
Single bone of the lower jaw in humans is
(A) Maxilla
(B) Mandible
(C) Squamosal
(D) Pterygoid
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: The lower jaw forms the lower part of the human skull. The lower jaw along with the upper jaw together forms the structure called the mouth.
Complete Answer:
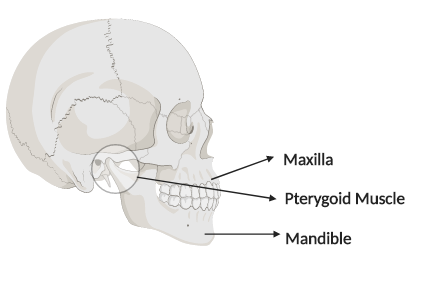
The human mouth is formed by two major bones namely, maxilla and mandible. The maxilla is the jaw and the mandible is called the lower jaw. The lower jaw fixes in the skull and is one of the largest bones that is present in the human skull. Both the jaw holds a set to teeth and the lower jaw specifically helps in the formation of the jawline.
Four different muscles namely, masseter, medial pterygoid, lateral pterygoid and the temporalis together are attached to the lower jaw in order to facilitate its proper movement. These muscles work in synchrony to assist the upward as well as side by side movement of the lower jaw. This mechanical process is termed as chewing. Chewing helps in proper mastication of the food and thereby assisting in proper digestion of the food.
Pterygoid is the set of muscles that is present in the lower jaw that helps in its movement. While, on the other hand, squamosal is the part of the temporal bone of the skull. In humans, it is seen present near the ear portion of the skull.
Therefore, option (A) Mandible is the correct answer.
Additional Information:
The human skull with a prime function of protecting the brain consists of 22 individual bones. Out of these bones, 14 are facial bones and 8 are cranial bones. The lower jaw (mandible) is the part of facial bones. During development, the lower jaw is made up of two bones which fuse together to form a mandible during the course of development.
Note: The human mouth is made up of jaw, namely the maxilla and the mandible. Mandible (lower jaw) lodges into the skull with the assistance of the coronoid and condylar process of the ramus.
Complete Answer:

The human mouth is formed by two major bones namely, maxilla and mandible. The maxilla is the jaw and the mandible is called the lower jaw. The lower jaw fixes in the skull and is one of the largest bones that is present in the human skull. Both the jaw holds a set to teeth and the lower jaw specifically helps in the formation of the jawline.
Four different muscles namely, masseter, medial pterygoid, lateral pterygoid and the temporalis together are attached to the lower jaw in order to facilitate its proper movement. These muscles work in synchrony to assist the upward as well as side by side movement of the lower jaw. This mechanical process is termed as chewing. Chewing helps in proper mastication of the food and thereby assisting in proper digestion of the food.
Pterygoid is the set of muscles that is present in the lower jaw that helps in its movement. While, on the other hand, squamosal is the part of the temporal bone of the skull. In humans, it is seen present near the ear portion of the skull.
Therefore, option (A) Mandible is the correct answer.
Additional Information:
The human skull with a prime function of protecting the brain consists of 22 individual bones. Out of these bones, 14 are facial bones and 8 are cranial bones. The lower jaw (mandible) is the part of facial bones. During development, the lower jaw is made up of two bones which fuse together to form a mandible during the course of development.
Note: The human mouth is made up of jaw, namely the maxilla and the mandible. Mandible (lower jaw) lodges into the skull with the assistance of the coronoid and condylar process of the ramus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




