
Saliva contains ____ enzyme which hydrolyses starch into
(a) Hydrolase, maltase
(b) Amylase, maltose
(c) Amylose, kinase
(d) None of these
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Saliva is a secretion that helps in the mastication and swallowing of food. It is a mixture of many constituents, one of which is an enzyme that begins the digestion of starch from the mouth.
Complete answer:
The fluid secreted by the salivary glands constitutes saliva which is a mixture of water, electrolytes, salivary amylase, and lysozyme. Salivary amylase or ptyalin is an enzyme that converts starch into maltose, isomaltose, and α-dextrins. Lysozyme is an antibacterial agent to kill any bacteria that may have entered via the food in our oral cavity. The optimal activity of salivary amylase is at pH 6.8 and thus it no longer remains functional once it enters the stomach acidic environment.
Additional Information: -Starch which is a form of complex carbohydrate is composed of a long and branched-chain of glucose monomers. The linear and helical form of starch is known as amylose while the branched-chain form is known as amylopectin.
- Maltose is a disaccharide with glucose as its monosaccharide. Disaccharides are condensation products of two monosaccharide units. They are connected by an α-1,4-glycosidic bond. Maltase is an enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of maltose into glucose units.
- Hydrolase is an enzyme that uses water to catalyze the breakdown of a chemical bond.
- Kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes phosphorylation wherein it adds a phosphate group to a substrate. This phosphate group is donated by a high energy compound like ATP.
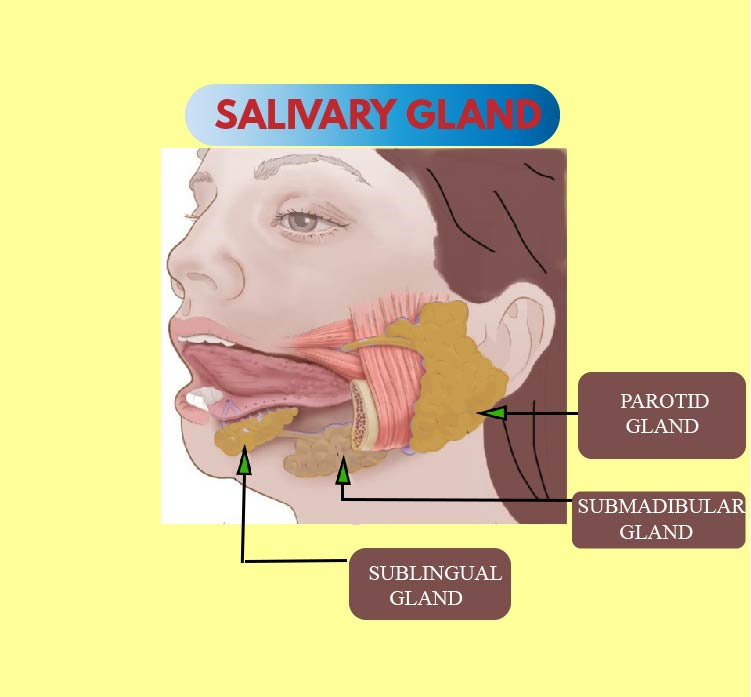
- Three pairs of salivary glands are present in humans - parotid glands, submandibular glands, and sublingual glands.
‘So, the correct answer is ‘Amylase, maltose.’
Note: -Parotid glands are the largest and sublingual are the smallest among the three. Parotid glands are situated on either side of the head and anterior to ears. They secrete much of the salivary amylase. Stenson’s duct releases its contents in the mouth.
-Submandibular or submaxillary are medium-sized salivary glands located at the angles of the lower jaw. They open through Wharton’s duct in the oral cavity.
- Sublingual glands are situated beneath the tongue and open via duct of the Rivinus into the oral cavity.
Complete answer:
The fluid secreted by the salivary glands constitutes saliva which is a mixture of water, electrolytes, salivary amylase, and lysozyme. Salivary amylase or ptyalin is an enzyme that converts starch into maltose, isomaltose, and α-dextrins. Lysozyme is an antibacterial agent to kill any bacteria that may have entered via the food in our oral cavity. The optimal activity of salivary amylase is at pH 6.8 and thus it no longer remains functional once it enters the stomach acidic environment.
Additional Information: -Starch which is a form of complex carbohydrate is composed of a long and branched-chain of glucose monomers. The linear and helical form of starch is known as amylose while the branched-chain form is known as amylopectin.
- Maltose is a disaccharide with glucose as its monosaccharide. Disaccharides are condensation products of two monosaccharide units. They are connected by an α-1,4-glycosidic bond. Maltase is an enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of maltose into glucose units.
- Hydrolase is an enzyme that uses water to catalyze the breakdown of a chemical bond.
- Kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes phosphorylation wherein it adds a phosphate group to a substrate. This phosphate group is donated by a high energy compound like ATP.
- Three pairs of salivary glands are present in humans - parotid glands, submandibular glands, and sublingual glands.
‘So, the correct answer is ‘Amylase, maltose.’
Note: -Parotid glands are the largest and sublingual are the smallest among the three. Parotid glands are situated on either side of the head and anterior to ears. They secrete much of the salivary amylase. Stenson’s duct releases its contents in the mouth.
-Submandibular or submaxillary are medium-sized salivary glands located at the angles of the lower jaw. They open through Wharton’s duct in the oral cavity.
- Sublingual glands are situated beneath the tongue and open via duct of the Rivinus into the oral cavity.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




