
State the two laws of reflection of light.
Answer
568.8k+ views
HINT laws of reflection are the rules which light rays follow when they enter from one medium to another medium. Reflection is the phenomena of bouncing back off light by an object. The surface is smooth and shiny. This is called specular reflection.
Complete step by step solution
As we know light is known to behave in a very predictable manner. If a ray of light could be observed approaching and reflecting off a flat manner, the behaviour of light as it reflects would follow a predictable law known as reflection. In other words, the process through which light rays fall on the surface and get bounced back in the same medium is known as reflection of light.
Almost every object reflects the light coming in our eye so the objects can be visualised. Generally, each type of mirror either plane mirror or a spherical mirror (concave mirror and a convex mirror) have shiny surfaces so they reflect the light. Means all mirrors form images on the principle of reflection.
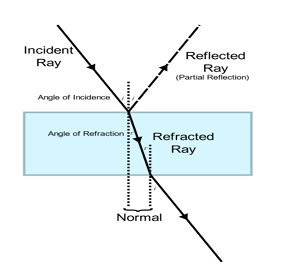
Two laws of reflection are
First law of reflection: The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Second law of reflection: The incident ray, the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence, and the reflected rays lie in the same plane.
These laws of reflection are applicable to all types of reflecting surfaces including spherical mirrors.
NOTE The principal is that when the light rays fall on the smooth surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Also the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface lie in the same plane.
Complete step by step solution
As we know light is known to behave in a very predictable manner. If a ray of light could be observed approaching and reflecting off a flat manner, the behaviour of light as it reflects would follow a predictable law known as reflection. In other words, the process through which light rays fall on the surface and get bounced back in the same medium is known as reflection of light.

Almost every object reflects the light coming in our eye so the objects can be visualised. Generally, each type of mirror either plane mirror or a spherical mirror (concave mirror and a convex mirror) have shiny surfaces so they reflect the light. Means all mirrors form images on the principle of reflection.

Two laws of reflection are
First law of reflection: The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Second law of reflection: The incident ray, the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence, and the reflected rays lie in the same plane.
These laws of reflection are applicable to all types of reflecting surfaces including spherical mirrors.
NOTE The principal is that when the light rays fall on the smooth surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Also the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface lie in the same plane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




