
Sound waves are electromagnetic waves like light.
A. True
B. False
C. Ambiguous
D. Data insufficient
Answer
604.2k+ views
Hint: Recall what a wave is and how it transfers through a medium. Note down the different types of waves- longitudinal and transverse. Compare and contrast between a light wave and sound wave with an electromagnetic wave.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When we throw a stone into a calm pond, we can find ripples. The disturbance created by the stone gives rise to ripples. We can explain waves as the disturbance or oscillation in a system. They will transfer the energy from the source point of the disturbance to the other parts of the system. Particles that experienced the disturbance won’t vibrate permanently. They will oscillate until the energy they gain will drain off.
Some waves travel through a medium with the speed which depends on the inertial and inelastic properties of the wave. Such waves are called mechanical waves. They can propagate through the three states of matter. That is they will travel through solid, liquid and gaseous states. A longitudinal wave is divided into two- longitudinal waves and transverse waves.
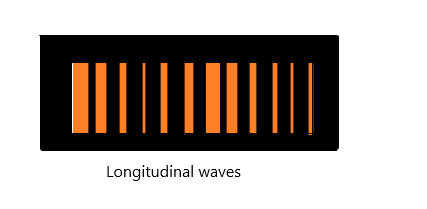
Longitudinal waves: Here, the wave particles oscillate in the direction perpendicular of the axis of propagation. They always show a to and froth motion. Consider if the longitudinal wave is propagating along the x axis, then the particles vibrate from –X to +X. The sound wave is an example of this kind of wave. When a spring is stretched along the x axis and is released, we can find this type of motion.
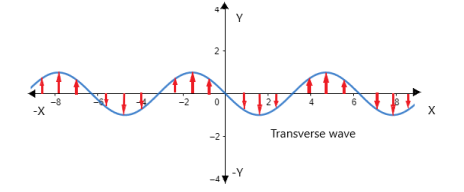
Transverse wave: in this type of waves, the particle will vibrate perpendicular to the axis of propagation of waves. They will exhibit up and down motion. For example, if the wave is propagating along the x-axis, then the wave particles will vibrate from +Y to –Y or along +Z to –Z direction which is shown in the figure. Thus the particle always vibrates perpendicular to the x-axis. A light wave is an example of this type of wave. When the stretched string of a guitar or violin is plucked, we can find this kind of oscillation.
Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature. They even can travel through vacuum, indicating that they don’t need a medium to propagate. Visible light is electromagnetic radiation. They can travel without a medium. Since sound shows longitudinal wave nature, they are not electromagnetic waves. They need a medium to propagate. So we can conclude that sound waves are not an electromagnetic wave like light.
So option B is the answer.
Note: Even though waves transfer energy, they won’t transfer mass. Mechanical waves won’t propagate continuously through the medium, unlike electromagnetic waves. Their energy is not long-lasting like electromagnetic waves. The primary source of the electromagnetic wave is the sun.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When we throw a stone into a calm pond, we can find ripples. The disturbance created by the stone gives rise to ripples. We can explain waves as the disturbance or oscillation in a system. They will transfer the energy from the source point of the disturbance to the other parts of the system. Particles that experienced the disturbance won’t vibrate permanently. They will oscillate until the energy they gain will drain off.
Some waves travel through a medium with the speed which depends on the inertial and inelastic properties of the wave. Such waves are called mechanical waves. They can propagate through the three states of matter. That is they will travel through solid, liquid and gaseous states. A longitudinal wave is divided into two- longitudinal waves and transverse waves.
Longitudinal waves: Here, the wave particles oscillate in the direction perpendicular of the axis of propagation. They always show a to and froth motion. Consider if the longitudinal wave is propagating along the x axis, then the particles vibrate from –X to +X. The sound wave is an example of this kind of wave. When a spring is stretched along the x axis and is released, we can find this type of motion.

Transverse wave: in this type of waves, the particle will vibrate perpendicular to the axis of propagation of waves. They will exhibit up and down motion. For example, if the wave is propagating along the x-axis, then the wave particles will vibrate from +Y to –Y or along +Z to –Z direction which is shown in the figure. Thus the particle always vibrates perpendicular to the x-axis. A light wave is an example of this type of wave. When the stretched string of a guitar or violin is plucked, we can find this kind of oscillation.

Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature. They even can travel through vacuum, indicating that they don’t need a medium to propagate. Visible light is electromagnetic radiation. They can travel without a medium. Since sound shows longitudinal wave nature, they are not electromagnetic waves. They need a medium to propagate. So we can conclude that sound waves are not an electromagnetic wave like light.
So option B is the answer.
Note: Even though waves transfer energy, they won’t transfer mass. Mechanical waves won’t propagate continuously through the medium, unlike electromagnetic waves. Their energy is not long-lasting like electromagnetic waves. The primary source of the electromagnetic wave is the sun.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




