
What is the reason for the stability of colloidal solution?
Answer
531.1k+ views
Hint: Colloids are heterogeneous solutions consisting of a dispersed phase and a dispersion medium. A colloid is stable if it does not get coagulated easily.
Complete step by step solution:
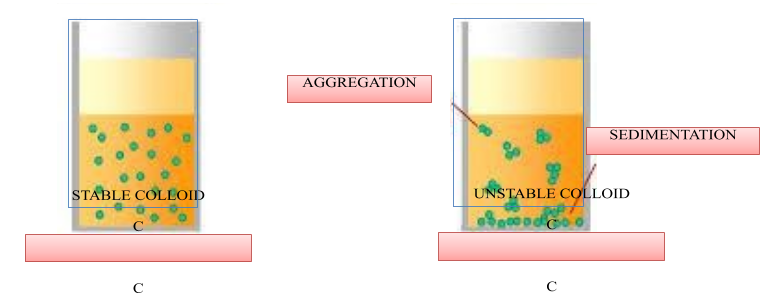
> The stability of colloids is due to two factors:
1) Charge present on the colloid
- The dispersed phase and dispersion medium have charges present on them. Colloidal particles form a sheath of charge on themselves thereby preventing any attraction between opposite charges. An electrical double layer is formed. This layer prevents the coagulation of the colloid in addition to an electrolyte.
2) Solvation of the colloidal particles
- Colloidal system is stable if the colloidal particles are present in the layers of the solvent uniformly. The more the particles are suspended in the layers the more will be the stability of the colloidal system.
> Now, to understand these two factors first we will define lyophilic and lyophobic colloids.
> Lyophilic colloids are those colloids which are solvent loving. These colloids are quite stable as they are extensively solvated. A quick shaking can get the coagulated colloid back to colloidal solution.
> Lyophobic colloids are those colloids which are solvent hating. The interactions among the colloidal particles and the solvent are very less and hence, these are unstable. Lyophilic colloids are used for their protection. They form a layer around them and protect from the attack of an electrolyte.
Hence, we have understood the reasons for the stability of colloids.
Note: Any factor which leads to the prevention of aggregation of colloids will help in stabilizing it. Lyophilic colloids are sometimes called protective colloids because they stabilize lyophobic colloids.
Complete step by step solution:
> The stability of colloids is due to two factors:
1) Charge present on the colloid
- The dispersed phase and dispersion medium have charges present on them. Colloidal particles form a sheath of charge on themselves thereby preventing any attraction between opposite charges. An electrical double layer is formed. This layer prevents the coagulation of the colloid in addition to an electrolyte.
2) Solvation of the colloidal particles
- Colloidal system is stable if the colloidal particles are present in the layers of the solvent uniformly. The more the particles are suspended in the layers the more will be the stability of the colloidal system.
> Now, to understand these two factors first we will define lyophilic and lyophobic colloids.
> Lyophilic colloids are those colloids which are solvent loving. These colloids are quite stable as they are extensively solvated. A quick shaking can get the coagulated colloid back to colloidal solution.
> Lyophobic colloids are those colloids which are solvent hating. The interactions among the colloidal particles and the solvent are very less and hence, these are unstable. Lyophilic colloids are used for their protection. They form a layer around them and protect from the attack of an electrolyte.
Hence, we have understood the reasons for the stability of colloids.
Note: Any factor which leads to the prevention of aggregation of colloids will help in stabilizing it. Lyophilic colloids are sometimes called protective colloids because they stabilize lyophobic colloids.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




