
State Gauss theorem and use it to derive the Coulomb’s inverse square law.
Answer
527.9k+ views
Hint: The gauss theorem is related to the flux due to an electric field. It says that the electric flux coming out of a closed region due to a certain amount of charge within it is directly related to the total amount of charge contained in that closed region.
Complete answer:
A stationary charge produces electric field. The amount of electric field lines passing through a given area is defined as the electric flux. The Gauss theorem relates the electric flux coming out of a closed region due to a certain amount of charge to the total amount of charge contained in that closed region.
The Gauss theorem states that the electric flux through a closed surface is equal to \[\dfrac{1}{{{ \in _0}}}\] times the total amount of charge contained in the region. The mathematical expression for Gauss theorem is given as
$\oint {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} } = \dfrac{{{Q_{net}}}}{{{ \in _0}}}$
Here E signifies the electric field passing through a certain area dS. ${Q_{net}}$ is the total amount of charge and ${ \in _0}$ signifies the permittivity of the vacuum.
Derivation of Coulomb’s inverse square law:
Consider a charge +q in place at origin in a vacuum. We want to calculate the electric field due to this charge at a distance r from the charge. Imagine that the charge is surrounded by an imaginary sphere of radius r as shown in the figure below. This sphere is called the Gaussian sphere.
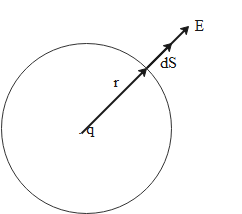
Consider a small area element dS on the Gaussian sphere. We can calculate the flux through this area element due to charge as follows:
$\oint {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} } = \int {EdS\cos 0^\circ } $ (Since angle between electric field and area element is 0$^\circ $)
The electric field due to the charge is constant and we can integrate the area element as follows:
$
\oint {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} } = E\int {dS} \\
= E\left( {4\pi {r^2}} \right) \\
$
Using this in Gauss theorem we get
$
E\left( {4\pi {r^2}} \right) = \dfrac{q}{{{ \in _0}}} \\
\Rightarrow E = \dfrac{q}{{4\pi { \in _0}{r^2}}} \\
$
This is the required Coulomb’s law obtained from Gauss theorem.
Note:
1. If the medium is other than vacuum then the permittivity of the vacuum is replaced by permittivity of that medium in the expression for Gauss theorem.
2. Every problem where Gauss theorem is used, we need a closed Gaussian surface for calculating the electric field.
Complete answer:
A stationary charge produces electric field. The amount of electric field lines passing through a given area is defined as the electric flux. The Gauss theorem relates the electric flux coming out of a closed region due to a certain amount of charge to the total amount of charge contained in that closed region.
The Gauss theorem states that the electric flux through a closed surface is equal to \[\dfrac{1}{{{ \in _0}}}\] times the total amount of charge contained in the region. The mathematical expression for Gauss theorem is given as
$\oint {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} } = \dfrac{{{Q_{net}}}}{{{ \in _0}}}$
Here E signifies the electric field passing through a certain area dS. ${Q_{net}}$ is the total amount of charge and ${ \in _0}$ signifies the permittivity of the vacuum.
Derivation of Coulomb’s inverse square law:
Consider a charge +q in place at origin in a vacuum. We want to calculate the electric field due to this charge at a distance r from the charge. Imagine that the charge is surrounded by an imaginary sphere of radius r as shown in the figure below. This sphere is called the Gaussian sphere.

Consider a small area element dS on the Gaussian sphere. We can calculate the flux through this area element due to charge as follows:
$\oint {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} } = \int {EdS\cos 0^\circ } $ (Since angle between electric field and area element is 0$^\circ $)
The electric field due to the charge is constant and we can integrate the area element as follows:
$
\oint {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} } = E\int {dS} \\
= E\left( {4\pi {r^2}} \right) \\
$
Using this in Gauss theorem we get
$
E\left( {4\pi {r^2}} \right) = \dfrac{q}{{{ \in _0}}} \\
\Rightarrow E = \dfrac{q}{{4\pi { \in _0}{r^2}}} \\
$
This is the required Coulomb’s law obtained from Gauss theorem.
Note:
1. If the medium is other than vacuum then the permittivity of the vacuum is replaced by permittivity of that medium in the expression for Gauss theorem.
2. Every problem where Gauss theorem is used, we need a closed Gaussian surface for calculating the electric field.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




