
Sodium chloride is used in the soap industry for soap’s ______.
(A) decomposition
(B) removal of hardness
(C) precipitation
(D) none of the above
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: Recollect the process of commercial manufacturing of soap. Make a note of all the reagents used in the process and the reason for using them. Find out for which process table salt is used to get the answer.
Complete step by step solution:
- The process of manufacturing of soap is known as saponification.
- Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long chains of fatty acids which contain more than 12 carbon atoms.
- In saponification, fats or oils are first hydrolysed by using sodium hydroxide, NaOH or potassium hydroxide, KOH to form a solution of glycerol and fatty acids.
- Soap is then precipitated from the solution by adding salt like sodium chloride, NaCl, potassium chloride, KCl, etc.
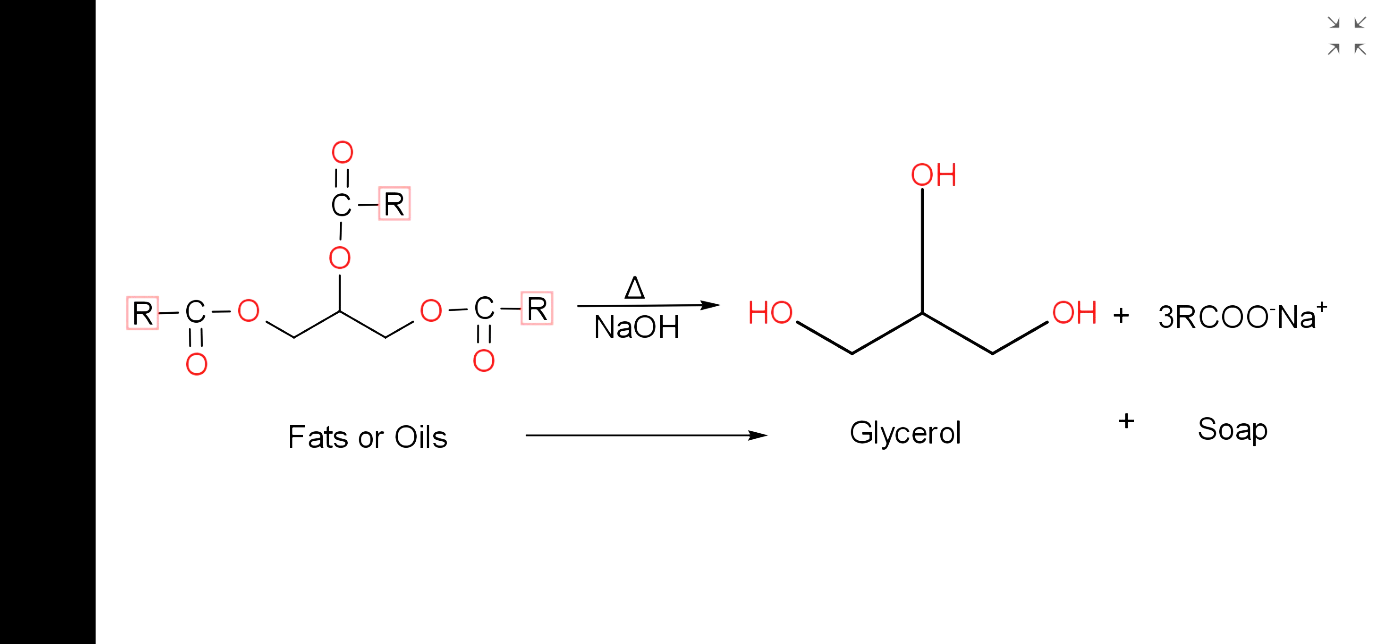
- The fatty acids react with salts and get precipitated out as soap due to the common ion effect and glycerol remains in the salt solution being soluble in salt solution.
- The fatty acids are soluble in the alkaline solution used for hydrolysis and that’s why, salt is added so that sodium salt of fatty acid is formed and it gets precipitated out.
- Potassium soaps are softer than sodium soaps. Potassium soaps are used in shampoo, shaving creams and bathing soaps (liquid or cake). Sodium soaps are toilet soaps used for washing purposes.
- Therefore, sodium chloride is used in the soap industry for soap’s precipitation.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Remember soaps are prepared by alkaline hydrolysis of fats or oils. Soaps are salts of fatty acids having a long chain of more than 12 carbon atoms. Soaps are insoluble in salt solution and precipitate out due to common ion effects. Glycerol is soluble in salt solution.
Complete step by step solution:
- The process of manufacturing of soap is known as saponification.
- Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long chains of fatty acids which contain more than 12 carbon atoms.
- In saponification, fats or oils are first hydrolysed by using sodium hydroxide, NaOH or potassium hydroxide, KOH to form a solution of glycerol and fatty acids.
- Soap is then precipitated from the solution by adding salt like sodium chloride, NaCl, potassium chloride, KCl, etc.

- The fatty acids react with salts and get precipitated out as soap due to the common ion effect and glycerol remains in the salt solution being soluble in salt solution.
- The fatty acids are soluble in the alkaline solution used for hydrolysis and that’s why, salt is added so that sodium salt of fatty acid is formed and it gets precipitated out.
- Potassium soaps are softer than sodium soaps. Potassium soaps are used in shampoo, shaving creams and bathing soaps (liquid or cake). Sodium soaps are toilet soaps used for washing purposes.
- Therefore, sodium chloride is used in the soap industry for soap’s precipitation.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Remember soaps are prepared by alkaline hydrolysis of fats or oils. Soaps are salts of fatty acids having a long chain of more than 12 carbon atoms. Soaps are insoluble in salt solution and precipitate out due to common ion effects. Glycerol is soluble in salt solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




