
Show variation of resistivity of copper as a function of temperature in a graph.
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: Resistivity, it is the resistance that is offered by a material. And resistance is the nature of a material for opposing the flow of electric current and the unit of resistance is ohms and the unit of resistivity is expressed as ohm-metres.
Complete answer:
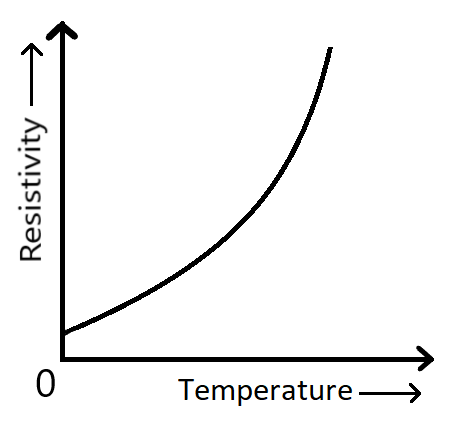
The graph shows the relation between the resistance and the temperature. The variation of resistivity of copper with temperature is parabolic in nature.
From the graph it is understood that the resistivity of copper increases with the rise in temperature. It is also understood that, whatever the temperature is, the copper has a certain resistivity. And it rises when temperature exceeds a particular value.
Resistivity, commonly denoted by the Greek letter rho, \[\rho \] , is quantitatively equal to
\[\rho \; = \;RA/l\]
Where, \[R\] =resistance of a specimen such as a wire
\[A\] =cross-sectional area
\[l\] = length
Both resistivity and resistance describe the characteristics of a material that make how much difficulty in the current flow through that particular material, but resistivity is an intrinsic property and resistance is not. This means that all pure copper wires have the same resistivity irrespective of their shape and size. But a thick, short copper wire has a much smaller resistance than a long, thin copper wire.
Copper is one of the best conductors of electric current. It has a low resistivity value. Hence it is used widely for all kinds of electrical purposes.
Note: Electrical conductivity or specific conductance can be considered as the reciprocal of electrical resistivity. As we mentioned resistivity shows the resistance to the current flowing through the conductor, but conductivity represents a material's ability to conduct electric current. It is commonly denoted by the Greek letter \[\sigma \] .
Complete answer:
The graph shows the relation between the resistance and the temperature. The variation of resistivity of copper with temperature is parabolic in nature.
From the graph it is understood that the resistivity of copper increases with the rise in temperature. It is also understood that, whatever the temperature is, the copper has a certain resistivity. And it rises when temperature exceeds a particular value.

Resistivity, commonly denoted by the Greek letter rho, \[\rho \] , is quantitatively equal to
\[\rho \; = \;RA/l\]
Where, \[R\] =resistance of a specimen such as a wire
\[A\] =cross-sectional area
\[l\] = length
Both resistivity and resistance describe the characteristics of a material that make how much difficulty in the current flow through that particular material, but resistivity is an intrinsic property and resistance is not. This means that all pure copper wires have the same resistivity irrespective of their shape and size. But a thick, short copper wire has a much smaller resistance than a long, thin copper wire.
Copper is one of the best conductors of electric current. It has a low resistivity value. Hence it is used widely for all kinds of electrical purposes.
Note: Electrical conductivity or specific conductance can be considered as the reciprocal of electrical resistivity. As we mentioned resistivity shows the resistance to the current flowing through the conductor, but conductivity represents a material's ability to conduct electric current. It is commonly denoted by the Greek letter \[\sigma \] .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




