
Reaction of aniline with \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] followed by treatment of dilute acid gives:
A) \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{NHOH}}\]
B) \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH}}\]
C) \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{NHN}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\]
D) \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_6}\]
Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint:Aniline reacts similarly to primary aliphatic amines. Aniline gives diazonium ion after treatment with nitrous acid. On further treatment with dilute acid undergo hydrolysis reaction.
Complete solution:
In this reaction, aniline is the reactant and reagent given to us is nitrous acid, \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] and dilute acid.
Aniline is the simplest aromatic amine that behaves similarly to primary aliphatic amines. It consists of an amino group bonded to a phenyl group.
Reagent nitrous acid is prepared by reaction of sodium nitrite with hydrochloric acid. It is a weak acid
\[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + HCl}} \to {\text{ NaCl + HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]
Now, we will see the reaction mechanism when of aniline reacts with \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] followed by treatment with dilute acid.
Step 1: Conversion of aniline to diazonium ion using nitrous acid, \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]reagent.
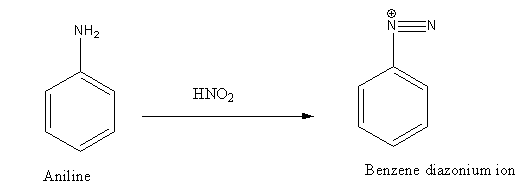
Step 2: Diazonium ion on further treatment with dilute acid undergoes hydrolysis reaction and gives phenol as the product.
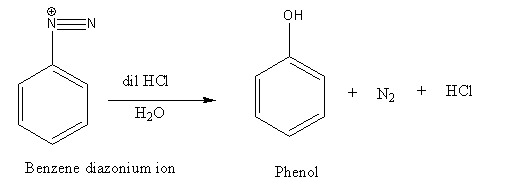
Thus, the correct options are (B).
Note:Aromatic diazonium ion is a very important intermediate to produce substituted benzene. The final product depends on reagent use. Here the reagent used is dilute acid so the diazonium ion undergoes a hydrolysis reaction. The addition of water molecules is known as the hydrolysis reaction. Amines on hydrolysis give alcohol as the product while aniline gives phenol as the product.
Complete solution:
In this reaction, aniline is the reactant and reagent given to us is nitrous acid, \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] and dilute acid.
Aniline is the simplest aromatic amine that behaves similarly to primary aliphatic amines. It consists of an amino group bonded to a phenyl group.
Reagent nitrous acid is prepared by reaction of sodium nitrite with hydrochloric acid. It is a weak acid
\[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + HCl}} \to {\text{ NaCl + HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]
Now, we will see the reaction mechanism when of aniline reacts with \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] followed by treatment with dilute acid.
Step 1: Conversion of aniline to diazonium ion using nitrous acid, \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]reagent.

Step 2: Diazonium ion on further treatment with dilute acid undergoes hydrolysis reaction and gives phenol as the product.

Thus, the correct options are (B).
Note:Aromatic diazonium ion is a very important intermediate to produce substituted benzene. The final product depends on reagent use. Here the reagent used is dilute acid so the diazonium ion undergoes a hydrolysis reaction. The addition of water molecules is known as the hydrolysis reaction. Amines on hydrolysis give alcohol as the product while aniline gives phenol as the product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




