
Residual volume is:
(a) Lesser than Tidal volume
(b) Greater than Inspiratory volume
(c) Greater than the vital capacity
(d) Greater than Tidal volume
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Residual volume remains unchanged regardless of the lung volume at which expiration was started.
Complete step by step answer:
Residual volume (RV): It is the volume of air remaining in the lungs even after a forcible expiration. It measures approximately 1100ml-1200ml. It is greater than the tidal volume.
Additional Information:
Tidal volume (TV): It is the volume of air inspired or expired during normal respiration. The tidal volume is about 500 ml. It measures approximately 6000 to 8000 mL of air per minute.
Based on all the information provided below it is inferred that RV is greater than TV.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV): It is the additional volume of air an individual can inspire by forcible inspiration. It measures approximately 2500ml-3000ml.
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV): It is the additional volume of air an individual can expire by a forcible expiration. It measures approximately 1000ml-1100ml.
Various pulmonary capacities can be derived by adding up a few respiratory volumes which are of clinical use.
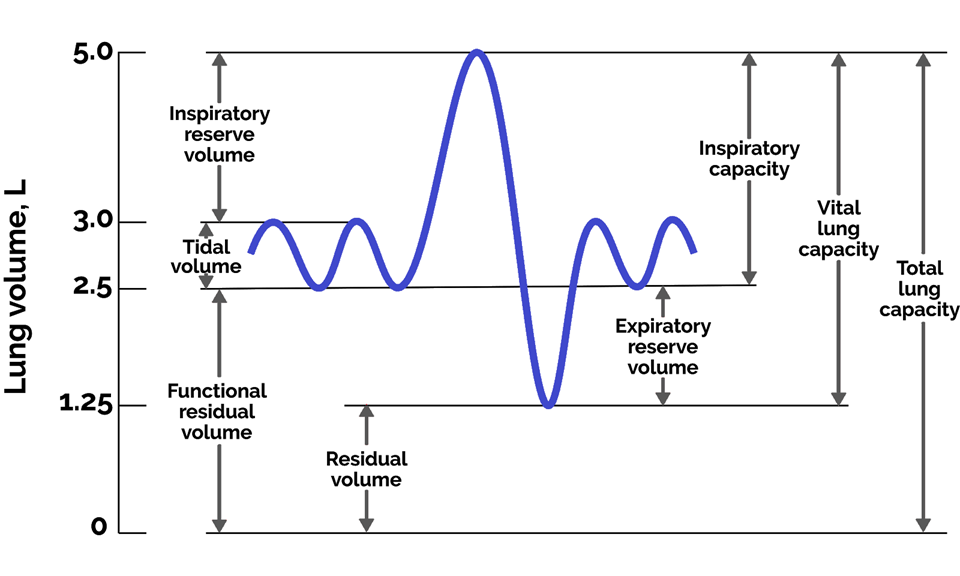
Inspiratory Capacity (IC): It is the total volume of air inspired by a normal individual after a normal expiration.
IC = TV+IRV
Expiratory Capacity (EC): It is the total volume of air expired by a normal individual after a normal inspiration. It is the sum of tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume. EC=TV+ERV
Expiratory Capacity (EC): It is the remaining volume of air present in the lungs after a normal expiration. FRC=ERV+RV
Vital Capacity (VC): It is the maximum volume of air an individual can breathe in after forced expiration or vice versa. VC=ERV+TV+IRV
Total Lung Capacity: It is the total volume of air accommodated in the lungs at the end of forced inspiration. Total Lung Capacity= RV+ERV+TV+IRV or VC+RV
The following diagram explains all the volumes and capacities in a graphical format.
So, the correct answer is ‘(d) Greater than tidal volume’.
Note: A healthy man breathes approximately 12-16 times/minute. The volume of air involved in breathing can be estimated by an instrument called a spirometer. It measures ventilation, the movement of air into and out of the lungs. The graph obtained by a spirometer of respiratory movements is called a spirogram.
Complete step by step answer:
Residual volume (RV): It is the volume of air remaining in the lungs even after a forcible expiration. It measures approximately 1100ml-1200ml. It is greater than the tidal volume.
Additional Information:
Tidal volume (TV): It is the volume of air inspired or expired during normal respiration. The tidal volume is about 500 ml. It measures approximately 6000 to 8000 mL of air per minute.
Based on all the information provided below it is inferred that RV is greater than TV.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV): It is the additional volume of air an individual can inspire by forcible inspiration. It measures approximately 2500ml-3000ml.
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV): It is the additional volume of air an individual can expire by a forcible expiration. It measures approximately 1000ml-1100ml.
Various pulmonary capacities can be derived by adding up a few respiratory volumes which are of clinical use.

Inspiratory Capacity (IC): It is the total volume of air inspired by a normal individual after a normal expiration.
IC = TV+IRV
Expiratory Capacity (EC): It is the total volume of air expired by a normal individual after a normal inspiration. It is the sum of tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume. EC=TV+ERV
Expiratory Capacity (EC): It is the remaining volume of air present in the lungs after a normal expiration. FRC=ERV+RV
Vital Capacity (VC): It is the maximum volume of air an individual can breathe in after forced expiration or vice versa. VC=ERV+TV+IRV
Total Lung Capacity: It is the total volume of air accommodated in the lungs at the end of forced inspiration. Total Lung Capacity= RV+ERV+TV+IRV or VC+RV
The following diagram explains all the volumes and capacities in a graphical format.
So, the correct answer is ‘(d) Greater than tidal volume’.
Note: A healthy man breathes approximately 12-16 times/minute. The volume of air involved in breathing can be estimated by an instrument called a spirometer. It measures ventilation, the movement of air into and out of the lungs. The graph obtained by a spirometer of respiratory movements is called a spirogram.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




