
What is the state of hybridization of carbon in (a) \[C{O_3}^{ - 2}\](b) diamond (c) graphite?
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: First we have to draw the hybridization structure of given compounds. As we know the hybridization of a compound depends upon the number of \[\sigma \]bonds. So we have to count the number of \[\sigma \] bonds which are formed by C.
Complete step by step solution:
In a compound, if the number of bonds is 4 then the Hybridisation will be \[s{p^3}\]. If the number of \[\sigma \] bond exists as 3 then hybridization will be $s{p^2}$ and if the number of \[\sigma \] bonds is 2 then the Hybridisation will be $sp$.
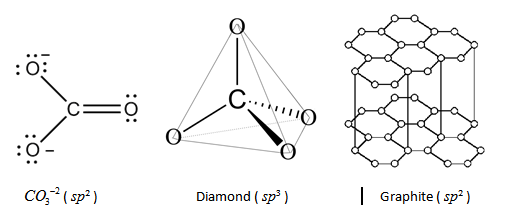
The state of hybridisation of Carbon in $C{O_3}^{ - 2}$ is $s{p^2}$, hybridization in diamond is $s{p^3}$ and hybridization in graphite is $s{p^2}$ respectively.
Note: We must know that diamond and graphite both are the allotropes of carbon and so they have identical chemical properties. In graphite, each atom shares electrons with 3 different carbon atoms, whereas in diamond, each atom here shares the electrons with 4 other carbon atoms. Diamond is very strong in comparison to graphite as graphite exhibits a brittle and soft state. The sheets of carbon become bonded with weak covalent bonds during a tetrahedral structure. The other sheets of carbon become bonded by weak intermolecular forces. Due to the weak intermolecular forces, the layers of graphite can slide upon each other and make the substance very weak in comparison with diamonds. Also, diamond is difficult to break due to its giant covalent lattice and its many strong covalent bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
In a compound, if the number of bonds is 4 then the Hybridisation will be \[s{p^3}\]. If the number of \[\sigma \] bond exists as 3 then hybridization will be $s{p^2}$ and if the number of \[\sigma \] bonds is 2 then the Hybridisation will be $sp$.

The state of hybridisation of Carbon in $C{O_3}^{ - 2}$ is $s{p^2}$, hybridization in diamond is $s{p^3}$ and hybridization in graphite is $s{p^2}$ respectively.
Note: We must know that diamond and graphite both are the allotropes of carbon and so they have identical chemical properties. In graphite, each atom shares electrons with 3 different carbon atoms, whereas in diamond, each atom here shares the electrons with 4 other carbon atoms. Diamond is very strong in comparison to graphite as graphite exhibits a brittle and soft state. The sheets of carbon become bonded with weak covalent bonds during a tetrahedral structure. The other sheets of carbon become bonded by weak intermolecular forces. Due to the weak intermolecular forces, the layers of graphite can slide upon each other and make the substance very weak in comparison with diamonds. Also, diamond is difficult to break due to its giant covalent lattice and its many strong covalent bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




