
State and explain Ampere’s circuital law.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Ampere's circuital law states that the closed line integral of magnetic field around a current carrying conductor is equal to absolute permeability times the total current threading the conductor. We can formulate it mathematically and understand the concept well.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Amperes circulate law mathematically state that the line integral of magnetic field of induction B around any closed path in free space is equal to absolute permeability of free space \[{{\mu }_{\circ }}\] times the total current flowing through area bounded by the path. The circuit is shown in the given picture
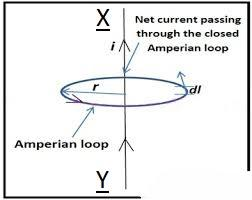
Mathematically, we can that the law as, \[\phi \overset{\to }{\mathop{B}}\,.\overset{\to }{\mathop{dl}}\,={{\mu }_{\circ }}I\] where,
B is magnetic induction
I is the total current flowing through the wire
Dl is length element of path
\[{{\mu }_{\circ }}\] is permeability of the space Ampere's law is a generalisation of Biot-Savart's law and can be derived from it and is used to determine magnetic field at any point due to distribution of current. Consider a long straight current carrying conductor XY, which is placed in a vacuum. A steady current I is flowing through it from the end Y to X. Now, imagine a closed curve (amperian loop) around the conductor having radius r as shown in the picture. The loop is assumed to be made of a very large number of small elements each of which is of length dl. Its direction is along the direction of the traced loop as shown in the picture. Now, let B be the strength of the magnetic field around the conductor. Hence, we get the final expression as
\[\phi =B.dl=B.dl.\cos \theta \]
where, \[\theta \]=angle between B and dl.
Note: Ampere's law gives us another method to calculate the magnetic field due to a given current distribution in a given fashion. Ampere's law can be derived from the Biot-Savart law and Biot-Savart law can also be derived from Ampere's law. Ampere's law is more useful under certain conditions where current distribution is symmetrical. We can calculate the magnetic field in a solenoid using this law.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Amperes circulate law mathematically state that the line integral of magnetic field of induction B around any closed path in free space is equal to absolute permeability of free space \[{{\mu }_{\circ }}\] times the total current flowing through area bounded by the path. The circuit is shown in the given picture

Mathematically, we can that the law as, \[\phi \overset{\to }{\mathop{B}}\,.\overset{\to }{\mathop{dl}}\,={{\mu }_{\circ }}I\] where,
B is magnetic induction
I is the total current flowing through the wire
Dl is length element of path
\[{{\mu }_{\circ }}\] is permeability of the space Ampere's law is a generalisation of Biot-Savart's law and can be derived from it and is used to determine magnetic field at any point due to distribution of current. Consider a long straight current carrying conductor XY, which is placed in a vacuum. A steady current I is flowing through it from the end Y to X. Now, imagine a closed curve (amperian loop) around the conductor having radius r as shown in the picture. The loop is assumed to be made of a very large number of small elements each of which is of length dl. Its direction is along the direction of the traced loop as shown in the picture. Now, let B be the strength of the magnetic field around the conductor. Hence, we get the final expression as
\[\phi =B.dl=B.dl.\cos \theta \]
where, \[\theta \]=angle between B and dl.
Note: Ampere's law gives us another method to calculate the magnetic field due to a given current distribution in a given fashion. Ampere's law can be derived from the Biot-Savart law and Biot-Savart law can also be derived from Ampere's law. Ampere's law is more useful under certain conditions where current distribution is symmetrical. We can calculate the magnetic field in a solenoid using this law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




