
How many radial nodes are present in the $ 3s $ orbital?
Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint: Find out the quantum numbers associated with the given orbital and use those quantum numbers to determine the number of radial nodes present in a particular orbital. Remember that all quantum numbers are not needed for radial note calculation.
Complete answer:
Each electron in an atom can be uniquely identified on the basis of its quantum numbers. No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of all four quantum numbers. Different quantum numbers provide different information about the position of an electron inside the atom.
The principal quantum number $ n $ tells us about the energy level i.e. the number of shells present in an atom.
The azimuthal quantum number $ l $ tells us the shape of the orbital and gives us information regarding the subshells present in an atom.
The s-orbital is perfectly spherical in nature and symmetrical around all the three axes.
Orbitals define the three dimensional spaces that are accessible to the electrons. Nodes are the empty spaces in between the orbitals that have zero probability of finding an electron.
Nodes can be angular or radial in nature. Radial nodes define spaces in between the orbitals of consecutive principal quantum numbers where electrons cannot be positioned.
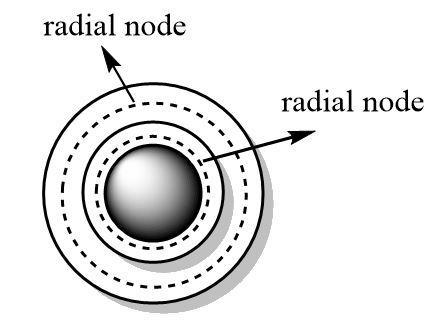
The formula for calculating the number of radial nodes is as follows:
$ {\text{radial nodes}} = n - l - 1 $
The $ 3s $ orbitals have the principal quantum number $ n = 3 $ and an s-subshell that has azimuthal quantum number $ l = 0 $ .
$ {\text{radial nodes(3s)}} = 3 - 0 - 1 $
$ {\text{radial nodes(3s)}} = 2 $
Hence, the number of radial nodes present in $ 3s $ orbital are two.
Note:
The quantum numbers defined for any orbital are not independent of each other. The azimuthal quantum number is always related to the principal quantum number and cannot have a value that exceeds the principal quantum number.
Complete answer:
Each electron in an atom can be uniquely identified on the basis of its quantum numbers. No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of all four quantum numbers. Different quantum numbers provide different information about the position of an electron inside the atom.
The principal quantum number $ n $ tells us about the energy level i.e. the number of shells present in an atom.
The azimuthal quantum number $ l $ tells us the shape of the orbital and gives us information regarding the subshells present in an atom.
The s-orbital is perfectly spherical in nature and symmetrical around all the three axes.
Orbitals define the three dimensional spaces that are accessible to the electrons. Nodes are the empty spaces in between the orbitals that have zero probability of finding an electron.
Nodes can be angular or radial in nature. Radial nodes define spaces in between the orbitals of consecutive principal quantum numbers where electrons cannot be positioned.

The formula for calculating the number of radial nodes is as follows:
$ {\text{radial nodes}} = n - l - 1 $
The $ 3s $ orbitals have the principal quantum number $ n = 3 $ and an s-subshell that has azimuthal quantum number $ l = 0 $ .
$ {\text{radial nodes(3s)}} = 3 - 0 - 1 $
$ {\text{radial nodes(3s)}} = 2 $
Hence, the number of radial nodes present in $ 3s $ orbital are two.
Note:
The quantum numbers defined for any orbital are not independent of each other. The azimuthal quantum number is always related to the principal quantum number and cannot have a value that exceeds the principal quantum number.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




