
State any two differences between primary and secondary rainbow.
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: Sunlight gets reflected on the water droplet and disintegrates into the constituent colours. These refracted rays are reflected inside the droplet and go through another refraction before reaching our eyes.
Complete step-by-step answer:
There are several differences between the primary and secondary rainbows. Let us look at the two most important differences.
(i) Primary rainbow forms about 40° to 42° from the antisolar point. And a secondary rainbow forms around 51° with the antisolar point. Let us look at the following diagram to understand what is the antisolar point.
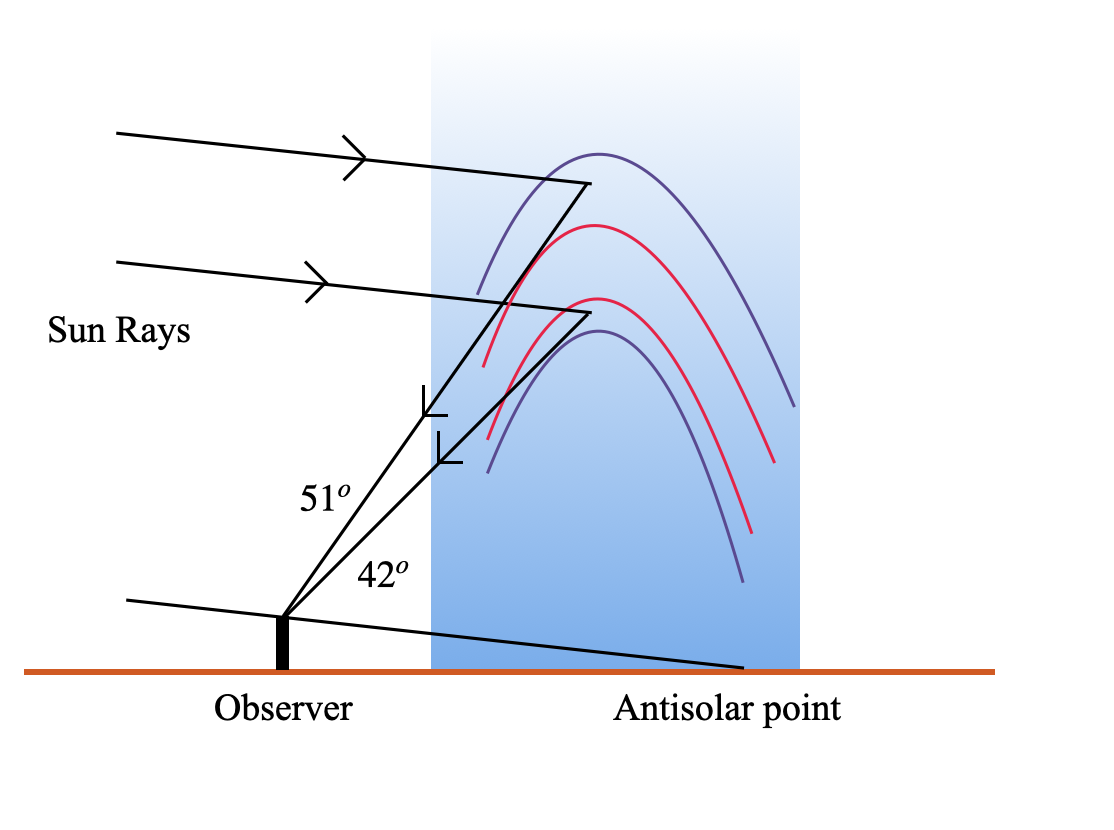
This difference in angle occurs due to the fact that the primary rainbow happens when the sunlight is reflected once in the water droplet. Whereas, the light goes double reflection inside the water droplet.
In simple terms, the secondary rainbow will always be above the primary rainbow.
(ii) The second difference between primary and secondary rainbows is the colours are inverted and less distinct in the secondary rainbow. Let’s look at the following diagram to understand this phenomenon.
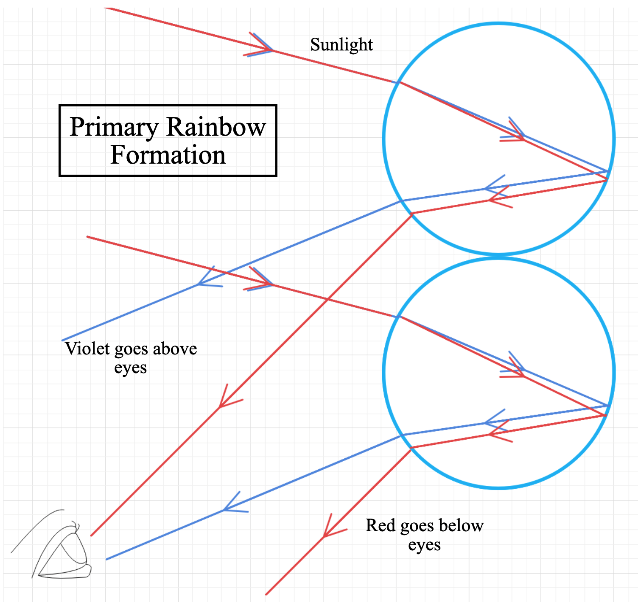
This shows how primary rainbows are formed. Light gets reflected twice for the secondary rainbow formation. As a result, the intensity of the light is decreased in the water droplet. So, the secondary rainbow is always lighter than the primary rainbow.
The inverted nature is explained in the following diagram:
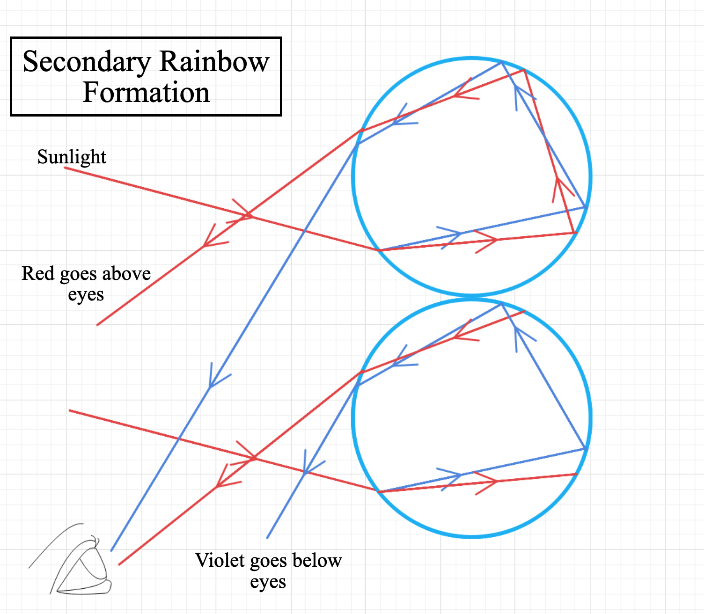
As you can see in the previous diagram, violet light is above the red light. As a result, the secondary rainbow is inverted.
Note:
It is not possible to see a complete rainbow from the ground. The angle 42° is below the horizon most of the time. It is possible to see a rainbow in the afternoon when you are facing away from the sun and after a shower. You can see a complete rainbow from an aeroplane.
Complete step-by-step answer:
There are several differences between the primary and secondary rainbows. Let us look at the two most important differences.
(i) Primary rainbow forms about 40° to 42° from the antisolar point. And a secondary rainbow forms around 51° with the antisolar point. Let us look at the following diagram to understand what is the antisolar point.

This difference in angle occurs due to the fact that the primary rainbow happens when the sunlight is reflected once in the water droplet. Whereas, the light goes double reflection inside the water droplet.
In simple terms, the secondary rainbow will always be above the primary rainbow.
(ii) The second difference between primary and secondary rainbows is the colours are inverted and less distinct in the secondary rainbow. Let’s look at the following diagram to understand this phenomenon.

This shows how primary rainbows are formed. Light gets reflected twice for the secondary rainbow formation. As a result, the intensity of the light is decreased in the water droplet. So, the secondary rainbow is always lighter than the primary rainbow.
The inverted nature is explained in the following diagram:

As you can see in the previous diagram, violet light is above the red light. As a result, the secondary rainbow is inverted.
Note:
It is not possible to see a complete rainbow from the ground. The angle 42° is below the horizon most of the time. It is possible to see a rainbow in the afternoon when you are facing away from the sun and after a shower. You can see a complete rainbow from an aeroplane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




