
Shape of $XeO{F_4}$ is:
A. Octahedral
B. Square pyramidal
C. Pyramidal
D. T-shaped
Answer
564.3k+ views
Hint:At first, the hybridisation state of the $XeO{F_4}$ molecule needs to be determined. This state of hybridisation will determine the shape of the given molecule and hence the shape will be according to the given configuration of the electrons in the orbitals.
Complete answer:
The shape of the molecule $XeO{F_4}$ has the electronic configuration in such a manner so that there is a chemistry of square pyramidal. The internal molecule which is the central atom is $Xe$ and there are four $F$ residues which are associated with the central atom. This forms the basal structure of the $XeO{F_4}$ molecule. The associated $O$ residue forms a double-bonded structure with the $Xe$ residue. Therefore, the internal $Xe$ residue forms six bonds with different molecules. There are $8$ valence electrons in the electronic configuration of $Xe$ residue. Therefore as electrons are already forming bonds, there is a lone pair of electrons which is left without any possible bond formation. This lone pair is present as the trans structure associated with $Xe$ residues. The hybridisation is based on the electron filling of the orbitals. The hybridisation of this chemical molecule $XeO{F_4}$ is $s{p^3}{d^2}$, which means according to the nature of hybridisation the structure is square pyramidal. The pyramidal structure is because of the $O$ residue which is present on a different plane. The resultant structure of the $XeO{F_4}$ is given in the diagram.
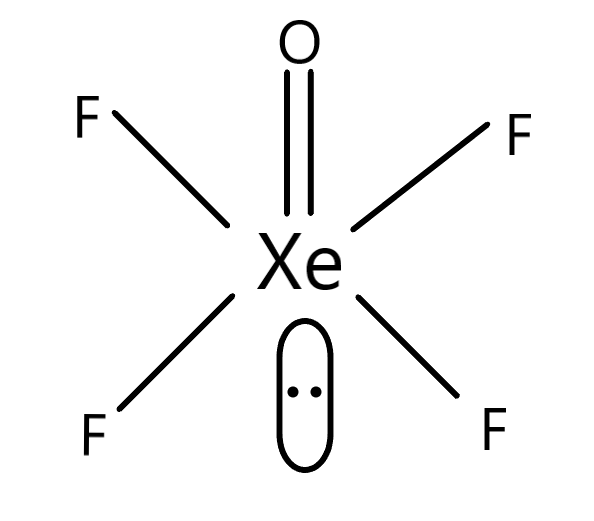
Hence, option B is correct.
Note:
The $XeO{F_4}$ molecule is a structure which has the super-octet character. This is because as a result of the covalent interactions of all the atoms with the central $Xe$ atom the number of electrons is more than the natural octet filled level. Hence this molecule does not follow the octet rule.
Complete answer:
The shape of the molecule $XeO{F_4}$ has the electronic configuration in such a manner so that there is a chemistry of square pyramidal. The internal molecule which is the central atom is $Xe$ and there are four $F$ residues which are associated with the central atom. This forms the basal structure of the $XeO{F_4}$ molecule. The associated $O$ residue forms a double-bonded structure with the $Xe$ residue. Therefore, the internal $Xe$ residue forms six bonds with different molecules. There are $8$ valence electrons in the electronic configuration of $Xe$ residue. Therefore as electrons are already forming bonds, there is a lone pair of electrons which is left without any possible bond formation. This lone pair is present as the trans structure associated with $Xe$ residues. The hybridisation is based on the electron filling of the orbitals. The hybridisation of this chemical molecule $XeO{F_4}$ is $s{p^3}{d^2}$, which means according to the nature of hybridisation the structure is square pyramidal. The pyramidal structure is because of the $O$ residue which is present on a different plane. The resultant structure of the $XeO{F_4}$ is given in the diagram.

Hence, option B is correct.
Note:
The $XeO{F_4}$ molecule is a structure which has the super-octet character. This is because as a result of the covalent interactions of all the atoms with the central $Xe$ atom the number of electrons is more than the natural octet filled level. Hence this molecule does not follow the octet rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




