
What role does adsorption play in heterogeneous catalysis?
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Adsorption is a surface phenomenon. It is a process in which the reacting species may be in different phases or in the same phase, one of the reactants gets adsorbed on the surface of the other to carry out the reaction. Adsorption plays an important role in heterogeneous catalysis.
Complete Step by step answer:
Catalysis is a process in which a substrate is converted into products by the action of a catalyst. Catalysis reactions are of two types – homogeneous catalysis, heterogeneous catalysis. Heterogeneous catalysis is a catalytic process in which the substrate and the catalyst are in two different phases.
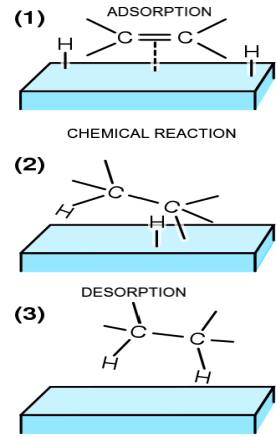
Adsorption theory of heterogeneous catalysis explains the reaction on the surface of the catalyst of a different phase. The process takes place typically in different steps such as adsorption, chemical reaction, desorption. The important step in the whole process is the formation of intermediate compounds. The mechanism of this reaction can be explained by the following processes. The first is that the reacting molecules (substrate molecules) get diffused towards the surface catalyst molecules, this is the diffusion process. The diffused molecules get adsorbed onto the surface of the catalyst, the particular binding sites where the chemical reaction between the catalyst of a different phase and the substrate of a different phase occurs. Before yielding the final products of the reaction, formation of an intermediate compound takes place on the surface of the catalyst. After the formation of the product, the product molecules get diffused away from the catalyst to provide the surface free for the incoming reactants. This process is called desorption.
Note: The catalyst does not change its phase or chemical nature but is involved in the reaction and also speeds up the reaction rate. The adsorption is explained by three theories where the old theory says that the reacting molecules should be gaseous or in solution phase, the second one mentions the formation of intermediate but the one discussed above is a combination of both.
Complete Step by step answer:
Catalysis is a process in which a substrate is converted into products by the action of a catalyst. Catalysis reactions are of two types – homogeneous catalysis, heterogeneous catalysis. Heterogeneous catalysis is a catalytic process in which the substrate and the catalyst are in two different phases.

Adsorption theory of heterogeneous catalysis explains the reaction on the surface of the catalyst of a different phase. The process takes place typically in different steps such as adsorption, chemical reaction, desorption. The important step in the whole process is the formation of intermediate compounds. The mechanism of this reaction can be explained by the following processes. The first is that the reacting molecules (substrate molecules) get diffused towards the surface catalyst molecules, this is the diffusion process. The diffused molecules get adsorbed onto the surface of the catalyst, the particular binding sites where the chemical reaction between the catalyst of a different phase and the substrate of a different phase occurs. Before yielding the final products of the reaction, formation of an intermediate compound takes place on the surface of the catalyst. After the formation of the product, the product molecules get diffused away from the catalyst to provide the surface free for the incoming reactants. This process is called desorption.
Note: The catalyst does not change its phase or chemical nature but is involved in the reaction and also speeds up the reaction rate. The adsorption is explained by three theories where the old theory says that the reacting molecules should be gaseous or in solution phase, the second one mentions the formation of intermediate but the one discussed above is a combination of both.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




