
State Kirchhoff’s second law (loop rule) as a mathematical equation, mentioning what the symbols used stand for.
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: In a given circuit if the circuit elements are connected in a simple manner then by using Ohm’s law
($V = IR$,at constant temperature)
would facilitate the complete analysis of the circuit.
As the circuit becomes more and more complex, then using or depending only upon Ohm’s law is of lesser use to analyse the circuit.
With regard to overcoming this difficulty, Gustov Robert Kirchhoff determined two important laws. These laws are called as Kirchhoff’s laws
Kirchhoff’s I law: Kirchhoff’s current law (KCL)
Kirchhoff’s II law: Kirchhoff’s voltage law (KVL)
Complete step by step solution:
Kirchhoff’s II law is known as Kirchhoff’s voltage law (KVL) as it deals with the analysis of voltage in the circuit.
It states that: “The algebraic sum of voltage in a closed loop is zero”.
$\sum {V = 0} $
This law is a consequence of conservation of energy.
To understand KVL let us consider an analogy:
Let us assume a ball is thrown up from the surface of the earth. As a consequence of gravitational force, the ball, after some time, comes back to its initial position. Since its not displacement is zero, the work done by gravity on it will be zero. Hence it would end up having the same energy with which it started off, i.e., it would come back to its initial potential, leading the potential difference to be zero.
Similarly, when a charge flows in a closed loop, it leads back to the same potential it started off from. Hence the algebraic sum of voltage in the closed loop is zero.
Let us draw a simple circuit and write the KVL for the same
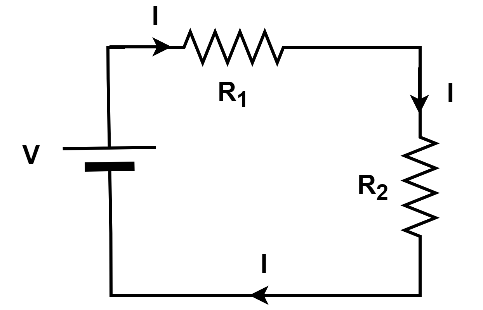
When a current flows through a resistor, there would be a voltage drop. Hence IR would be negative.
According to KVL,
$\sum {V = 0} $
\[{
\Rightarrow V - I{R_1} - I{R_2} = 0.......(1) \\
} \]
\[V = I({R_1} + {R_2})\]Equation 1 represents the KVL for the above given loop.
Here, V is voltage, I is current, $R_1$ and $R_2$ are the values of the resistance of the resistors.
Note:
1) Since KVL is applied to loops, it is also called as loop rule
2) In case of complex loop, KVL should be applied to each loop and add algebraically to get $\sum {V = 0}$
3) KVL is applicable for both ac and dc circuits.
($V = IR$,at constant temperature)
would facilitate the complete analysis of the circuit.
As the circuit becomes more and more complex, then using or depending only upon Ohm’s law is of lesser use to analyse the circuit.
With regard to overcoming this difficulty, Gustov Robert Kirchhoff determined two important laws. These laws are called as Kirchhoff’s laws
Kirchhoff’s I law: Kirchhoff’s current law (KCL)
Kirchhoff’s II law: Kirchhoff’s voltage law (KVL)
Complete step by step solution:
Kirchhoff’s II law is known as Kirchhoff’s voltage law (KVL) as it deals with the analysis of voltage in the circuit.
It states that: “The algebraic sum of voltage in a closed loop is zero”.
$\sum {V = 0} $
This law is a consequence of conservation of energy.
To understand KVL let us consider an analogy:
Let us assume a ball is thrown up from the surface of the earth. As a consequence of gravitational force, the ball, after some time, comes back to its initial position. Since its not displacement is zero, the work done by gravity on it will be zero. Hence it would end up having the same energy with which it started off, i.e., it would come back to its initial potential, leading the potential difference to be zero.
Similarly, when a charge flows in a closed loop, it leads back to the same potential it started off from. Hence the algebraic sum of voltage in the closed loop is zero.
Let us draw a simple circuit and write the KVL for the same

When a current flows through a resistor, there would be a voltage drop. Hence IR would be negative.
According to KVL,
$\sum {V = 0} $
\[{
\Rightarrow V - I{R_1} - I{R_2} = 0.......(1) \\
} \]
\[V = I({R_1} + {R_2})\]Equation 1 represents the KVL for the above given loop.
Here, V is voltage, I is current, $R_1$ and $R_2$ are the values of the resistance of the resistors.
Note:
1) Since KVL is applied to loops, it is also called as loop rule
2) In case of complex loop, KVL should be applied to each loop and add algebraically to get $\sum {V = 0}$
3) KVL is applicable for both ac and dc circuits.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




