
Pure tall plant is crossed to the dwarf plant. ${ F_1 }$ generation has only tall plants, while the ${ F_2 }$ generation has both tall and dwarf in a ratio of 3: 1. The phenomenon is due to
(A)Dominance
(B)Codominance
(C)Incomplete dominance
(D)Heredity
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: The phenomena where ${ F_1 }$ generation has only tall plants while ${ F_2 }$ generation has both tall and dwarf plant is due to an individual containing two allelic forms of a gene, one is expressed to the exclusion of the other.
Complete answer:
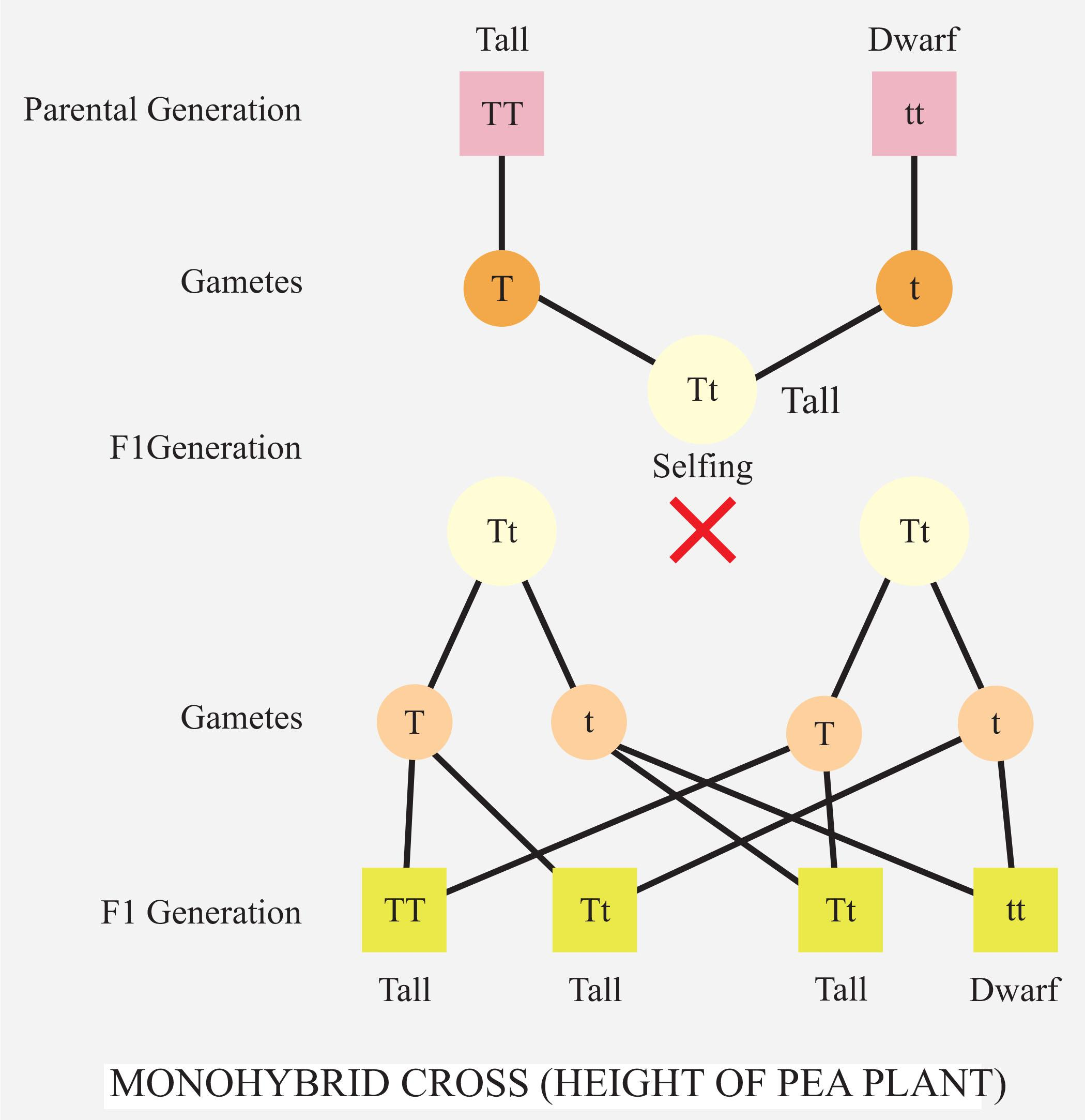
A cross between pure breeding tall plant (TT) and dwarf (tt) plant produce all tall hybrids (Tt). The allele/factor which will express itself within the heterozygous individual is named as the dominant factor; here tallness is expressed in heterozygotes and hence is that the dominant character. The opposite factor whose effect is masked by the presence of the dominant factor is named the recessive factor (dwarfism). The selfing of “Tt” produces the phenotypic ratio of 3:1 in the ${ F_2 }$ generation which suggests that both homozygous dominant (TT) and heterozygous dominant (Tt) show “tall” phenotype and homozygous recessive (tt) shows “dwarf” phenotype.
Additional Information: Alleles are often either dominant or recessive. Dominant alleles show their effect even though the individual only has one copy of the allele (also referred to as being heterozygous). As an example, the allele for brown eyes is dominant, therefore you simply need one copy of the 'brown eye' allele to possess brown eyes (although, with two copies you'll still have brown eyes). When the individuals have two copies of alleles then only the effects of recessive alleles are shown. As an example, the allele for blue eyes is recessive, therefore to possess blue eyes you would like to possess two copies of the 'blue eye' allele.
So, the correct answer is ‘ Dominance’.
Note: If both alleles are dominant, it's called codominance. The resulting characteristic is because of both alleles being expressed equally. An example of this is the blood type AB which is the results of codominance of the A and B dominant alleles.
Complete answer:
A cross between pure breeding tall plant (TT) and dwarf (tt) plant produce all tall hybrids (Tt). The allele/factor which will express itself within the heterozygous individual is named as the dominant factor; here tallness is expressed in heterozygotes and hence is that the dominant character. The opposite factor whose effect is masked by the presence of the dominant factor is named the recessive factor (dwarfism). The selfing of “Tt” produces the phenotypic ratio of 3:1 in the ${ F_2 }$ generation which suggests that both homozygous dominant (TT) and heterozygous dominant (Tt) show “tall” phenotype and homozygous recessive (tt) shows “dwarf” phenotype.
Additional Information: Alleles are often either dominant or recessive. Dominant alleles show their effect even though the individual only has one copy of the allele (also referred to as being heterozygous). As an example, the allele for brown eyes is dominant, therefore you simply need one copy of the 'brown eye' allele to possess brown eyes (although, with two copies you'll still have brown eyes). When the individuals have two copies of alleles then only the effects of recessive alleles are shown. As an example, the allele for blue eyes is recessive, therefore to possess blue eyes you would like to possess two copies of the 'blue eye' allele.
So, the correct answer is ‘ Dominance’.

Note: If both alleles are dominant, it's called codominance. The resulting characteristic is because of both alleles being expressed equally. An example of this is the blood type AB which is the results of codominance of the A and B dominant alleles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




