
State Hess’s law of constant heat summation and explain it with an example.
Answer
527.6k+ views
Hint: Before attempting this question, prior knowledge of Enthalpy is a must. Enthalpy is a thermodynamic quantity,equal to the sum of internal energy of the system and the product of pressure and volume $(H = U + pV)$.
Complete step by step solution:
Hess’s law of constant heat summation-
According to this law, the change in enthalpy for a reaction is always the same and does not depend on whether the reaction occurs in one step or multiple steps.
OR
The Hess’s law states that the total enthalpy change during a complete chemical reaction is the same regardless of the path taken by the chemical reaction.
OR
This law states that, the change in enthalpy in a chemical reaction, at a constant pressure is not dependent on the process, and only dependent on the initial and final states of the chemical reaction.
It can be more easily understood by the following diagram.
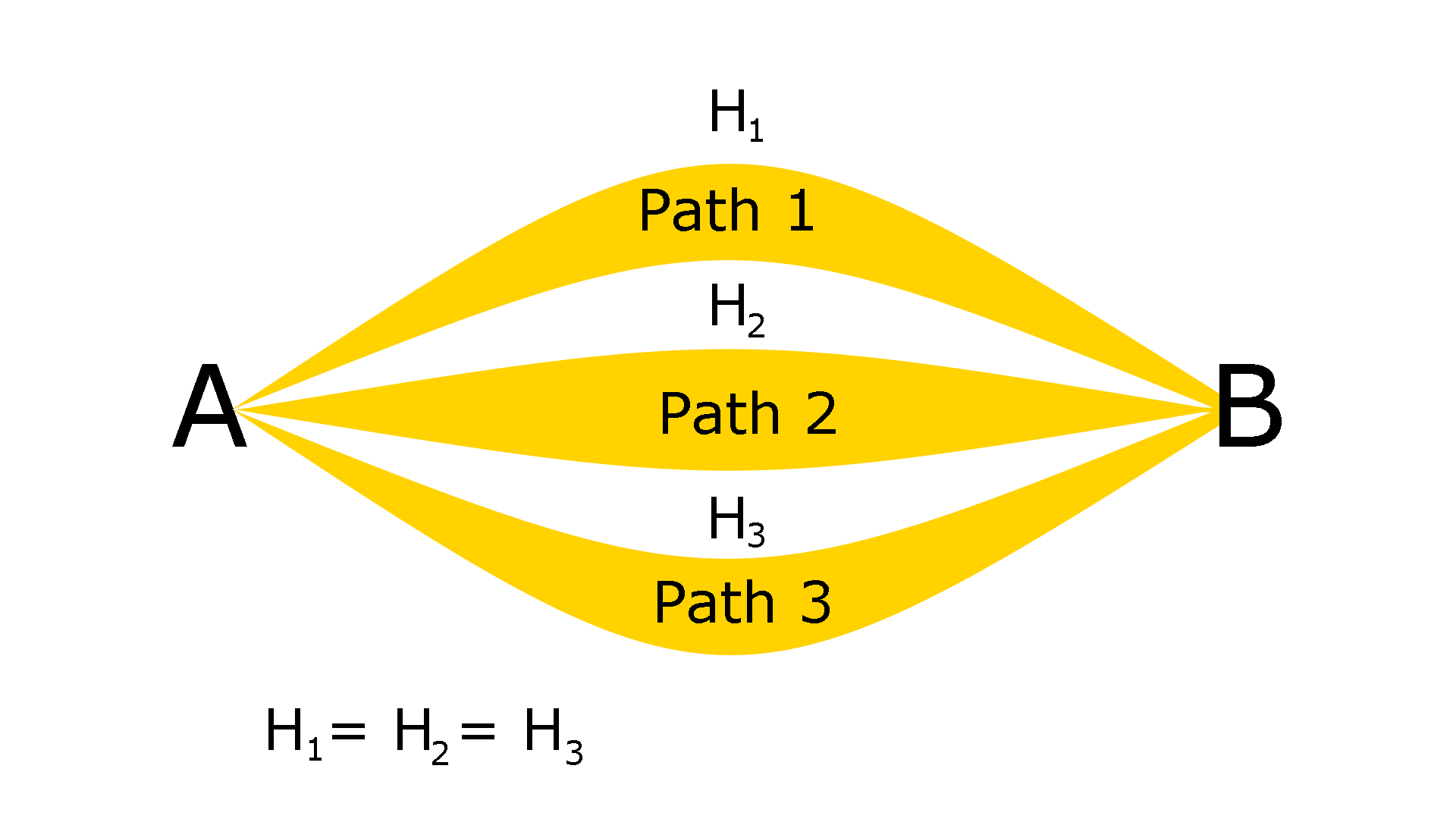
Hess’s law can be seen as an application of the principle of conservation of energy.
As enthalpy only depends upon the initial and final state of the chemical reaction, it is also considered as a state function.
Example:-
Consider the following two routes for preparation of methylene chloride\[(C{H_2}C{l_2})\] from the reaction between methane$(C{H_4})$ and chlorine$(C{l_2})$
Route I:
$C{H_4}(g) + 2C{l_2}(g) \to C{H_2}C{l_2}(g) + 2HCl(g),\Delta H_1^0 = - 202.3kJ$
Route II:
$C{H_4}(g) + C{l_2}(g) \to C{H_3}Cl(g) + HCl(g),\Delta H_2^0 = - 98.3kJ \\
C{H_3}Cl(g) + C{l_2}(g) \to C{H_2}C{l_2}(g) + HCl(g),\Delta H_3^2 = - 104.0kJ \\ $
Adding change in enthalpy of both steps
$C{H_4}(g) + 2C{l_2}(g) \to C{H_2}C{l_2}(g) + 2HCl(g),\Delta H_3^0 = - 202.3kJ$
Thus, it can be clearly seen that no matter what path we follow, the total enthalpy change in the reaction is always the same.
$\Delta H_1^0 = \Delta H_2^0 + \Delta H_3^2 = - 202.3kJ$
Note: Hess’s law is named after Germain Hess, a Russian chemist who was born in Switzerland. Germain’s Hess’s law of constant heat summation was published in 1840, which is before 1850, when Rudolf Clausius proposed the first law of thermodynamics.
Complete step by step solution:
Hess’s law of constant heat summation-
According to this law, the change in enthalpy for a reaction is always the same and does not depend on whether the reaction occurs in one step or multiple steps.
OR
The Hess’s law states that the total enthalpy change during a complete chemical reaction is the same regardless of the path taken by the chemical reaction.
OR
This law states that, the change in enthalpy in a chemical reaction, at a constant pressure is not dependent on the process, and only dependent on the initial and final states of the chemical reaction.
It can be more easily understood by the following diagram.

Hess’s law can be seen as an application of the principle of conservation of energy.
As enthalpy only depends upon the initial and final state of the chemical reaction, it is also considered as a state function.
Example:-
Consider the following two routes for preparation of methylene chloride\[(C{H_2}C{l_2})\] from the reaction between methane$(C{H_4})$ and chlorine$(C{l_2})$
Route I:
$C{H_4}(g) + 2C{l_2}(g) \to C{H_2}C{l_2}(g) + 2HCl(g),\Delta H_1^0 = - 202.3kJ$
Route II:
$C{H_4}(g) + C{l_2}(g) \to C{H_3}Cl(g) + HCl(g),\Delta H_2^0 = - 98.3kJ \\
C{H_3}Cl(g) + C{l_2}(g) \to C{H_2}C{l_2}(g) + HCl(g),\Delta H_3^2 = - 104.0kJ \\ $
Adding change in enthalpy of both steps
$C{H_4}(g) + 2C{l_2}(g) \to C{H_2}C{l_2}(g) + 2HCl(g),\Delta H_3^0 = - 202.3kJ$
Thus, it can be clearly seen that no matter what path we follow, the total enthalpy change in the reaction is always the same.
$\Delta H_1^0 = \Delta H_2^0 + \Delta H_3^2 = - 202.3kJ$
Note: Hess’s law is named after Germain Hess, a Russian chemist who was born in Switzerland. Germain’s Hess’s law of constant heat summation was published in 1840, which is before 1850, when Rudolf Clausius proposed the first law of thermodynamics.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




