
Sodium phenoxide reacts with \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] at \[{\text{400k}}\] and \[{\text{4 - 7atm}}\] pressure to give:
A) Cathchol
B) Salicyaldehyde
C) Salocylic acid
D) Sodium salicylate
Answer
518.7k+ views
Hint: We must have to remember that in organic chemistry benzene is one of the important compounds. It is one of the aromatic compounds. The molecular formula of benzene is \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\]. Phenol is one of the derivatives of benzene. I simply said phenol is one of the aromatic alcohols. Kolbe’s reaction is one of the electrophilic substitution reactions in phenol.
Complete answer:
We must have to know that in Kolbe’s reaction, phenol is first treated with sodium hydroxide to form sodium phenoxide. This sodium phenoxide is treated with carbon dioxide at \[{\text{400k}}\]and \[{\text{4 - 7 atm}}\]to give sodium salicylate. His sodium salicylate is followed by hydrolysis to give product of salicylic acid.
The chemical reaction for sodium phenoxide react with carbon dioxide is given below,
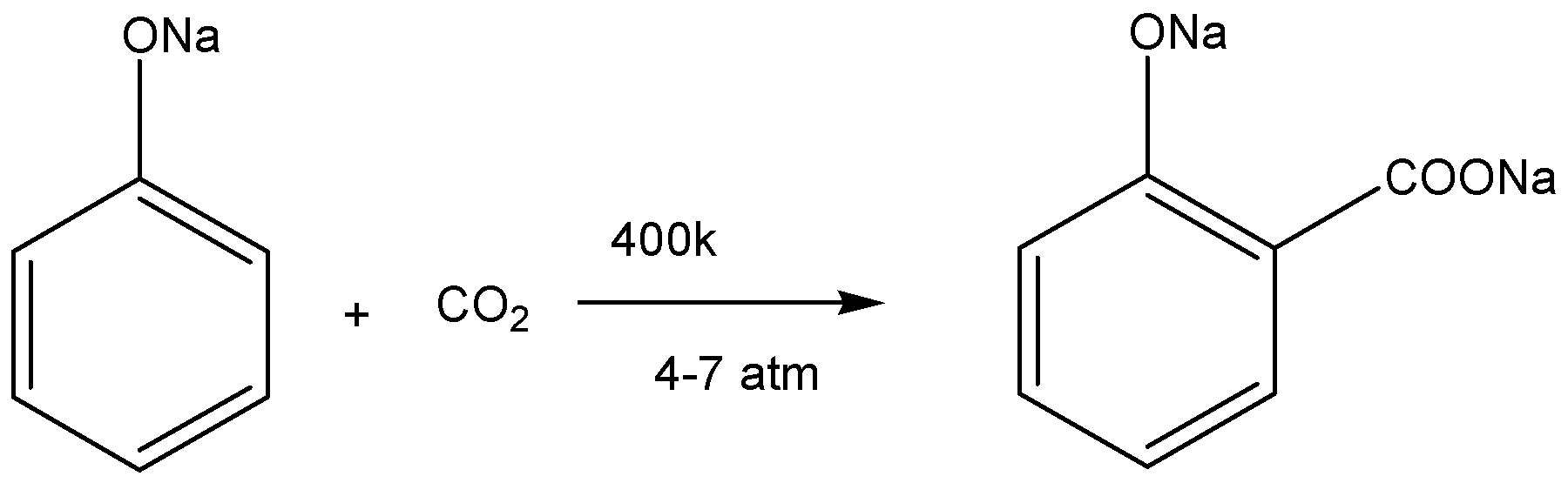
According from above reaction, we conclude sodium phenoxide reacts with \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] at \[{\text{400k}}\] and \[{\text{4 - 7atm}}\]pressure to give sodium salicylate.
Option A is not correct, because Sodium phenoxide reacts with \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] at \[{\text{400k}}\] and \[{\text{4 - 7atm}}\] pressure to not give cathchol.
Option B is not correct, because Sodium phenoxide reacts with \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] at \[{\text{400k}}\] and \[{\text{4 - 7atm}}\] pressure to not give Salicyaldehyde.
Option C is not correct, because Sodium phenoxide reacts with \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] at \[{\text{400k}}\] and \[{\text{4 - 7atm}}\] pressure to not give Salocylic acid.
Option D is correct, because Sodium phenoxide reacts with \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] at \[{\text{400k}}\] and \[{\text{4 - 7atm}}\] pressure to give sodium salicylate.
Note:
We must have to remember that phenol is one of the mono substituent benzene compounds. Each mono-substituent moiety has three named positions in the ring. In the ring a nearby mono substituent group is called ortho position, that means two ortho positions are in the ring, because of the left and right side of the substituent group. The alternatively position of the substituent group in the ring is called meta position, here also two meta positions possible in the left and right side of the substituent group. Para position is nothing but directly opposite to the substituent group in the ring. Electrophilic substitutions are attacked in ortho and para position in the ring.
Complete answer:
We must have to know that in Kolbe’s reaction, phenol is first treated with sodium hydroxide to form sodium phenoxide. This sodium phenoxide is treated with carbon dioxide at \[{\text{400k}}\]and \[{\text{4 - 7 atm}}\]to give sodium salicylate. His sodium salicylate is followed by hydrolysis to give product of salicylic acid.
The chemical reaction for sodium phenoxide react with carbon dioxide is given below,

According from above reaction, we conclude sodium phenoxide reacts with \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] at \[{\text{400k}}\] and \[{\text{4 - 7atm}}\]pressure to give sodium salicylate.
Option A is not correct, because Sodium phenoxide reacts with \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] at \[{\text{400k}}\] and \[{\text{4 - 7atm}}\] pressure to not give cathchol.
Option B is not correct, because Sodium phenoxide reacts with \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] at \[{\text{400k}}\] and \[{\text{4 - 7atm}}\] pressure to not give Salicyaldehyde.
Option C is not correct, because Sodium phenoxide reacts with \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] at \[{\text{400k}}\] and \[{\text{4 - 7atm}}\] pressure to not give Salocylic acid.
Option D is correct, because Sodium phenoxide reacts with \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] at \[{\text{400k}}\] and \[{\text{4 - 7atm}}\] pressure to give sodium salicylate.
Note:
We must have to remember that phenol is one of the mono substituent benzene compounds. Each mono-substituent moiety has three named positions in the ring. In the ring a nearby mono substituent group is called ortho position, that means two ortho positions are in the ring, because of the left and right side of the substituent group. The alternatively position of the substituent group in the ring is called meta position, here also two meta positions possible in the left and right side of the substituent group. Para position is nothing but directly opposite to the substituent group in the ring. Electrophilic substitutions are attacked in ortho and para position in the ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




