
How many resonance structures are there for carbon trioxide?
Answer
539.4k+ views
Hint :We must first know the meaning of resonance structures to solve this question. Resonance structures
are a set of two or more Lewis structures that describes the electronic bonding between a single polyatomic species. Resonance structures help us in understanding the delocalized electrons that cannot be expressed by a single Lewis formula with an integer number of covalent bonds.
Carbon trioxide is an unstable oxide of carbon.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
There are three different isomers for carbon trioxide.
Structure $1$
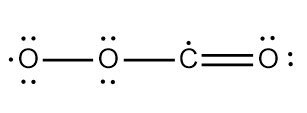
This structure has two unpaired electrons and only one resonance contributor.
Structure $2$

It has two unpaired electrons and three resonance structures.
Structure $3$
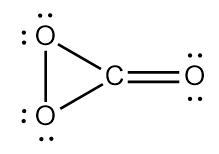
This structure has no unpaired electrons and has one contributor. This isomer is said to be the most stable one out of the three isomers.
Additional Information:
The purpose of resonance is to describe the combination of several contributing structures which is also called resonance structures or canonical structures into a hybrid resonance in valence bond theory. During resonance if the frequency matches the object’s resonant frequency, we will get what is called as resonance. Resonance occurs when the frequency of the oscillations of an object is raised by another object’s corresponding vibrations.
Note :
Some molecules have two or more chemically equivalent Lewis electron structures which are called the resonance structures. Resonance is a method within the valence bond theory of bonding which describes the delocalization of electrons within the molecules. These structures are written with a double-headed arrow between them, which indicates that none of the Lewis structures describes the bonding. The net sum of valid resonance structures is defined as a resonance hybrid, which represents the overall delocalization of electrons within the molecule. A molecule that has several resonance structures is more stable than one with fewer.
are a set of two or more Lewis structures that describes the electronic bonding between a single polyatomic species. Resonance structures help us in understanding the delocalized electrons that cannot be expressed by a single Lewis formula with an integer number of covalent bonds.
Carbon trioxide is an unstable oxide of carbon.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
There are three different isomers for carbon trioxide.
Structure $1$
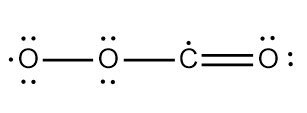
This structure has two unpaired electrons and only one resonance contributor.
Structure $2$

It has two unpaired electrons and three resonance structures.
Structure $3$

This structure has no unpaired electrons and has one contributor. This isomer is said to be the most stable one out of the three isomers.
Additional Information:
The purpose of resonance is to describe the combination of several contributing structures which is also called resonance structures or canonical structures into a hybrid resonance in valence bond theory. During resonance if the frequency matches the object’s resonant frequency, we will get what is called as resonance. Resonance occurs when the frequency of the oscillations of an object is raised by another object’s corresponding vibrations.
Note :
Some molecules have two or more chemically equivalent Lewis electron structures which are called the resonance structures. Resonance is a method within the valence bond theory of bonding which describes the delocalization of electrons within the molecules. These structures are written with a double-headed arrow between them, which indicates that none of the Lewis structures describes the bonding. The net sum of valid resonance structures is defined as a resonance hybrid, which represents the overall delocalization of electrons within the molecule. A molecule that has several resonance structures is more stable than one with fewer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




