
Spike of spikelet inflorescence is characteristic of
A. Asteraceae
B. Poaceae (Gramineae)
C. Brassicaceae
D. Malvaceae
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: Spikelet inflorescence is a type of elongated main-axis inflorescence which further is a type of racemose inflorescence. Spikelets are seen in grass species. Spikelets are represented by individual flower units. There is no calyx or corolla in a floret.
Complete answer: Inflorescence refers to the arrangement pattern of flowers attached to the main axis. There are mainly two types of inflorescences namely, racemose and cymose. The spike of spikelet inflorescence is a subtype of the racemose inflorescence. The racemose inflorescence is characterized by the continuous growth of the main axis and it does not terminate into flowers. It is also known as indefinite inflorescence. Flower buds are produced on the lateral sides of the main axis. The arrangement of flowers is in an acropetal manner. This means that flowers at the base are older and at the tip are younger. Elongated main axis inflorescence is a type of racemose inflorescence and spike of spikelet is a type of this inflorescence.
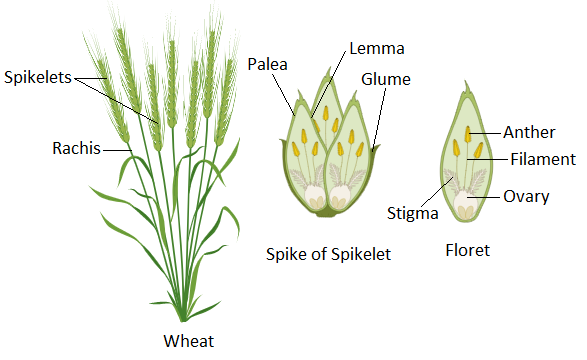
In the spike inflorescence, the main axis continues to grow without branching and flowers are without pedicel. The flowers are directly attached to the stalk. A compound type of spike is known as a spike of spikelets. The sessile flowers or spikelets which are without pedicel are present on the branched main-axis. This type of inflorescence is seen in wheat, barley, etc. which comes under grass species. The grass species are placed under the Poaceae family or Gramineae. Individual flower units are spikelets and the central axis to which they are attached is called the rachis. The spikelets together form a spike and that is why these are called spikelets.
Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
Note: Spikelets have glumes which are two scaly bracts at the base. The number of florets in a spikelet varies in different species. The florets have no corolla or calyx. The bracts enclose the reproductive organs of the floret. The external bract is larger and called lemma and the interior bract is smaller called palea.
Complete answer: Inflorescence refers to the arrangement pattern of flowers attached to the main axis. There are mainly two types of inflorescences namely, racemose and cymose. The spike of spikelet inflorescence is a subtype of the racemose inflorescence. The racemose inflorescence is characterized by the continuous growth of the main axis and it does not terminate into flowers. It is also known as indefinite inflorescence. Flower buds are produced on the lateral sides of the main axis. The arrangement of flowers is in an acropetal manner. This means that flowers at the base are older and at the tip are younger. Elongated main axis inflorescence is a type of racemose inflorescence and spike of spikelet is a type of this inflorescence.

In the spike inflorescence, the main axis continues to grow without branching and flowers are without pedicel. The flowers are directly attached to the stalk. A compound type of spike is known as a spike of spikelets. The sessile flowers or spikelets which are without pedicel are present on the branched main-axis. This type of inflorescence is seen in wheat, barley, etc. which comes under grass species. The grass species are placed under the Poaceae family or Gramineae. Individual flower units are spikelets and the central axis to which they are attached is called the rachis. The spikelets together form a spike and that is why these are called spikelets.
Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
Note: Spikelets have glumes which are two scaly bracts at the base. The number of florets in a spikelet varies in different species. The florets have no corolla or calyx. The bracts enclose the reproductive organs of the floret. The external bract is larger and called lemma and the interior bract is smaller called palea.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




