
Some of the nutrient cycles are labelled as below.
Sulphur cycle (A), phosphorus cycle (B), carbon cycle (C) and nitrogen cycle (D), of these, the sedimentary cycle is represented by
A. (A) only
B. (B) only
C. (C) only
D. (A) and (B) only
E. (C) and (D) only
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: Sedimentary cycles are those cycles which incorporate the enduring of rocks and disintegration of minerals alongside its course in the climate and back to earth hull. It incorporates those of iron, calcium, phosphorus and other more terrestrial components. Phosphorus cycle is additionally a kind of sedimentary cycle.
Complete Solution:
There are 4 layers of Earth, specifically lithosphere (land), hydrosphere (water), biosphere (living), and climate (air). Lithosphere of Earth makes up the hard and inflexible external layer of the Earth. It is a supply of phosphorus.
The biggest repository of phosphorus is dregs or sedimentary rocks. Consequently, phosphorus cycle speaks to sedimentary kind of supplement cycle or essentially sedimentary cycle.
Phosphorus moves in a cycle through rocks, water, soil and residue and living beings. Over the long haul, downpour and enduring reason rocks to deliver phosphate particles and different minerals. This inorganic phosphate is then conveyed in soils and water.
Plants take up inorganic phosphate from the dirt. Vaporous cycles incorporate those of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon, and water; sedimentary cycles incorporate those of iron, calcium, phosphorus, and other more terrestrial components.
Here are the vital strides of the phosphorus cycle
Over time, downpour and enduring reason rocks to release phosphate particles and different minerals. This inorganic phosphate is then conveyed in soils and water.
Plants take up inorganic phosphate from the soil. The plants may then be devoured by creatures. Once in the plant or creature, the phosphate is fused into natural particles, for example, DNA. At the point when the plant or creature bites the dust, it rots, and the natural phosphate is gotten back to the dirt.
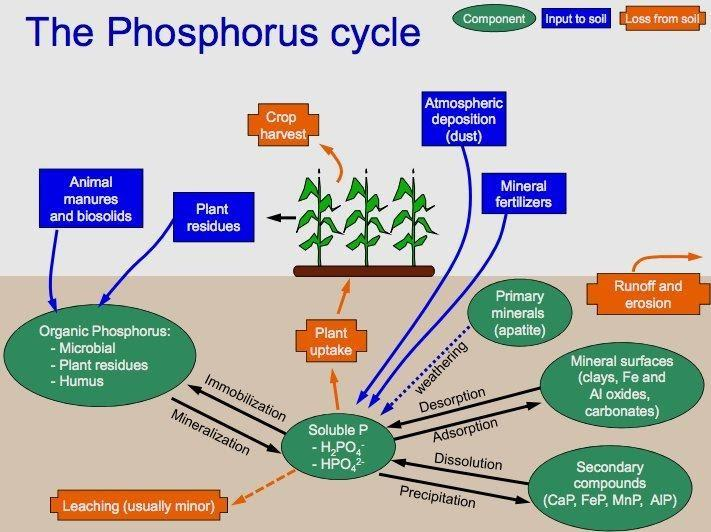
Within the soil, natural types of phosphate can be made accessible to plants by microbes that separate natural issues to inorganic types of phosphorus. This cycle is known as mineralization.
Phosphorus in soil can wind up in streams and in the long run seas. Once there, it very well may be consolidated into dregs over the long run.
Hence, the correct answer is choice (D).
Note:
Many plant crops need more phosphorus than is disintegrated in the dirt to develop ideally. Furthermore, crops are typically collected and eliminated – leaving no rotting vegetation to supplant phosphorus. Consequently, ranchers renew the phosphorus 'pool' by adding manures or gushing to supplant the phosphorus taken up by plants.
Complete Solution:
There are 4 layers of Earth, specifically lithosphere (land), hydrosphere (water), biosphere (living), and climate (air). Lithosphere of Earth makes up the hard and inflexible external layer of the Earth. It is a supply of phosphorus.
The biggest repository of phosphorus is dregs or sedimentary rocks. Consequently, phosphorus cycle speaks to sedimentary kind of supplement cycle or essentially sedimentary cycle.
Phosphorus moves in a cycle through rocks, water, soil and residue and living beings. Over the long haul, downpour and enduring reason rocks to deliver phosphate particles and different minerals. This inorganic phosphate is then conveyed in soils and water.
Plants take up inorganic phosphate from the dirt. Vaporous cycles incorporate those of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon, and water; sedimentary cycles incorporate those of iron, calcium, phosphorus, and other more terrestrial components.
Here are the vital strides of the phosphorus cycle
Over time, downpour and enduring reason rocks to release phosphate particles and different minerals. This inorganic phosphate is then conveyed in soils and water.
Plants take up inorganic phosphate from the soil. The plants may then be devoured by creatures. Once in the plant or creature, the phosphate is fused into natural particles, for example, DNA. At the point when the plant or creature bites the dust, it rots, and the natural phosphate is gotten back to the dirt.

Within the soil, natural types of phosphate can be made accessible to plants by microbes that separate natural issues to inorganic types of phosphorus. This cycle is known as mineralization.
Phosphorus in soil can wind up in streams and in the long run seas. Once there, it very well may be consolidated into dregs over the long run.
Hence, the correct answer is choice (D).
Note:
Many plant crops need more phosphorus than is disintegrated in the dirt to develop ideally. Furthermore, crops are typically collected and eliminated – leaving no rotting vegetation to supplant phosphorus. Consequently, ranchers renew the phosphorus 'pool' by adding manures or gushing to supplant the phosphorus taken up by plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




