methyl ether is reacted with hot $HI$ instead of cold $HI$ , following reaction takes place at $373K$
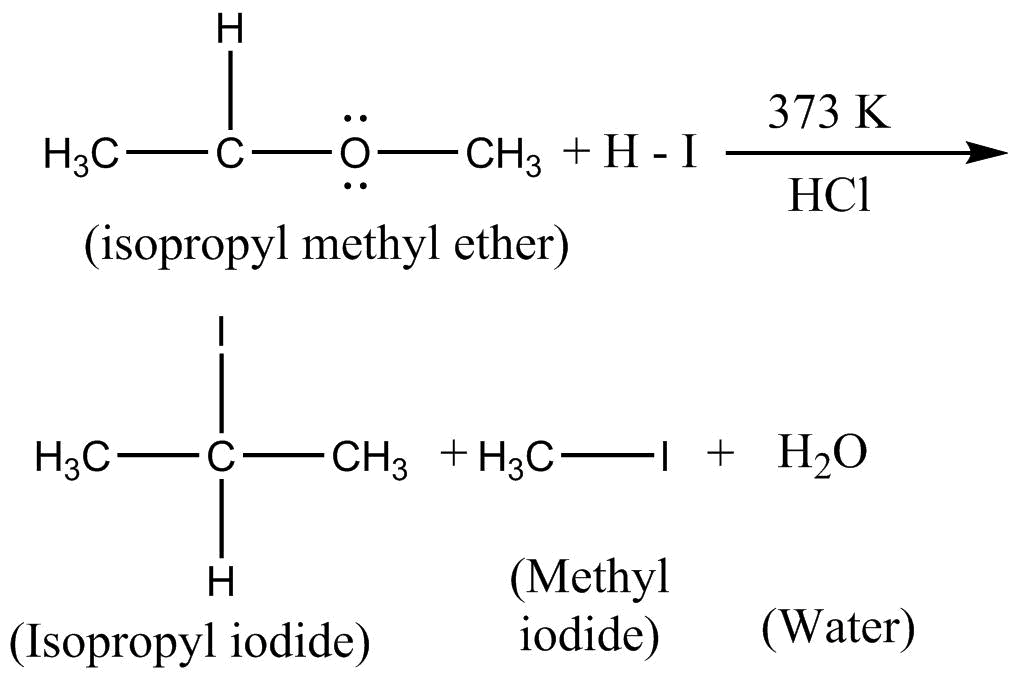
Hence, isopropyl iodine, methyl iodine and water are obtained upon the reaction of isopropyl methyl ether with hot conc $HI$ .
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: $S{N_2}$ reaction is a common reaction in organic chemistry. In this reaction one bond is broken and another bond is formed simultaneously. In this reaction, the nucleophile attacks from the back side of the substrate, to break the carbon-leaving group bond. It then forms a new carbon-nucleophile bond. For observing the maximum rate of $S{N_2}$ reaction, the substrate must be least hindered. Therefore, the primary and methyl substrate show maximum rate of $S{N_2}$ reaction, the secondary substrates have a lower rate of reaction and the tertiary substrate do not participate at all in the $S{N_2}$ reaction because of large amount of steric hindrance in them.
Complete step by step answer:
When isopropyl methyl ether reacts with cold $HI$ , it undergoes $S{N_2}$ reaction. In $S{N_2}$ reaction, the elimination of the leaving group and attack of the nucleophile occurs simultaneously.
In the reaction, isopropyl methyl ether (mixed ether) or reacting with cold $HI$ yields methyl iodine (lower alkyl halide) and isopropyl alcohol (higher alcohol), as show in the reaction below:

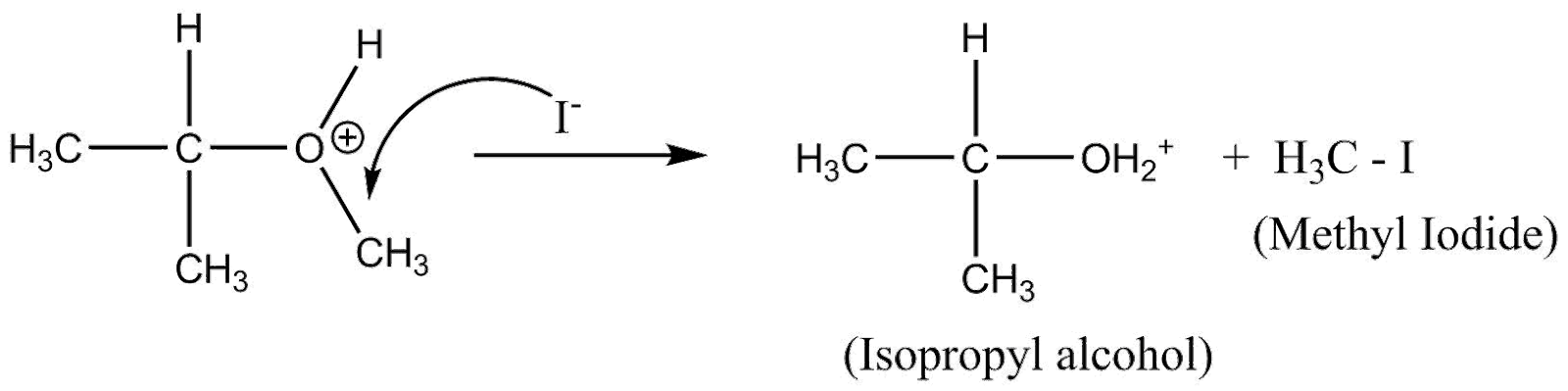
The ${(C{H_3})_2} - CH - O - $ is formed and $H$ from $H - I$ attaches to it. Whereas, the $I$ from $H - I$ attaches to $ - C{H_3}$ (leaving group)
Additional Information:
When isopropyl methyl ether is reacted with hot $HI$ instead of cold $HI$ , following reaction takes place at $373K$
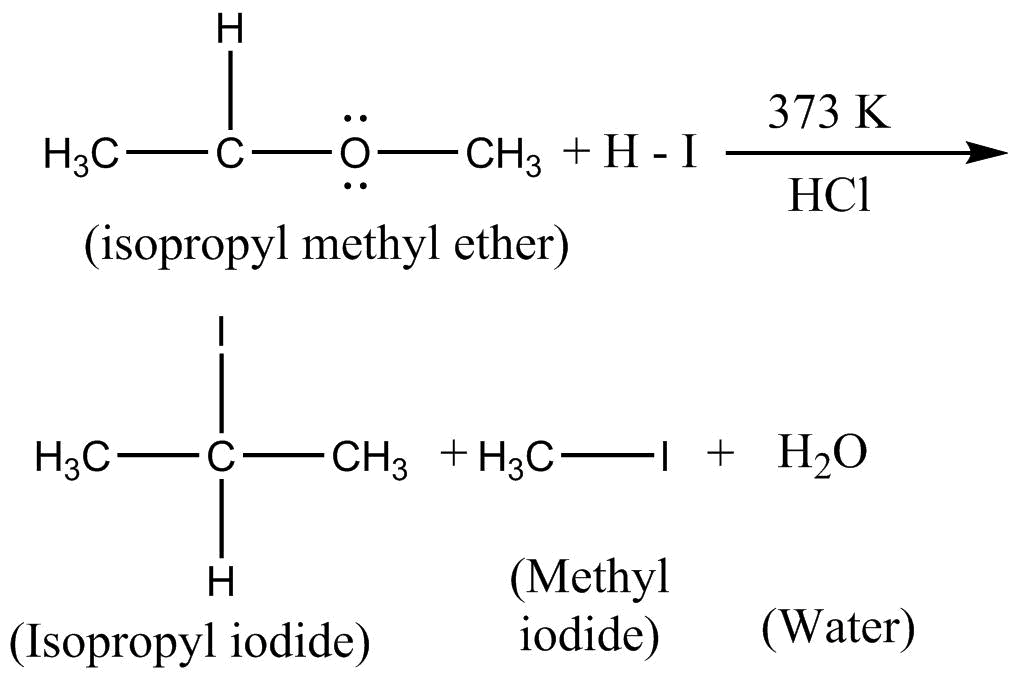
Hence, isopropyl iodine, methyl iodine and water are obtained upon the reaction of isopropyl methyl ether with hot conc $HI$ .
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: $S{N_2}$ reaction is a common reaction in organic chemistry. In this reaction one bond is broken and another bond is formed simultaneously. In this reaction, the nucleophile attacks from the back side of the substrate, to break the carbon-leaving group bond. It then forms a new carbon-nucleophile bond. For observing the maximum rate of $S{N_2}$ reaction, the substrate must be least hindered. Therefore, the primary and methyl substrate show maximum rate of $S{N_2}$ reaction, the secondary substrates have a lower rate of reaction and the tertiary substrate do not participate at all in the $S{N_2}$ reaction because of large amount of steric hindrance in them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




