
Select the option that contains all plants that produce non-endospermic seeds.
(A) Gram, pea, bean, groundnut
(B) Castor, peanut, orchid, wheat
(C) Coconut, walnut, wheat, gram
(D) Castor, maize, coconut, orchid
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Endosperm is the source of nutrition to the seed until germination. They surround the embryo and provide food in the form of starch. The mature seed is of two types: endospermic and non-endospermic.
Complete answer:
First, let us understand the difference between endospermic and non-endospermic seeds. Endospermic seeds, also known as albuminous seeds, have endosperm inside after maturation, as they are not consumed completely. Some of the plants/crops with this type of seed are: coconut, wheat, maize, barley, etc.
Non-endospermic seeds or exalbuminous seeds do not have endosperm as they are completely consumed by the developing embryo and fills the cotyledon with stored food. Legumes, oak, squash, radish, sunflower are some of the examples with such seeds.
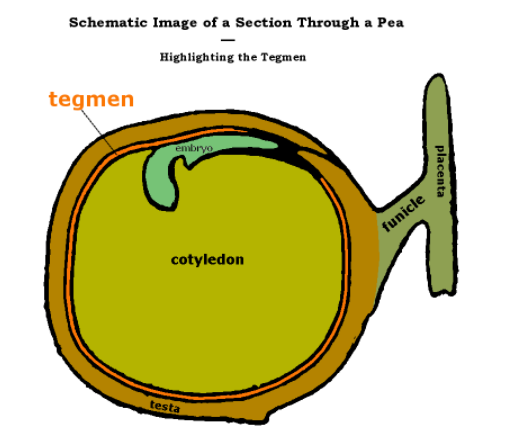
Thus, the option with all plants that produce non-endospermic seeds is (A) gram, pea, bean, groundnut.
Additional information:
The nature of endosperm in endospermic seeds vary widely. It may be farinaceous (starchy) like in cereal grains; fleshy as in coconut; oily as in castor. The gymnosperms have endospermic seeds.
Note:
> Some plants, like orchids and coffee, produce seeds which do not have endosperm. They contain nucellus, which has perisperm from which the seeds get the nutrients.
> The endosperms also play an important role in human diet through cereal grains. The grains are primarily the endosperms, which is the nutritive part. The seeds are sometimes processed during which either the endosperm is retained or the embryo (germ) and bran (seed coat) are removed. Processed grains usually have reduced nutritive value.
> A protein coat known as aleurone sometimes surrounds the endosperm. The seeds might have single or multiple coats of aleurone. Their tissue accumulates large quantities of oil. So they are important for the growing as well as mature plant.
Complete answer:
First, let us understand the difference between endospermic and non-endospermic seeds. Endospermic seeds, also known as albuminous seeds, have endosperm inside after maturation, as they are not consumed completely. Some of the plants/crops with this type of seed are: coconut, wheat, maize, barley, etc.
Non-endospermic seeds or exalbuminous seeds do not have endosperm as they are completely consumed by the developing embryo and fills the cotyledon with stored food. Legumes, oak, squash, radish, sunflower are some of the examples with such seeds.

Thus, the option with all plants that produce non-endospermic seeds is (A) gram, pea, bean, groundnut.
Additional information:
The nature of endosperm in endospermic seeds vary widely. It may be farinaceous (starchy) like in cereal grains; fleshy as in coconut; oily as in castor. The gymnosperms have endospermic seeds.
Note:
> Some plants, like orchids and coffee, produce seeds which do not have endosperm. They contain nucellus, which has perisperm from which the seeds get the nutrients.
> The endosperms also play an important role in human diet through cereal grains. The grains are primarily the endosperms, which is the nutritive part. The seeds are sometimes processed during which either the endosperm is retained or the embryo (germ) and bran (seed coat) are removed. Processed grains usually have reduced nutritive value.
> A protein coat known as aleurone sometimes surrounds the endosperm. The seeds might have single or multiple coats of aleurone. Their tissue accumulates large quantities of oil. So they are important for the growing as well as mature plant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




