
What sort of striated muscles constitutes the muscle of the eyeball? how is that this specific sort of muscle advantageous?
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: Striated muscles are highly organized tissues that convert energy to physical work. The first function of striated muscles is to get force and accept an order to support respiration, locomotion, and posture (skeletal muscle) and to pump blood throughout the body (cardiac muscle).
Complete answer:
The medial rectus muscle is one of seven extraocular muscles that are striated muscles of the eyeball. These include four rectus muscles, two oblique muscles, and therefore the levator palpebrae superioris. The medial rectus muscle is one among the four rectus muscles, which also include the abducens muscle, the superior rectus muscle, and therefore the inferior rectus muscle. The oblique muscles are the superior and inferior obliques.
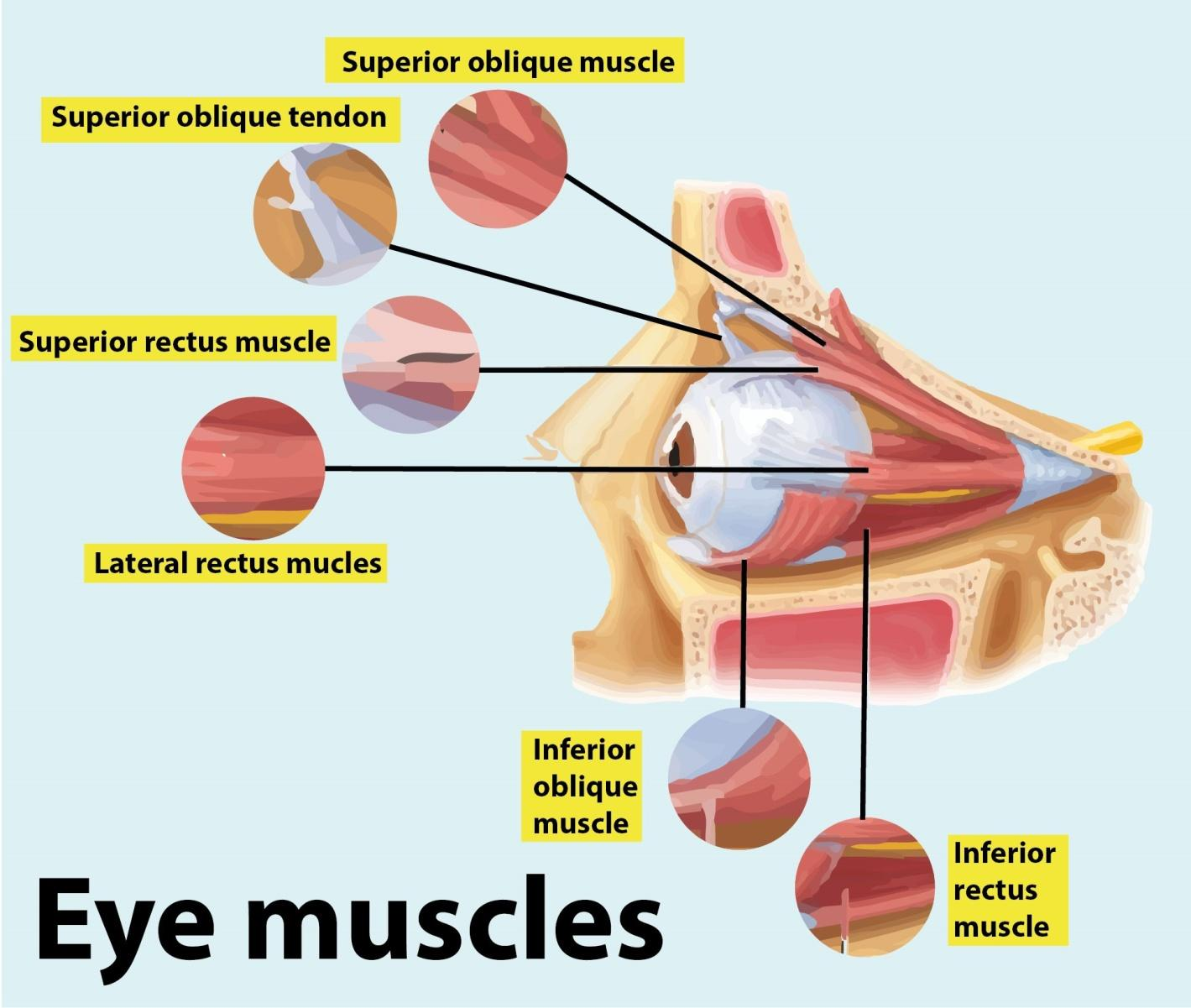
The medial rectus muscle is an adductor, and functions alongside the abducens muscle which abducts the attention. These two muscles allow the eyes to maneuver from side to side. With the head facing straight and therefore the eyes facing straight ahead, the eyes are said to be in primary gaze. Although the world is often moved about 50 degrees from primary position, usually during normal eye movement only 15 degrees of extraocular muscle movement occurs before the top movement begins.
The medial rectus muscle receives blood through the inferior muscular branch of the arteria ophthalmica. The first blood supply for all of the extraocular muscles is the muscular branches of the arteria ophthalmica. The 2 branches are the inferior muscular branch and therefore the superior muscular branch. The larger inferior muscular branch supplies the medial rectus muscle, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique. The superior muscular branch supplies the abducens muscle, superior rectus, superior oblique, and levator palpebrae superioris. Additionally, the abducens muscle receives some blood supply from the arteria lacrimalis
The medial rectus muscle and the abducens muscle structure are horizontal rectus muscles. The superior and inferior rectus muscle muscles form the vertical rectus muscles. Each of the rectus muscles originates posteriorly at the Annulus of Zinn and courses anteriorly.
Note:
- Tenon's capsule is elastic animal tissue that attaches to the nervus opticus posteriorly and is pierced by all of the extraocular muscles except the levator palpebrae superioris. When surgery is performed, care must be taken to not compromise Tenon's capsule 10 mm posterior to the limbus. Otherwise, fat may prolapse and cause adhesions which could limit extraocular movement.
- Strabismus, or ocular misalignment, is often caused by abnormalities, insights or abnormalities of neuromuscular control. Weakness, injury, or paralysis that involves the medial rectus muscle are often involved in strabismus.
- Medial rectus muscle aligns along the medial orbital wall. Each of the rectus muscles inserts on the world at varying distances from the limbus, and therefore the curved line drawn along the insertion points makes a spiral that's referred to as the Spiral of Tillaux.
Complete answer:
The medial rectus muscle is one of seven extraocular muscles that are striated muscles of the eyeball. These include four rectus muscles, two oblique muscles, and therefore the levator palpebrae superioris. The medial rectus muscle is one among the four rectus muscles, which also include the abducens muscle, the superior rectus muscle, and therefore the inferior rectus muscle. The oblique muscles are the superior and inferior obliques.

The medial rectus muscle is an adductor, and functions alongside the abducens muscle which abducts the attention. These two muscles allow the eyes to maneuver from side to side. With the head facing straight and therefore the eyes facing straight ahead, the eyes are said to be in primary gaze. Although the world is often moved about 50 degrees from primary position, usually during normal eye movement only 15 degrees of extraocular muscle movement occurs before the top movement begins.
The medial rectus muscle receives blood through the inferior muscular branch of the arteria ophthalmica. The first blood supply for all of the extraocular muscles is the muscular branches of the arteria ophthalmica. The 2 branches are the inferior muscular branch and therefore the superior muscular branch. The larger inferior muscular branch supplies the medial rectus muscle, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique. The superior muscular branch supplies the abducens muscle, superior rectus, superior oblique, and levator palpebrae superioris. Additionally, the abducens muscle receives some blood supply from the arteria lacrimalis
The medial rectus muscle and the abducens muscle structure are horizontal rectus muscles. The superior and inferior rectus muscle muscles form the vertical rectus muscles. Each of the rectus muscles originates posteriorly at the Annulus of Zinn and courses anteriorly.
Note:
- Tenon's capsule is elastic animal tissue that attaches to the nervus opticus posteriorly and is pierced by all of the extraocular muscles except the levator palpebrae superioris. When surgery is performed, care must be taken to not compromise Tenon's capsule 10 mm posterior to the limbus. Otherwise, fat may prolapse and cause adhesions which could limit extraocular movement.
- Strabismus, or ocular misalignment, is often caused by abnormalities, insights or abnormalities of neuromuscular control. Weakness, injury, or paralysis that involves the medial rectus muscle are often involved in strabismus.
- Medial rectus muscle aligns along the medial orbital wall. Each of the rectus muscles inserts on the world at varying distances from the limbus, and therefore the curved line drawn along the insertion points makes a spiral that's referred to as the Spiral of Tillaux.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




