
What proportion of the offspring obtained from cross AABBCC X AaBbCc will be completely heterozygous for all the genes segregated independently?
A. \[\dfrac{1}{8}\]
B. \[\dfrac{1}{4}\]
C. \[\dfrac{1}{2}\]
D. \[\dfrac{1}{16}\]
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: Zygosity is the extent where both copies of a chromosome or of a gene have the very same genome sequence. The diploid species is heterozygous in the genetic locus since its cells produce two distinct alleles (one wild-type allele and the other mutated allele) of a gene.
Complete answer:
The first parent genotype is AABBCC, so the possible gamete formed is only one type ABC, which is completely homozygous. The second parent is heterozygous for all the genes with genotype AaBbCc, so the possible gametes formed are Abc, ABc, aBc, aBC, abC, AbC, abc, ABC. Thus, only one offspring out of eight is completely heterozygous. Hence, the proportion of the offspring obtained from the cross AABBCC X AaBbCc is \[\frac{1}{8}\] for all the genes segregated independently.
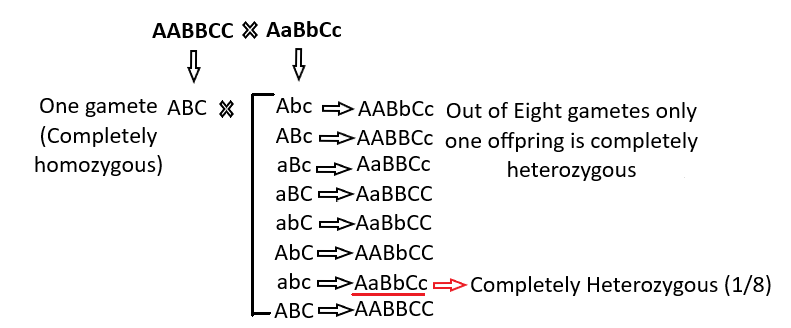
So, the correct answer is option (A).
Additional information:
An organism is defined to be homozygous for a specific gene since the same alleles of the gene are represented on both homologous chromosomes. An individual who will be homozygous-dominant for a specific trait holds two copies of an allele that codes for a dominant trait. This allele is also referred to as the "dominant allele" Whenever the species is homozygous-dominant for a specific trait, the genotype of the species is depicted by a doubling of the symbol for that characteristic, such as "PP". A person who really is homozygous-recessive to a specific feature beheld two copies of the allele that will be encoded for the recessive trait. The genotype of a species that is homozygous-recessive to a specific feature is defined by a doubling of the relevant letter, like "pp".
Note: Heterozygous is a phenomenon wherein multiple variants of a single gene are being inherited from each one of the biological parents. The two distinct alleles associate with one another in a heterozygous genotype. This influences how the features are expressed. Diseases such as Huntington's disease, Marfan's syndrome, and hypercholesterolemia are linked with heterozygous gene variants.
Complete answer:
The first parent genotype is AABBCC, so the possible gamete formed is only one type ABC, which is completely homozygous. The second parent is heterozygous for all the genes with genotype AaBbCc, so the possible gametes formed are Abc, ABc, aBc, aBC, abC, AbC, abc, ABC. Thus, only one offspring out of eight is completely heterozygous. Hence, the proportion of the offspring obtained from the cross AABBCC X AaBbCc is \[\frac{1}{8}\] for all the genes segregated independently.

So, the correct answer is option (A).
Additional information:
An organism is defined to be homozygous for a specific gene since the same alleles of the gene are represented on both homologous chromosomes. An individual who will be homozygous-dominant for a specific trait holds two copies of an allele that codes for a dominant trait. This allele is also referred to as the "dominant allele" Whenever the species is homozygous-dominant for a specific trait, the genotype of the species is depicted by a doubling of the symbol for that characteristic, such as "PP". A person who really is homozygous-recessive to a specific feature beheld two copies of the allele that will be encoded for the recessive trait. The genotype of a species that is homozygous-recessive to a specific feature is defined by a doubling of the relevant letter, like "pp".
Note: Heterozygous is a phenomenon wherein multiple variants of a single gene are being inherited from each one of the biological parents. The two distinct alleles associate with one another in a heterozygous genotype. This influences how the features are expressed. Diseases such as Huntington's disease, Marfan's syndrome, and hypercholesterolemia are linked with heterozygous gene variants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




