
Show by means of a diagram how the pattern of d-orbital changes as an octahedral complex undergoes tetragonal distortion and eventually becomes a square planar complex.
Answer
502.2k+ views
Hint :Crystal field theory: It states that the electrons donated by ligands to transition metal, then while pairing in d-orbitals, the electrons experience repulsions due to which d-subshell splits into two parts and the energy of each orbital is decided by the type of complex formed.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
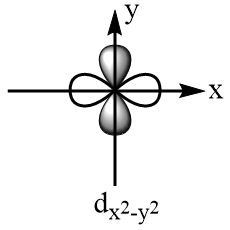
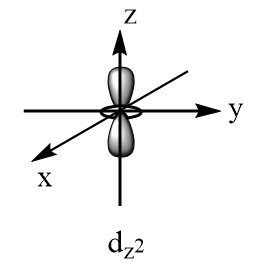
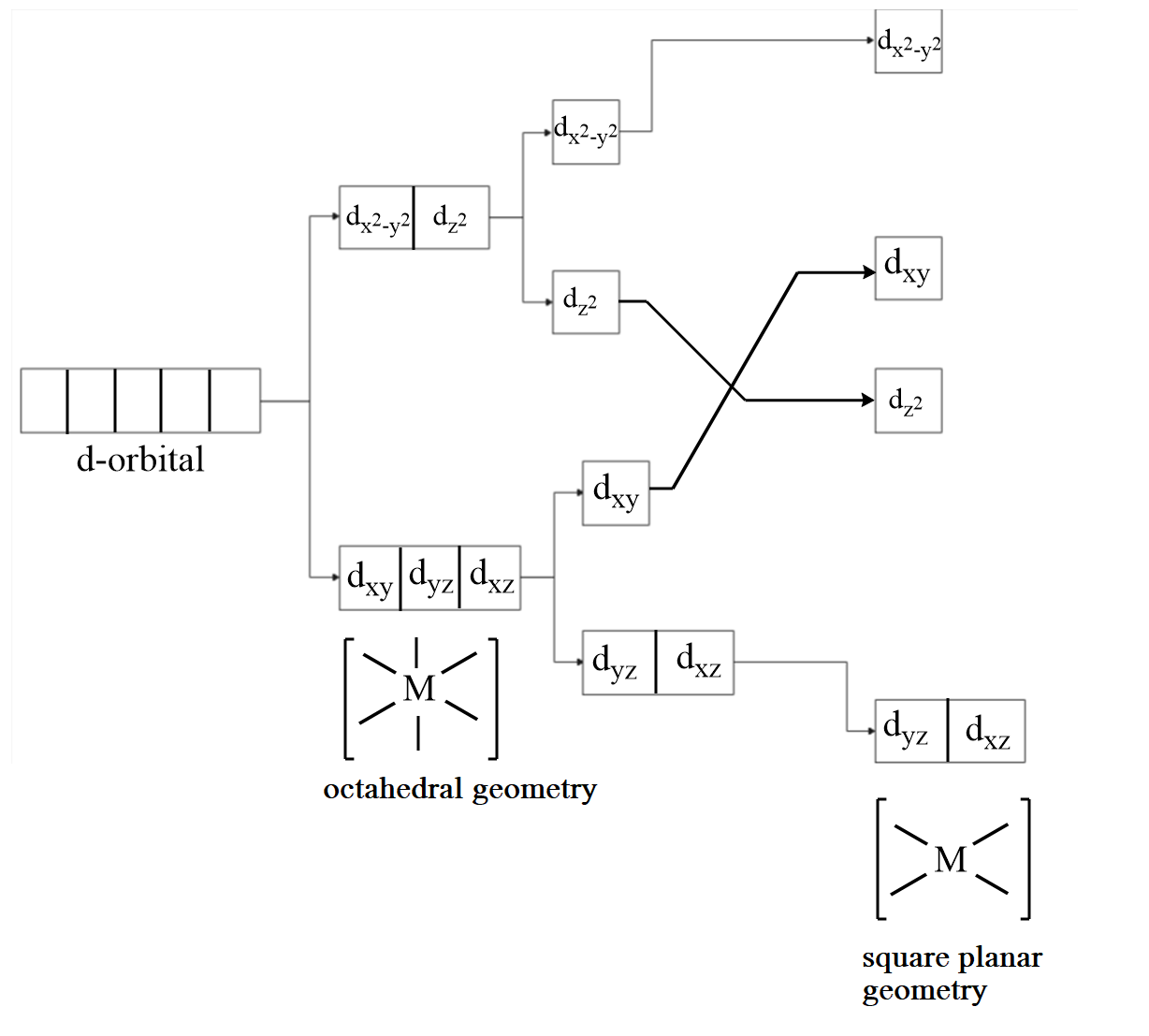
According to crystal field theory, the metal is considered as the point charge and the ligands are considered as the negatively charged species which approach the metal via fixed axes. Therefore, the d-subshell of an octahedral complex experiences degeneracy and splits into two parts. The three orbitals that are $ {d_{xy}} $ , $ {d_{yz}} $ and $ {d_{xz}} $ are present at the diagonals of the planes and hence experience relatively less repulsions and hence are more stable. So, $ {d_{xy}} $ , $ {d_{yz}} $ and $ {d_{xz}} $ consist of lesser energy while the other two orbitals i.e., $ {d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}} $ and $ {d_{{z^2}}} $ are present along the axes of the plane, hence experience more repulsions and consist of greater energy. The shapes of d-orbitals are represented as follows:
Orbitals present at the diagonals of the plane:
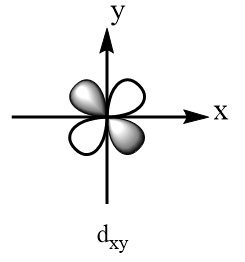

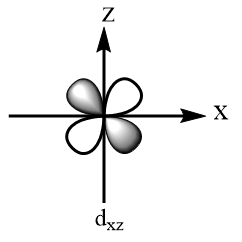
Orbitals present along the axes of the plane:
Now, to convert an octahedral complex into a square plane complex, distortion of geometry takes place via the z axis. The electrons from z axis leave the complex, so on further splitting $ {d_{{z^2}}} $ orbitals are more stable than $ {d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}} $ orbitals. Therefore, it will have lower energy in the further splitting of orbitals. As the electrons from z axis are released, so the orbitals along the diagonals of z axis will be more stable i.e., $ {d_{yz}} $ and $ {d_{xz}} $ will have lesser energy than $ {d_{xy}} $ orbital.
At the last step, when electrons of the z axis are completely removed then the $ {d_{{z^2}}} $ orbital becomes vacant and will be more stable than $ {d_{xy}} $ orbital. Hence, the distortion in the d-orbitals while changing an octahedral geometry to a square planar geometry is represented as follows:
Note :
It is important to note that the difference between the energy levels obtained after splitting of orbitals is known as crystal field stabilization energy i.e., CFSE. For a complex, higher the value of CFSE, greater will be its thermodynamic stability and kinetically inert.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
According to crystal field theory, the metal is considered as the point charge and the ligands are considered as the negatively charged species which approach the metal via fixed axes. Therefore, the d-subshell of an octahedral complex experiences degeneracy and splits into two parts. The three orbitals that are $ {d_{xy}} $ , $ {d_{yz}} $ and $ {d_{xz}} $ are present at the diagonals of the planes and hence experience relatively less repulsions and hence are more stable. So, $ {d_{xy}} $ , $ {d_{yz}} $ and $ {d_{xz}} $ consist of lesser energy while the other two orbitals i.e., $ {d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}} $ and $ {d_{{z^2}}} $ are present along the axes of the plane, hence experience more repulsions and consist of greater energy. The shapes of d-orbitals are represented as follows:
Orbitals present at the diagonals of the plane:



Orbitals present along the axes of the plane:


Now, to convert an octahedral complex into a square plane complex, distortion of geometry takes place via the z axis. The electrons from z axis leave the complex, so on further splitting $ {d_{{z^2}}} $ orbitals are more stable than $ {d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}} $ orbitals. Therefore, it will have lower energy in the further splitting of orbitals. As the electrons from z axis are released, so the orbitals along the diagonals of z axis will be more stable i.e., $ {d_{yz}} $ and $ {d_{xz}} $ will have lesser energy than $ {d_{xy}} $ orbital.
At the last step, when electrons of the z axis are completely removed then the $ {d_{{z^2}}} $ orbital becomes vacant and will be more stable than $ {d_{xy}} $ orbital. Hence, the distortion in the d-orbitals while changing an octahedral geometry to a square planar geometry is represented as follows:

Note :
It is important to note that the difference between the energy levels obtained after splitting of orbitals is known as crystal field stabilization energy i.e., CFSE. For a complex, higher the value of CFSE, greater will be its thermodynamic stability and kinetically inert.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




