
SI unit of electric polarization is
A) $C{m^{ - 2}}$
B) Coulomb
C) Ampere
D) Volt
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint:Electric polarization is defined as the separation of positive charge from that of negative charges in the material on the application of the electric field to the material. Electric polarization is the electric dipole moment per unit volume of the material.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To know the SI unit of electric polarization we first need to understand the meaning of the term ‘electric polarization’. Electric polarization is defined as the current development in the presence of an external field. The dipole moment developed per unit volume in a dielectric placed in an external electric field is called polarization (P). It is also known as polarization density. The substances in which the dipole moment is in the direction of the field and is proportional to the field strength are called linear isotropic dielectrics.
Therefore, for linear isotropic dielectrics $P = {\chi _e}E$ where ${\chi _e}$ is constant of proportionality called electric susceptibility of the dielectric. It is a dimensionless constant.
Now from the definition of electric polarization, it is the electric current per unit square meter.
We know that, current has the unit of coulombs which can be denoted as (C) and square meter is the area which has the units of ${m^2}$ or $c{m^2}$.Thus formula for the polarization can be written as,
$\dfrac{c}{{{m^2}}}$ Or $c{m^{ - 2}}$ that is coulombs per square meter.
Therefore the SI unit is $\dfrac{c}{{{m^2}}}$or coulombs per square meter.
Thus correct option is (A)
Additional information:
Let us Consider, a rectangular dielectric slab placed in a uniform external field E parallel to two of its faces. The field causes a uniform polarization P of the dielectric. The dipole moment of every small element $\Delta {\text{v}}$ of the slab is P$\Delta {\text{v}}$ which is in the direction of the field.
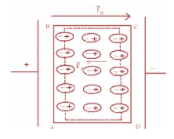
The volume element is microscopically small but contains a very large number of molecular dipoles. Anywhere inside the dielectric, the volume element has no net charge (though it has net dipole moment). This is, because, the positive charge of one dipole sits close to the negative charge of the adjacent dipole. However, at surfaces of the dielectric normal to the electric field, there is a net charge density. The positive end of the dipole remains unnaturalised at the right surface and the negative ends at the left surface. The unbalanced charges are the produced charges due to the external field.
The maximum value of electric field intensity that can be applied to a dielectric without its electric breakdown is called dielectric strength of the dielectric.
Note:Polarization that is P in the quantitative term is the amount of dipole moment i.e. p per unit volume i.e. V of a polarized material.
The behaviour of the electric field, magnetic field, and current density are given by Maxwell’s equation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To know the SI unit of electric polarization we first need to understand the meaning of the term ‘electric polarization’. Electric polarization is defined as the current development in the presence of an external field. The dipole moment developed per unit volume in a dielectric placed in an external electric field is called polarization (P). It is also known as polarization density. The substances in which the dipole moment is in the direction of the field and is proportional to the field strength are called linear isotropic dielectrics.
Therefore, for linear isotropic dielectrics $P = {\chi _e}E$ where ${\chi _e}$ is constant of proportionality called electric susceptibility of the dielectric. It is a dimensionless constant.
Now from the definition of electric polarization, it is the electric current per unit square meter.
We know that, current has the unit of coulombs which can be denoted as (C) and square meter is the area which has the units of ${m^2}$ or $c{m^2}$.Thus formula for the polarization can be written as,
$\dfrac{c}{{{m^2}}}$ Or $c{m^{ - 2}}$ that is coulombs per square meter.
Therefore the SI unit is $\dfrac{c}{{{m^2}}}$or coulombs per square meter.
Thus correct option is (A)
Additional information:
Let us Consider, a rectangular dielectric slab placed in a uniform external field E parallel to two of its faces. The field causes a uniform polarization P of the dielectric. The dipole moment of every small element $\Delta {\text{v}}$ of the slab is P$\Delta {\text{v}}$ which is in the direction of the field.

The volume element is microscopically small but contains a very large number of molecular dipoles. Anywhere inside the dielectric, the volume element has no net charge (though it has net dipole moment). This is, because, the positive charge of one dipole sits close to the negative charge of the adjacent dipole. However, at surfaces of the dielectric normal to the electric field, there is a net charge density. The positive end of the dipole remains unnaturalised at the right surface and the negative ends at the left surface. The unbalanced charges are the produced charges due to the external field.
The maximum value of electric field intensity that can be applied to a dielectric without its electric breakdown is called dielectric strength of the dielectric.
Note:Polarization that is P in the quantitative term is the amount of dipole moment i.e. p per unit volume i.e. V of a polarized material.
The behaviour of the electric field, magnetic field, and current density are given by Maxwell’s equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




