
Recombinant DNA vaccines have proved to be an important tool for the treatment of many diseases. How are these vaccines produced? Explain with examples.
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint:-A recombinant vaccination is a vaccine created through recombinant DNA technology. This includes embedding the DNA encoding an antigen, (for example, a bacterial surface protein) that animates an insusceptible reaction into bacterial or mammalian cells, communicating the antigen in these cells and afterward cleansing it from them.
Complete Answer:-DNA inoculation is a procedure used to secure an organism against illness by infusing it with hereditarily designed DNA to deliver an immunological reaction. Normally vaccines have a possible risk of the vaccine being fatal but in DNA vaccines there is no need of using actual infectious organism.
DNA vaccines provide both cellular and humoral immunity, on the other hand normal vaccines provide only humoral immunity.
Production of recombinant DNA Vaccines
A DNA vaccine is made with a circular double stranded DNA molecule also called plasmid, fabricated with a DNA sequence containing genes encoding one or more proteins of a pathogen. As this DNA is inserted into the cells, it is translated to form antigenic protein. As this protein is foreign to cells, immune response is raised against this protein.
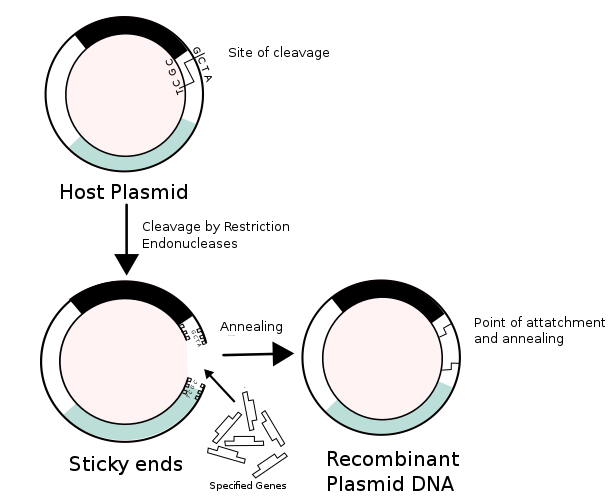
Note:- There is no risk of infection in recombinant DNA vaccination. In earlier times, large scale vaccine production is done by using cell culture. In this technique strains of pathogens were injected into suitable animals and allowed them to proliferate. Then the serum of the animals was collected to extract the antigens. These antigens were used to produce vaccines. There were chances of contamination and also there were chances of some diseases. All these problems are overcome due to recombinant DNA technology.
Complete Answer:-DNA inoculation is a procedure used to secure an organism against illness by infusing it with hereditarily designed DNA to deliver an immunological reaction. Normally vaccines have a possible risk of the vaccine being fatal but in DNA vaccines there is no need of using actual infectious organism.
DNA vaccines provide both cellular and humoral immunity, on the other hand normal vaccines provide only humoral immunity.
Production of recombinant DNA Vaccines
A DNA vaccine is made with a circular double stranded DNA molecule also called plasmid, fabricated with a DNA sequence containing genes encoding one or more proteins of a pathogen. As this DNA is inserted into the cells, it is translated to form antigenic protein. As this protein is foreign to cells, immune response is raised against this protein.

Note:- There is no risk of infection in recombinant DNA vaccination. In earlier times, large scale vaccine production is done by using cell culture. In this technique strains of pathogens were injected into suitable animals and allowed them to proliferate. Then the serum of the animals was collected to extract the antigens. These antigens were used to produce vaccines. There were chances of contamination and also there were chances of some diseases. All these problems are overcome due to recombinant DNA technology.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




