
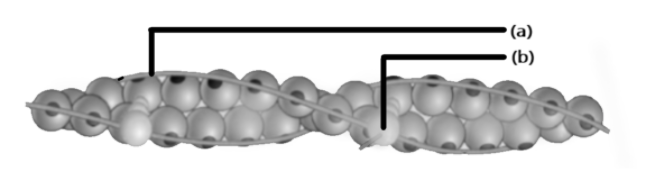
Select the correct option for contractile proteins from the given diagram labelled as (a) and (b)
A. a = G actin; b = F- actin
B. a= Meromycin; b= Myosin
C. a = Tropomyosin; b = Troponin
D. a = Troponin; b = Tropomyosin

Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: The tropomyosin and troponin are contractile proteins which with the other proteins like actin and myosin, functions to regulate contraction and relaxation in the muscle and nonmuscle cells. Among these proteins, the thick filaments contain myosin, thin filaments contain actin , troponin and tropomyosin. Troponins are present in a lesser amount compared to the actin and myosin.
Complete answer:
Contractile proteins of muscle are actin and myosin. Actin is the main component of thin filaments while myosin is the main component of thick filaments. The given figure is of actin filament containing one troponin per 6-8 actin molecules present. In this, the molecule of troponin which is shown as (b) is attached to the protein tropomyosin, shown as (a). They are present in the groove between actin filaments.
The main function of the protein tropomyosin is to prevent the contraction during relaxed condition of the muscle by blocking the attachment site for the myosin crossbridge.
Hence, The correct answer is option (C).
Additional information:
Skeletal muscle in humans is composed of several muscle fibers which have smaller units called myofibrils. There are mainly three types of proteins that make each myofibril. They are- contractile, regulatory and structural proteins.
The contractile proteins contain actin (or thin filament) and myosin (or thick filament). Each actin filament is composed of two helical “F” actin and each of the ‘F’ actin contains many ‘G’ actin in them. Two filaments of regulatory proteins tropomyosin and troponin are also present. During the process of muscle relaxation, the troponin covers up the binding sites for myosin which are present at the actin filaments.
Each myosin contains meromyosin which is further divided into two important parts- a globular head known as heavy meromyosin and a tail known as light meromyosin. The head carries the active sites for action and binding sites for ATP.
Note: The protein troponin remains attached to the other protein tropomyosin. They remain within a groove that is formed between actin filaments in muscle tissue. During excitation, calcium ions bind to TnC. This then interacts with the protein tropomyosin and unblocks the active sites present between the myosin filament and actin. This allows a cross-bridge cycling, which results in contraction of the myofibrils, constituting the systole. In a relaxed muscle, tropomyosin blocks this attachment site, causing no myosin crossbridge formation and this prevents the contraction in a muscle.
Complete answer:
Contractile proteins of muscle are actin and myosin. Actin is the main component of thin filaments while myosin is the main component of thick filaments. The given figure is of actin filament containing one troponin per 6-8 actin molecules present. In this, the molecule of troponin which is shown as (b) is attached to the protein tropomyosin, shown as (a). They are present in the groove between actin filaments.
The main function of the protein tropomyosin is to prevent the contraction during relaxed condition of the muscle by blocking the attachment site for the myosin crossbridge.
Hence, The correct answer is option (C).
Additional information:
Skeletal muscle in humans is composed of several muscle fibers which have smaller units called myofibrils. There are mainly three types of proteins that make each myofibril. They are- contractile, regulatory and structural proteins.
The contractile proteins contain actin (or thin filament) and myosin (or thick filament). Each actin filament is composed of two helical “F” actin and each of the ‘F’ actin contains many ‘G’ actin in them. Two filaments of regulatory proteins tropomyosin and troponin are also present. During the process of muscle relaxation, the troponin covers up the binding sites for myosin which are present at the actin filaments.
Each myosin contains meromyosin which is further divided into two important parts- a globular head known as heavy meromyosin and a tail known as light meromyosin. The head carries the active sites for action and binding sites for ATP.
Note: The protein troponin remains attached to the other protein tropomyosin. They remain within a groove that is formed between actin filaments in muscle tissue. During excitation, calcium ions bind to TnC. This then interacts with the protein tropomyosin and unblocks the active sites present between the myosin filament and actin. This allows a cross-bridge cycling, which results in contraction of the myofibrils, constituting the systole. In a relaxed muscle, tropomyosin blocks this attachment site, causing no myosin crossbridge formation and this prevents the contraction in a muscle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




