
What is the resonance effect? What are its various types? In what respect, does the resonance effect differ from the inductive effect?
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint: Resonance effect can be defined as the polarity induced in a molecule because of the interaction between a pi bond and a lone pair of electrons or the polarity induced because of the two pi bonds in conjugation. Resonance effect is of different types considering the substituent (electron donating or electron withdrawing) present on compound.
Complete answer:
We can define resonance effect as the polarity induced in a molecule because of the interaction between a pi bond and a lone pair of electrons or the polarity induced because of the two pi bonds in conjugation. It is also referred to as delocalization of pi electrons.
Resonance effect can be of two types:
$ + R$ EFFECT: In this type of resonance, an electron donating group is present which donates its electron pair in the resonance by the process of delocalization. It is known as the positive resonance effect. For example: $$ - OH, - SH, - OR, - SR$$ .
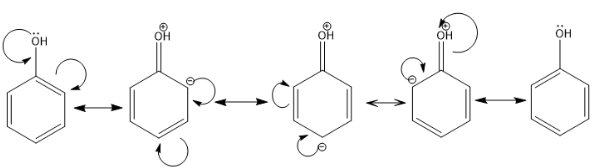
In the above example, the hydroxyl group is donating its lone pair of electrons to the benzene ring and pi bond delocalization is taking place.
$ - R$ EFFECT: In this type of resonance, an electron withdrawing group is present which pulls the electron density from the benzene ring by the process of delocalization. It is known as the negative resonance effect. For example: $$ - N{O_2},C = O, - COOH, - C \equiv N$$ .
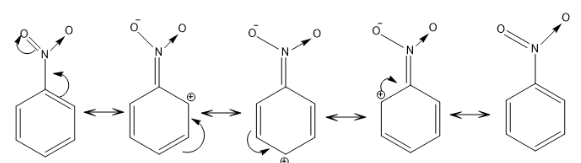
In the above example, the nitro group is pulling electron density from the benzene ring and showing a negative resonance effect.
Now, if we compare the inductive effect and the resonance effect, we can say that the inductive effect shows the transmission of charges between atoms in a molecule while resonance effect shows the transmission of lone pairs or pi bonds between atoms of a molecule.
Note:
We should not get confused between inductive effect, resonance effect and the hyperconjugation. Hyperconjugation is known as sigma bond resonance because in this type of delocalization, sigma bond gets delocalised on atoms of a molecule. For example alkyl groups show hyperconjugation.
Complete answer:
We can define resonance effect as the polarity induced in a molecule because of the interaction between a pi bond and a lone pair of electrons or the polarity induced because of the two pi bonds in conjugation. It is also referred to as delocalization of pi electrons.
Resonance effect can be of two types:
$ + R$ EFFECT: In this type of resonance, an electron donating group is present which donates its electron pair in the resonance by the process of delocalization. It is known as the positive resonance effect. For example: $$ - OH, - SH, - OR, - SR$$ .

In the above example, the hydroxyl group is donating its lone pair of electrons to the benzene ring and pi bond delocalization is taking place.
$ - R$ EFFECT: In this type of resonance, an electron withdrawing group is present which pulls the electron density from the benzene ring by the process of delocalization. It is known as the negative resonance effect. For example: $$ - N{O_2},C = O, - COOH, - C \equiv N$$ .

In the above example, the nitro group is pulling electron density from the benzene ring and showing a negative resonance effect.
Now, if we compare the inductive effect and the resonance effect, we can say that the inductive effect shows the transmission of charges between atoms in a molecule while resonance effect shows the transmission of lone pairs or pi bonds between atoms of a molecule.
Note:
We should not get confused between inductive effect, resonance effect and the hyperconjugation. Hyperconjugation is known as sigma bond resonance because in this type of delocalization, sigma bond gets delocalised on atoms of a molecule. For example alkyl groups show hyperconjugation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




