
Refer to the given diagrams showing different types of syngamy and select the option that gives the correct example of each of these.
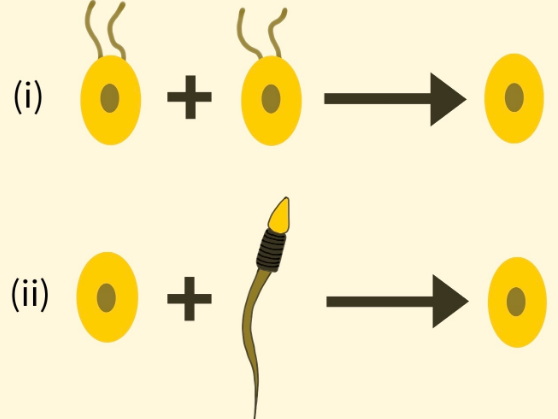
(a) Fucus, Chlamydomonas
(b) Homo sapiens, Fucus
(c) Ficus, Cladophora
(d) Cladophora, Homo sapiens

Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: In the given question image the first option shows the fusion of two morphologically similar gametes known as isogametes whereas the second option shows the fusion of a small male gamete or sperm and a large female gamete or ova which are morphologically different known as anisogametes or oogametes.
Complete answer:
In reference to the given diagrams showing different types of syngamy, the first option represents the fusion of two morphologically different gametes which may differ physiologically are known as isogametes and fusion of isogametes is called isogamy. Isogamy is the characteristic of Cladophora. The only difference between Cladophora's gametes and spores is that there are two flagella in the gametes and four in the spores. The second option represents the fusion of morphologically different gametes known as anisogametes or oogametes and fusion of gametes is called oogamy. Oogamy is the characteristic of Homo sapiens. Syngamy is a process of complete and permanent fusion of male and female gametes for the formation of a zygote.
Additional information:
-Reproduction is a trait that is shared by Homo sapiens with all living beings. Specifically, a kind of sexual reproduction in humans. The mechanism includes two groups of sex cells, also called gametes. The masculine gamete, the spermatozoon, and the feminine gamete, the ovule.
-Cladophora is a genus of filamentous reticulated Ulvophyceae. There are several species in the genus Cladophora that are very difficult to identify and categorize, mostly because of the great variation in their appearances, which is influenced by habitat, age, and environmental conditions.
-Unlike Spirogyra the filaments of the branch of Cladophora do not undergo conjugation.
-In its life cycle, there are two multicellular stages - a haploid gametophyte and a diploid sporophyte - that look extremely similar. Either counting their genes or testing their offspring, is the only way to tell the two phases apart.
-By mitosis, the haploid gametophyte generates haploid gametes and by meiosis, the diploid sporophyte generates haploid spores.
-The only difference between Cladophora's gametes and spores is that there are two flagella in the gametes and four in the spores.
-The flagella are soon retracted and the zygote is secreted around a wall. This zygote immediately germinates and does not have a rest time.
So, the correct answer is ‘Cladophora, Homo sapiens’.
Note:
-With vegetative, asexual, and sexual methods, Cladophora reproduces.
-The erect portion of the thallus falls back in some species during vegetative reproduction, while the rhizoidal system persists. Many of the rhizoid cells become bloated and have a pear-shaped appearance.
-Anisogamy is the fusion of gametes which are different in size or mortality. For example in Homo sapiens there occurs fusion of a large immotile female gamete or ova and a small motile male gamete or sperm.
Complete answer:
In reference to the given diagrams showing different types of syngamy, the first option represents the fusion of two morphologically different gametes which may differ physiologically are known as isogametes and fusion of isogametes is called isogamy. Isogamy is the characteristic of Cladophora. The only difference between Cladophora's gametes and spores is that there are two flagella in the gametes and four in the spores. The second option represents the fusion of morphologically different gametes known as anisogametes or oogametes and fusion of gametes is called oogamy. Oogamy is the characteristic of Homo sapiens. Syngamy is a process of complete and permanent fusion of male and female gametes for the formation of a zygote.
Additional information:
-Reproduction is a trait that is shared by Homo sapiens with all living beings. Specifically, a kind of sexual reproduction in humans. The mechanism includes two groups of sex cells, also called gametes. The masculine gamete, the spermatozoon, and the feminine gamete, the ovule.
-Cladophora is a genus of filamentous reticulated Ulvophyceae. There are several species in the genus Cladophora that are very difficult to identify and categorize, mostly because of the great variation in their appearances, which is influenced by habitat, age, and environmental conditions.
-Unlike Spirogyra the filaments of the branch of Cladophora do not undergo conjugation.
-In its life cycle, there are two multicellular stages - a haploid gametophyte and a diploid sporophyte - that look extremely similar. Either counting their genes or testing their offspring, is the only way to tell the two phases apart.
-By mitosis, the haploid gametophyte generates haploid gametes and by meiosis, the diploid sporophyte generates haploid spores.
-The only difference between Cladophora's gametes and spores is that there are two flagella in the gametes and four in the spores.
-The flagella are soon retracted and the zygote is secreted around a wall. This zygote immediately germinates and does not have a rest time.
So, the correct answer is ‘Cladophora, Homo sapiens’.
Note:
-With vegetative, asexual, and sexual methods, Cladophora reproduces.
-The erect portion of the thallus falls back in some species during vegetative reproduction, while the rhizoidal system persists. Many of the rhizoid cells become bloated and have a pear-shaped appearance.
-Anisogamy is the fusion of gametes which are different in size or mortality. For example in Homo sapiens there occurs fusion of a large immotile female gamete or ova and a small motile male gamete or sperm.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




