
Prove by vector method:
$\cos \left( {A + B} \right) = \cos A\cos B - \sin A\sin B$
Answer
545.4k+ views
Hint: Here, we will first draw a figure showing two unit vectors with one of the angles negative i.e. below the $x$ axis. Hence, using the dot-product with vector form and the Cartesian form, after drawing the figure, we will be able to equate both the dot-products. Hence, we will be able to prove the given trigonometric identity.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to prove the given trigonometric identity using vector method, we will, first of all, let $OP$ and $OQ$ be two unit vectors such that they are making the angles $A$ and $B$ respectively with the positive direction of $x$ axis but above and below the axis respectively.
Hence, we have the figure:
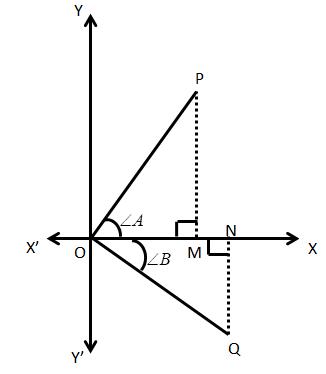
Hence, clearly from the figure, $\angle QOP = \angle A + B$
Now, we know that,
$\widehat {OP} = \overrightarrow {OM} + \overrightarrow {MP} $
$ \Rightarrow \widehat {OP} = \widehat i\cos A + \widehat j\sin A$
Similarly,
$\widehat {OQ} = \overrightarrow {ON} + \overrightarrow {NQ} $
$ \Rightarrow \widehat {OQ} = \widehat i\cos B - \widehat j\sin B$
Now, by using dot-product,
$\widehat {OP} \cdot \widehat {OQ} = \left| {OP} \right|\left| {OQ} \right|\cos \left( {A + B} \right)$
And since, these are unit vectors, thus, we get,
$\widehat {OP} \cdot \widehat {OQ} = 1 \times \cos \left( {A + B} \right) = \cos \left( {A + B} \right)$……………………….$\left( 1 \right)$
Also, in terms of components, we have,
$\widehat {OP} \cdot \widehat {OQ} = \left( {\widehat i\cos A + \widehat j\sin A} \right)\left( {\widehat i\cos B - \widehat j\sin B} \right)$
Solving this further, we get,
$\widehat {OP} \cdot \widehat {OQ} = \cos A\cos B - \sin A\sin B$………………………….$\left( 2 \right)$
Hence, equating $\left( 1 \right)$ and $\left( 2 \right)$, we get,
$\cos \left( {A + B} \right) = \cos A\cos B - \sin A\sin B$
Therefore, this is the required answer.
Hence, proved
Note:
A scalar is a quantity that has a magnitude whereas; a vector is a mathematical quantity that has both magnitude and direction. A line of given length and pointing along a given direction, such as an arrow, is a typical representation of a vector. Now, position vector is also known as location vector, it is a straight line having one end fixed and the other end attached to a moving point, it is used to describe the position of a certain point, which turns out to be its respective coordinates.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to prove the given trigonometric identity using vector method, we will, first of all, let $OP$ and $OQ$ be two unit vectors such that they are making the angles $A$ and $B$ respectively with the positive direction of $x$ axis but above and below the axis respectively.
Hence, we have the figure:

Hence, clearly from the figure, $\angle QOP = \angle A + B$
Now, we know that,
$\widehat {OP} = \overrightarrow {OM} + \overrightarrow {MP} $
$ \Rightarrow \widehat {OP} = \widehat i\cos A + \widehat j\sin A$
Similarly,
$\widehat {OQ} = \overrightarrow {ON} + \overrightarrow {NQ} $
$ \Rightarrow \widehat {OQ} = \widehat i\cos B - \widehat j\sin B$
Now, by using dot-product,
$\widehat {OP} \cdot \widehat {OQ} = \left| {OP} \right|\left| {OQ} \right|\cos \left( {A + B} \right)$
And since, these are unit vectors, thus, we get,
$\widehat {OP} \cdot \widehat {OQ} = 1 \times \cos \left( {A + B} \right) = \cos \left( {A + B} \right)$……………………….$\left( 1 \right)$
Also, in terms of components, we have,
$\widehat {OP} \cdot \widehat {OQ} = \left( {\widehat i\cos A + \widehat j\sin A} \right)\left( {\widehat i\cos B - \widehat j\sin B} \right)$
Solving this further, we get,
$\widehat {OP} \cdot \widehat {OQ} = \cos A\cos B - \sin A\sin B$………………………….$\left( 2 \right)$
Hence, equating $\left( 1 \right)$ and $\left( 2 \right)$, we get,
$\cos \left( {A + B} \right) = \cos A\cos B - \sin A\sin B$
Therefore, this is the required answer.
Hence, proved
Note:
A scalar is a quantity that has a magnitude whereas; a vector is a mathematical quantity that has both magnitude and direction. A line of given length and pointing along a given direction, such as an arrow, is a typical representation of a vector. Now, position vector is also known as location vector, it is a straight line having one end fixed and the other end attached to a moving point, it is used to describe the position of a certain point, which turns out to be its respective coordinates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




