
When sodium toluate is treated with soda lime the final product will be:
(A)
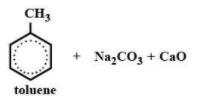
(B)
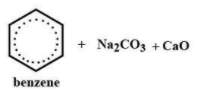
(C)
(D) None of these
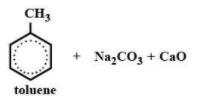
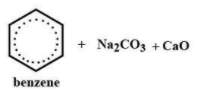

Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: When sodium toluene is treated with soda lime decarboxylation reaction takes place which means that the carbonyl group is removed and carbon dioxide is released.
Complete step by step solution:
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction in which the carbonyl group is removed and carbon dioxide is released. Generally, the decarboxylation means the reaction of carboxylic acids where it is used in the removal of one carbon from the carbon chain. It is one of the oldest reactions of organic chemistry.
Decarboxylation is the basic step in many of the name reactions which includes Barton decarboxylation, Kochi reaction, Hunsdiecker reaction etc.
Soda-lime is a mixture of sodium carbonate and calcium hydroxide having molecular formula$CaHNa{{O}_{2}}$it is basically used in the breathing systems to absorb the carbon dioxide during anaesthesia. Decarboxylation of the sodium salts of a carboxylic acid is done using soda-lime and for the formation of alkane, it is known as duma reaction.
Benzene is formed when sodium benzoate is treated with a mixture of sodium hydroxide and calcium oxide, it is also a type of decarboxylation reaction, and the product form is benzene and sodium carbonate.
Sodium toluate ${{C}_{8}}{{H}_{7}}Na{{O}_{2}}$ when treated with soda lime give rise to toluene and sodium carbonate and calcium oxide.
Reaction involved-
$\text{sodium toluate + NaOH + Cao}\xrightarrow{heat}\text{ Toluene + N}{{\text{a}}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}$
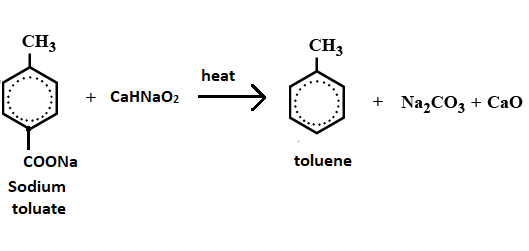
Hence the correct option is option (A) which is the formation of toluene, sodium carbonate and calcium oxide.
Note: While dealing with any reaction in organic chemistry make sure to check the reaction condition before the formation of the product. The Condition in which the reactant is kept plays a major role in the formation of a product; it may include the use of a catalyst or carrying out the reaction at a particular temperature or pressure.
Complete step by step solution:
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction in which the carbonyl group is removed and carbon dioxide is released. Generally, the decarboxylation means the reaction of carboxylic acids where it is used in the removal of one carbon from the carbon chain. It is one of the oldest reactions of organic chemistry.
Decarboxylation is the basic step in many of the name reactions which includes Barton decarboxylation, Kochi reaction, Hunsdiecker reaction etc.
Soda-lime is a mixture of sodium carbonate and calcium hydroxide having molecular formula$CaHNa{{O}_{2}}$it is basically used in the breathing systems to absorb the carbon dioxide during anaesthesia. Decarboxylation of the sodium salts of a carboxylic acid is done using soda-lime and for the formation of alkane, it is known as duma reaction.
Benzene is formed when sodium benzoate is treated with a mixture of sodium hydroxide and calcium oxide, it is also a type of decarboxylation reaction, and the product form is benzene and sodium carbonate.
Sodium toluate ${{C}_{8}}{{H}_{7}}Na{{O}_{2}}$ when treated with soda lime give rise to toluene and sodium carbonate and calcium oxide.
Reaction involved-
$\text{sodium toluate + NaOH + Cao}\xrightarrow{heat}\text{ Toluene + N}{{\text{a}}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}$

Hence the correct option is option (A) which is the formation of toluene, sodium carbonate and calcium oxide.
Note: While dealing with any reaction in organic chemistry make sure to check the reaction condition before the formation of the product. The Condition in which the reactant is kept plays a major role in the formation of a product; it may include the use of a catalyst or carrying out the reaction at a particular temperature or pressure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




