
What is respiration? Give a balanced equation for aerobic respiration.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: This is a process depicted by the entire living organisms, and it ensures their survival. Most of the aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondrion in most of the plants and animals.
Complete step by step answer:
Respiration is of two types, aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration occurs in higher organisms, in the presence of oxygen while the anaerobic respiration occurs in the lower organisms, in the absence of oxygen. The ultimate motive of respiration is the production of energy.
In the case of aerobic respiration in humans, it is a catabolic-physicochemical process, which involves the exchange of environmental oxygen and body carbon dioxide through a liquid medium (blood). This oxygen is used for the oxidation of glucose to produce energy. The aerobic respiration occurs inside the cell. It is divided into 4 phases
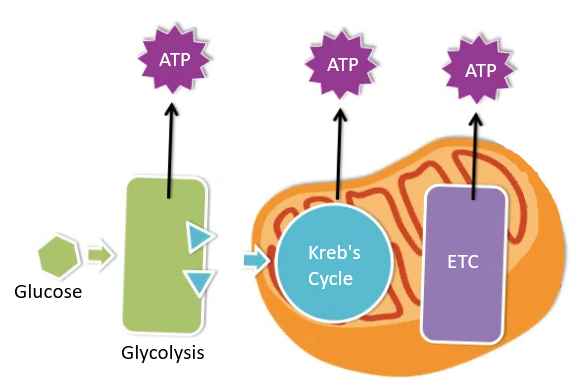
- Glycolysis: this is an anaerobic phase, inside the cytoplasm producing energy, which is partly stored in the high energy bonds of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) molecules. Here one molecule of glucose(6C) breaks into two molecules of pyruvic acid(3C). Two $NADH_{2}$ is also produced.
- Oxidative decarboxylation: this is an aerobic phase, where the pyruvic acid and $NADH_{2}$ enter the mitochondrion of the cell to produce two molecules of Acetyl- CoA(2C).
- Krebs cycle: It occurs in the inner chamber of the mitochondrion and completed in 8 steps. It produces two GTP (Guanosine triphosphate) molecules, 6 $NADH_{2}$, and 2 $FADH_{2}$ molecules, which later produces ATP in the electron transfer chain.
- Electron Transport Chain (ETC): It is a set of seven electron carriers, present in a specific sequence along with inner mitochondria. Energy is released during the electron transfer.
The balanced equation for aerobic respiration is:
${C_6H_{12}O_6}$ + $6O_2$ $\rightarrow$ $6{CO_2}$ +$6{H_2}O$ + energy
Additional information:
- The nutrient, which provides energy by its oxidation inside the body, is called respiratory fuel.
- The main respiratory fuel in our body is glucose, it is present abundantly in the body fluids.
- The physiological value of glucose is 4 Kcal.
- The fats are concentrated fuel with a physiological value of 9 Kcal.
- Fats are used as respiratory fuel after their hydrolysis to fatty acids and glycerol by lipase enzyme and their subsequent conversion to hexose sugar.
- Proteins serve as a respiratory fuel after their breakdown of amino acids. By proteolytic enzymes.
- Protoplasmic respiration is the term used when proteins are used as respiratory fuels.
- When carbohydrates or fats are used as respiratory fuel, then it is called as floating respiration.
Note: The released energy during the process of respiration may not be required immediately and the site of endergonic processes may be away from the site of exergonic processes. ATP provides a quick source of energy when required, so the ATP is commonly called as energy currency.
Complete step by step answer:
Respiration is of two types, aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration occurs in higher organisms, in the presence of oxygen while the anaerobic respiration occurs in the lower organisms, in the absence of oxygen. The ultimate motive of respiration is the production of energy.
In the case of aerobic respiration in humans, it is a catabolic-physicochemical process, which involves the exchange of environmental oxygen and body carbon dioxide through a liquid medium (blood). This oxygen is used for the oxidation of glucose to produce energy. The aerobic respiration occurs inside the cell. It is divided into 4 phases
- Glycolysis: this is an anaerobic phase, inside the cytoplasm producing energy, which is partly stored in the high energy bonds of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) molecules. Here one molecule of glucose(6C) breaks into two molecules of pyruvic acid(3C). Two $NADH_{2}$ is also produced.
- Oxidative decarboxylation: this is an aerobic phase, where the pyruvic acid and $NADH_{2}$ enter the mitochondrion of the cell to produce two molecules of Acetyl- CoA(2C).
- Krebs cycle: It occurs in the inner chamber of the mitochondrion and completed in 8 steps. It produces two GTP (Guanosine triphosphate) molecules, 6 $NADH_{2}$, and 2 $FADH_{2}$ molecules, which later produces ATP in the electron transfer chain.
- Electron Transport Chain (ETC): It is a set of seven electron carriers, present in a specific sequence along with inner mitochondria. Energy is released during the electron transfer.

The balanced equation for aerobic respiration is:
${C_6H_{12}O_6}$ + $6O_2$ $\rightarrow$ $6{CO_2}$ +$6{H_2}O$ + energy
Additional information:
- The nutrient, which provides energy by its oxidation inside the body, is called respiratory fuel.
- The main respiratory fuel in our body is glucose, it is present abundantly in the body fluids.
- The physiological value of glucose is 4 Kcal.
- The fats are concentrated fuel with a physiological value of 9 Kcal.
- Fats are used as respiratory fuel after their hydrolysis to fatty acids and glycerol by lipase enzyme and their subsequent conversion to hexose sugar.
- Proteins serve as a respiratory fuel after their breakdown of amino acids. By proteolytic enzymes.
- Protoplasmic respiration is the term used when proteins are used as respiratory fuels.
- When carbohydrates or fats are used as respiratory fuel, then it is called as floating respiration.
Note: The released energy during the process of respiration may not be required immediately and the site of endergonic processes may be away from the site of exergonic processes. ATP provides a quick source of energy when required, so the ATP is commonly called as energy currency.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




