
Pyrimidine bases present in RNA are:
A. Adenine and Guanine
B. Thymine and Uracil
C. Uracil and Cytosine
D. Thymine and Cytosine
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: A pyrimidine is a six-membered nitrogenous heterocyclic compound. Pyrimidine bases are weak bases. They are stabilized by resonance in the ring, due to which there is partial double bond character. Substituted pyrimidines are components of (RNA) ribonucleic acids and (DNA) deoxyribonucleic acids.
Complete step by step answer:
Pyrimidines are aromatic nitrogen heterocycles with a structure similar to benzene but containing two nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 3 positions of the ring, with the molecular formula (${{\text{C}}_{4}}{{\text{H}}_{4}}{{\text{N}}_{2}}$). The structure of pyrimidine is
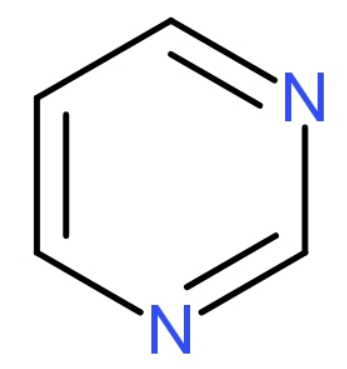
The pyrimidine bases present in RNA:
-Cytosine: Cytosine is a pyrimidine derivative base, with a heterocyclic, aromatic ring, with two substituents attached one, an amine group at positioned 4 and a keto group at positioned 2. It is present in both DNA and RNA. The molecular mass of cytosine is 111 grams. Structure of cytosine is
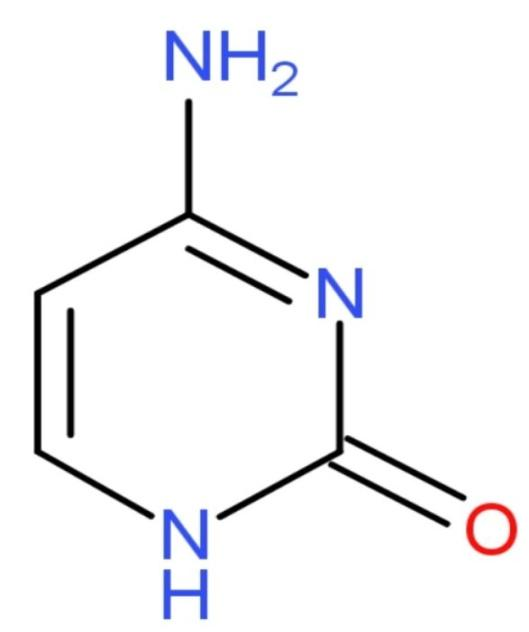
-Uracil: The IUPAC name of uracil is Pyrimidine-2,4(1 H, 3H)-dione with molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{4}}{{\text{H}}_{4}}{{\text{N}}_{2}}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$. In the RNA, uracil is the one which binds to adenine through two hydrogen bonds. It is replaced by Thymine in DNA. It is a demethylated form of Thymine. The molecular mass of uracil is 112 grams. The structure of Uracil is
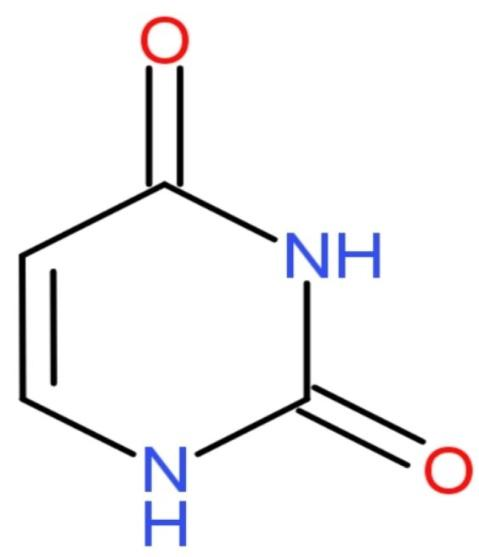
- The purine bases include Adenine and Guanine whereas the pyrimidines include Thymine, Cytosine and Uracil.
A. Guanine and Adenine: Adenine and Guanine both are not pyrimidines, hence it is incorrect.
B. Thymine and Uracil: Thymine and Uracil both are pyrimidines, not Uracil is present in RNA and Thymine is present in DNA, hence it is incorrect.
D. Cytosine and Thymine: Cytosine is pyrimidine and Thymine is also a pyrimidine but it is not present in RNA, it is present in DNA, hence it is also incorrect.
So, the correct answer of the question is option ‘c’, which is Uracil and Cytosine.
Note: The purines and pyrimidines bases are different. The purine bases include Adenine and Guanine whereas the pyrimidines include Thymine, Cytosine and Uracil. Thymine is in DNA. Thymine is replaced by uracil in RNA.
Complete step by step answer:
Pyrimidines are aromatic nitrogen heterocycles with a structure similar to benzene but containing two nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 3 positions of the ring, with the molecular formula (${{\text{C}}_{4}}{{\text{H}}_{4}}{{\text{N}}_{2}}$). The structure of pyrimidine is

The pyrimidine bases present in RNA:
-Cytosine: Cytosine is a pyrimidine derivative base, with a heterocyclic, aromatic ring, with two substituents attached one, an amine group at positioned 4 and a keto group at positioned 2. It is present in both DNA and RNA. The molecular mass of cytosine is 111 grams. Structure of cytosine is

-Uracil: The IUPAC name of uracil is Pyrimidine-2,4(1 H, 3H)-dione with molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{4}}{{\text{H}}_{4}}{{\text{N}}_{2}}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$. In the RNA, uracil is the one which binds to adenine through two hydrogen bonds. It is replaced by Thymine in DNA. It is a demethylated form of Thymine. The molecular mass of uracil is 112 grams. The structure of Uracil is

- The purine bases include Adenine and Guanine whereas the pyrimidines include Thymine, Cytosine and Uracil.
A. Guanine and Adenine: Adenine and Guanine both are not pyrimidines, hence it is incorrect.
B. Thymine and Uracil: Thymine and Uracil both are pyrimidines, not Uracil is present in RNA and Thymine is present in DNA, hence it is incorrect.
D. Cytosine and Thymine: Cytosine is pyrimidine and Thymine is also a pyrimidine but it is not present in RNA, it is present in DNA, hence it is also incorrect.
So, the correct answer of the question is option ‘c’, which is Uracil and Cytosine.
Note: The purines and pyrimidines bases are different. The purine bases include Adenine and Guanine whereas the pyrimidines include Thymine, Cytosine and Uracil. Thymine is in DNA. Thymine is replaced by uracil in RNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




