
State the function of the fallopian tube.
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: They serve to transport ova from the ovaries to the uterus; they are also the site for fertilization of the ovum by sperm. The finger-like projections are associated with these structures.
Complete answer:
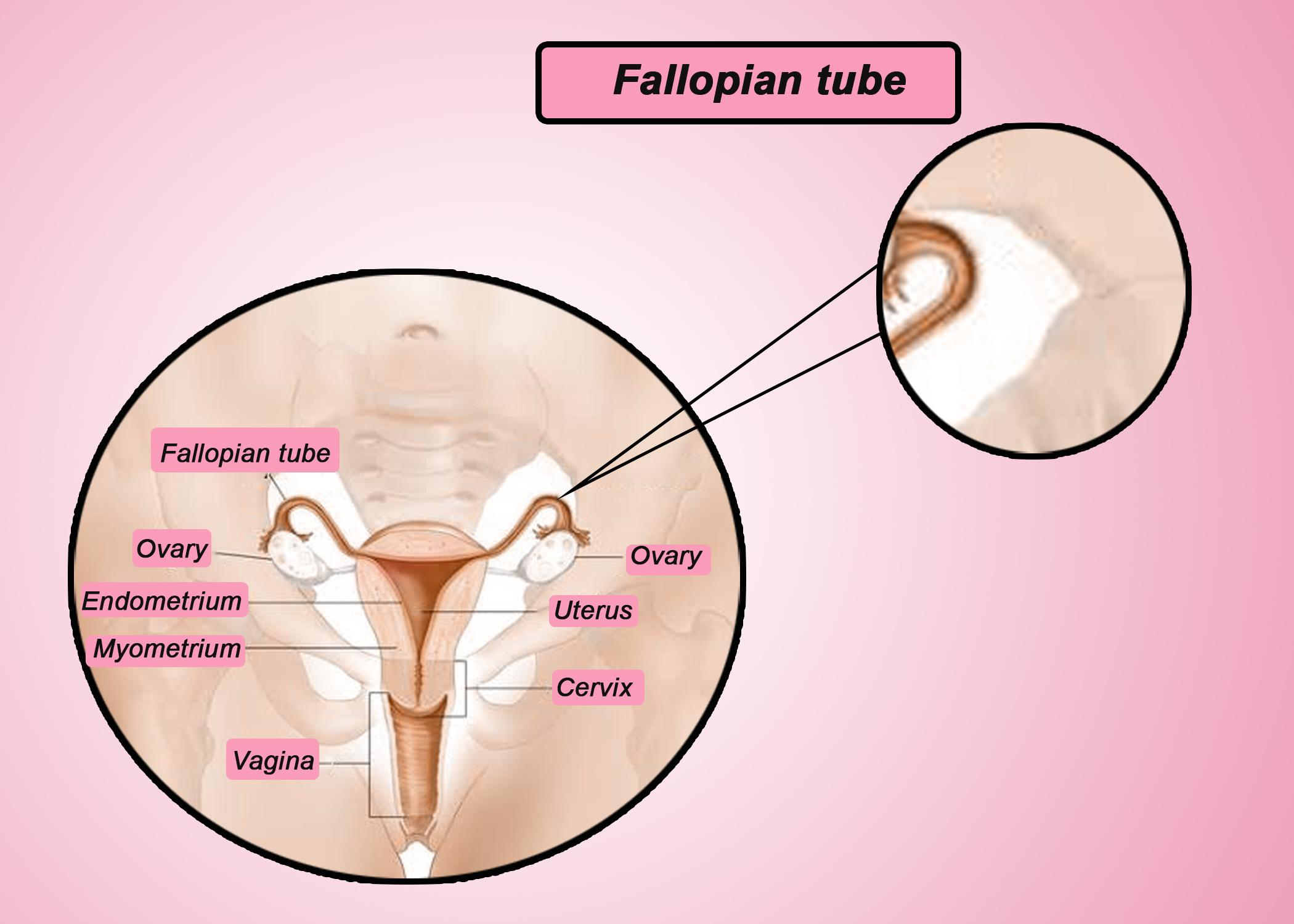
-The fallopian tubes are primary structures in the female reproductive tract, which connect the peritoneal cavity and uterine cavity.
-The Fallopian tubes are two tubes that extend from the uterus to the ovaries.
-The fallopian tube has three sections: the isthmus (narrow) which connects to the uterus, the bulb (wider) in the middle, and the infundibulum with fimbriae which serve to transport the ovum released from the ovary to the uterus.
- Fertilization of the ovum with sperm takes place in the ampulla, after that the fertilized ovum is transferred to the uterus for implantation.
- Each month, during the process of ovulation, one of the ovaries releases an egg that goes to one of the fallopian tubes, where it may or may not be fertilized by sperm.
-An ovary is not directly connected to the Fallopian tube. When ovulation is about to occur, the sex hormones activate the fimbriae (finger-like projections of the fallopian tubes), causing them to fill with blood and hit the ovary in slow motion.
Note: -The main function of the uterine tubes is to help transport the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
.-Women who no longer want children can have their tubes tied to prevent eggs from moving from the fallopian tubes into the uterus. This process is called Tubectomy.
-Transport of the sperm occurs due to the peristaltic movements of the fallopian tubes.
Complete answer:
-The fallopian tubes are primary structures in the female reproductive tract, which connect the peritoneal cavity and uterine cavity.
-The Fallopian tubes are two tubes that extend from the uterus to the ovaries.
-The fallopian tube has three sections: the isthmus (narrow) which connects to the uterus, the bulb (wider) in the middle, and the infundibulum with fimbriae which serve to transport the ovum released from the ovary to the uterus.
- Fertilization of the ovum with sperm takes place in the ampulla, after that the fertilized ovum is transferred to the uterus for implantation.
- Each month, during the process of ovulation, one of the ovaries releases an egg that goes to one of the fallopian tubes, where it may or may not be fertilized by sperm.
-An ovary is not directly connected to the Fallopian tube. When ovulation is about to occur, the sex hormones activate the fimbriae (finger-like projections of the fallopian tubes), causing them to fill with blood and hit the ovary in slow motion.

Note: -The main function of the uterine tubes is to help transport the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
.-Women who no longer want children can have their tubes tied to prevent eggs from moving from the fallopian tubes into the uterus. This process is called Tubectomy.
-Transport of the sperm occurs due to the peristaltic movements of the fallopian tubes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




